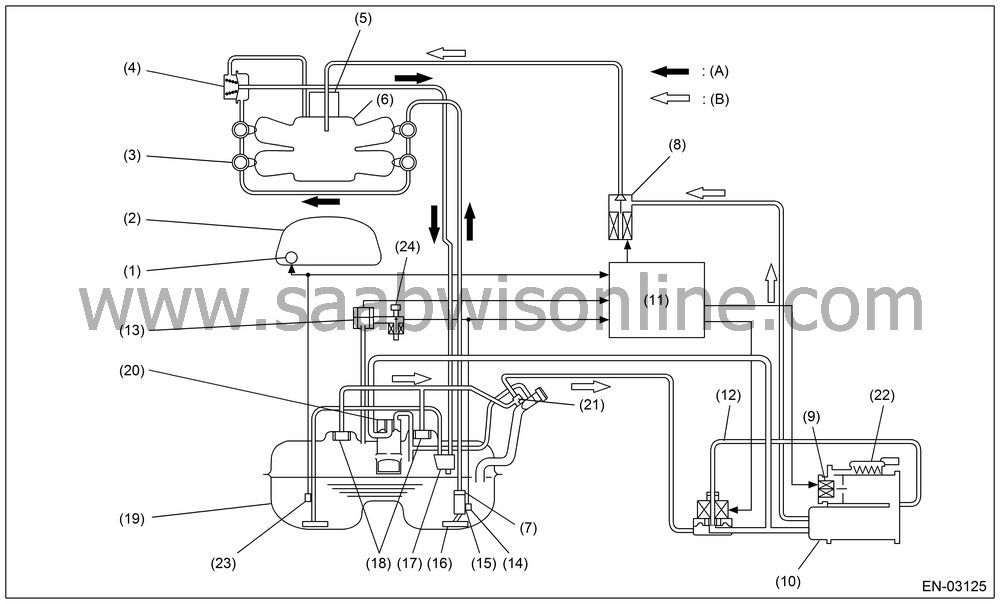
DTC P0442 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LEAK DETECTED (SMALL LEAK)
| DTC P0442 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LEAK DETECTED (SMALL LEAK) |
|
(1)
|
Fuel meter
|
(9)
|
Drain valve
|
(17)
|
Jet pump
|
|
(2)
|
Combination
meter
|
(10)
|
Canister
|
(18)
|
Fuel cut
valve
|
|
(3)
|
Fuel injector
|
(11)
|
Engine
control module (ECM)
|
(19)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(4)
|
Pressure
regulator
|
(12)
|
Pressure
control solenoid valve
|
(20)
|
Vent valve
|
|
(5)
|
Throttle
body
|
(13)
|
Fuel tank
pressure sensor
|
(21)
|
Shut-off
valve
|
|
(6)
|
Intake
manifold
|
(14)
|
Fuel temperature
sensor
|
(22)
|
Drain filter
|
|
(7)
|
Fuel filter
|
(15)
|
Fuel level
sensor
|
(23)
|
Fuel sub
level sensor
|
|
(8)
|
Purge control
solenoid valve
|
(16)
|
Fuel pump
|
(24)
|
Tank pressure
switching solenoid valve
|
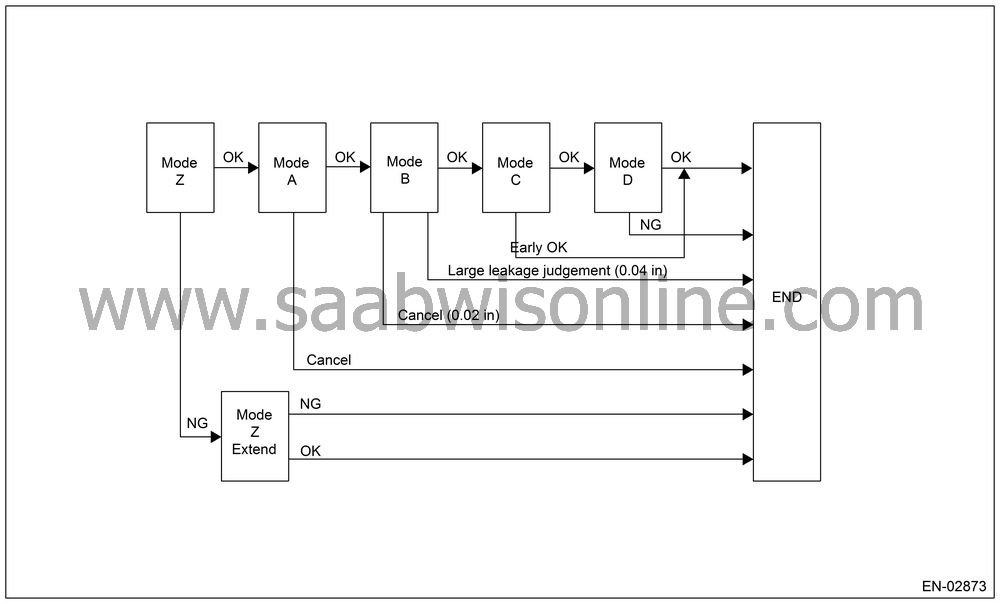
In this system diagnosis, filter tank pressure is changed. And leakage andnormality & abnormality of valve operation are judged by monitoring the pressure change status using the fuel tank pressure sensor. The diagnosis is performed for 0.04-inch diagnosis in the order of Mode A, Mode B, Mode C and Mode D. For 0.02-inch diagnosis, perform in the order of Mode Y, Mode A, Mode B, Mode C and Mode D.
0.04-inch Diagnosis
| Mode | Mode Description | Diagnosis Period |
|
Mode
Z
(Purge control solenoid valve open fail diagnosis) |
Perform
the diagnosis of purge control solenoid valve open fail depending
on the magnitude of the tank pressure change after diagnosis started.
|
3 — 16
seconds
|
|
Mode
A
(Evaluation of EVAP. generation amount) |
Calculate
the tank pressure change amount (P1).
|
16
seconds
|
|
Mode
B
(Negative pressure sealed/large leak judgment) |
Introduce
the intake manifold pressure into the fuel tank. If the tank pressure
cannot be reduced, diagnose that there is large leakage.
|
4 — 35
seconds
|
|
Mode
C
(Pressure increase check/premature OK judgment) |
Wait until
the tank pressure returns to the target value (Tank pressure when
P2 calculation started). If the pressure does not return, perform
the premature OK judgment.
|
4 — 15
seconds
|
|
Mode
D
(Negative pressure change amount measurement/EVAP. leakage diagnosis) |
Calculate
the tank pressure change amount (P2), and measure the diagnosis
value using P1 calculated in Mode A. Perform the EVAP. leakage diagnosis
using the diagnosis value.
|
12 — 16
seconds
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
| Mode | Mode Description | Diagnosis Period |
|
Mode
A
(Evaluation of EVAP. generation amount) |
Calculate
the tank pressure change amount (P1).
|
29
seconds
|
|
Mode
B
(Negative pressure seal) |
Introduce
the intake manifold pressure into the fuel tank, and reduce the
tank pressure to the target pressure.
|
10 — 20
seconds
|
|
Mode
C
(Pressure increase check/premature OK judgment) |
Wait until
the tank pressure returns to the target value (Tank pressure when
P2 calculation started). If the tank pressure does not return, perform
the premature OK judgment.
|
5 — 20
seconds
|
|
Mode
D (Negative pressure change amount measurement/EVAP. leakage
diagnosis)
|
Calculate
the tank pressure change value (P2), measure the diagnosis value
using P1 calculated in Mode A. Perform the EVAP. leakage diagnosis
using the diagnosis value.
|
20 — 25
seconds
|
Mode table for Evaporative Emission Control System diagnosis
| Mode | Behavior of tank internal pressure under normal conditions | Diagnostic item | DTC |
|
Mode
Z
|
Nearly
same as atmospheric pressure (equivalent pressure of 0 kPa (0 mmHg, 0
inHg))
|
Purge
control solenoid valve is judged to be stuck open.
|
P0457
|
|
Mode
A
|
Pressure
is in proportion to amount of evaporative emission.
|
—
|
—
|
|
Mode
B
|
Negative
pressure is formed due to intake manifold negative pressure
|
Judged
as large leak
|
P0457
|
|
Mode
C
|
Target
pressure is reached.
|
—
|
—
|
|
Mode D
|
Pressure change is small.
|
EVAP
system is judged to have large leak [1.0 mm (0.04 in.)].
|
P0442
|
|
EVAP
system is judged to have small leak [0.5 mm (0.02 in.)].
|
P0456
|
| COMPONENT DESCRIPTION |
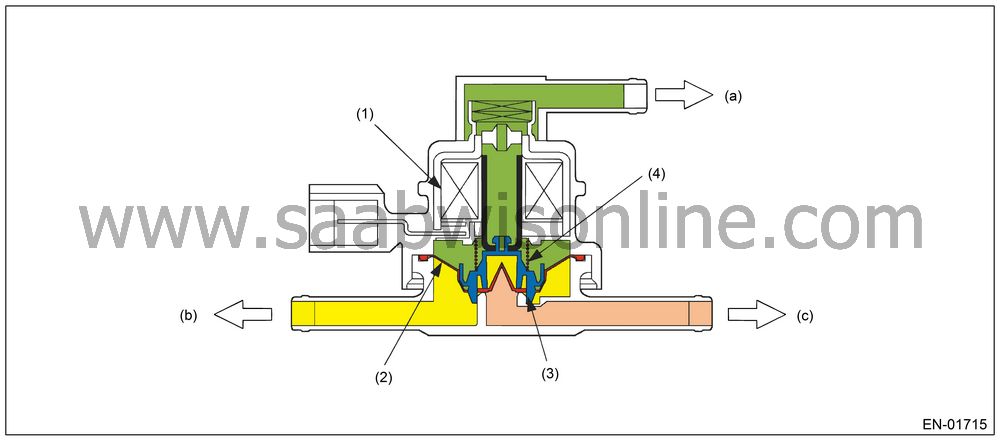
Pressure Control Solenoid Valve
Pressure control solenoid valve maintains the fuel tank pressure equal to the atmospheric air pressure. Normally, the solenoid is set to OFF, and the valve mechanically opens and closes in accordance with the difference between the tank pressure and atmospheric air pressure, and the tank pressure and canister pressure.The solenoid which is set to ON forces to open the valve.
|
(1)
|
Solenoid
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
|
(2)
|
Diaphragm
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(3)
|
Valve
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
|
(4)
|
Spring
|
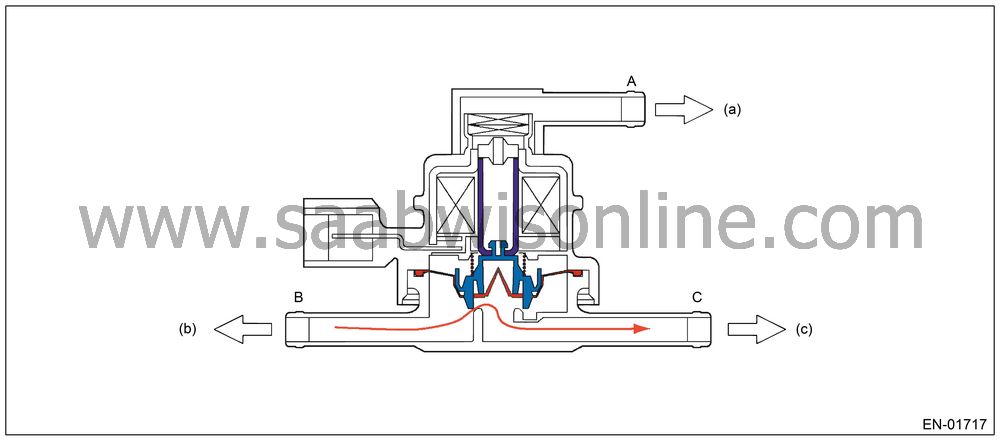
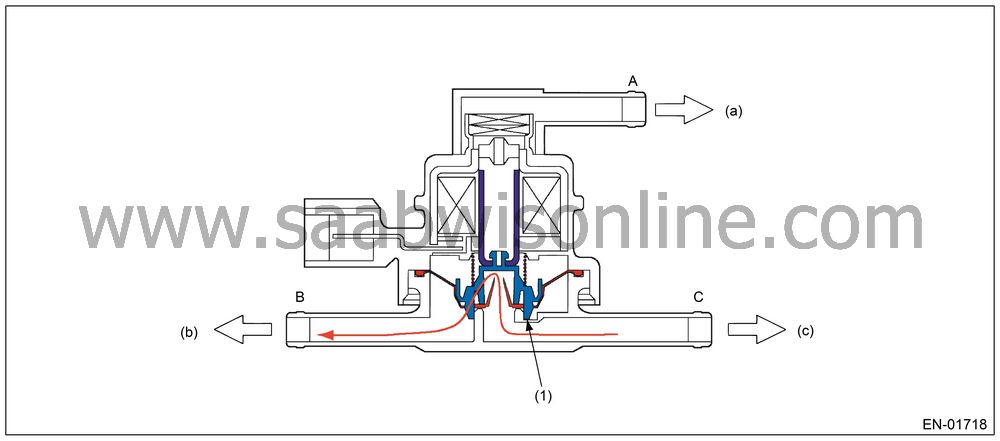
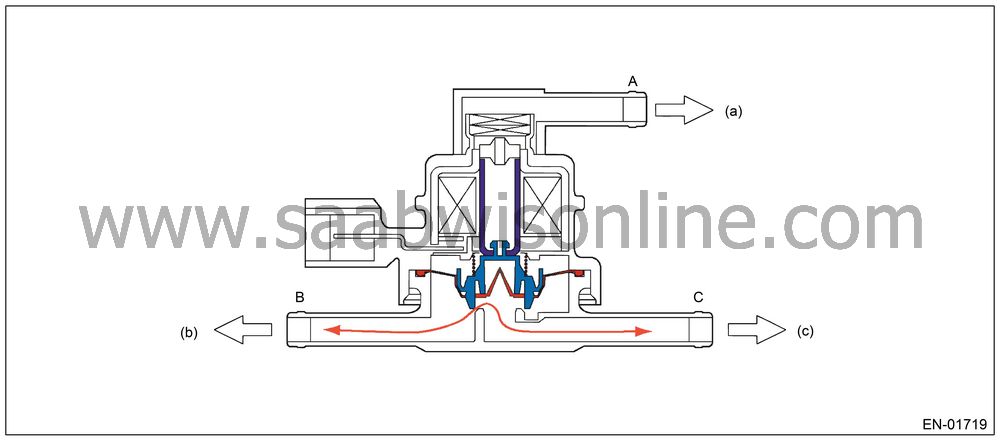
Valve Operation and Air Flow
As in the X parts below, there are the area with atmospheric air pressure above the diaphragm and the area with tank pressure below the diaphragm. Also, as in the Y parts below, there are the area with tank pressure above the diaphragm and the area with canister pressure below the diaphragm. In the table below the air flow from each port in accordance with pressure difference is shown with the atmospheric air pressure port A, tank pressure port B and canister pressure port C.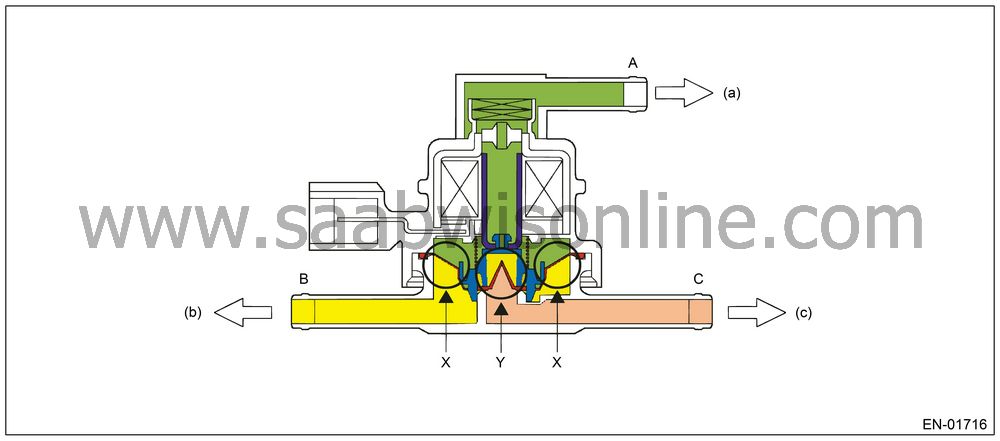
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
| Pressure Status | Flow |
|
A < B
(Solenoid OFF)
|
B → C
|
|
B < C
(Solenoid OFF)
|
C → B
|
|
Solenoid
ON
|
B ←→ C
|
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
|
(1)
|
Valve
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
||
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
Drain valve
Drain valve controls the ambient air to be introduced to the canister.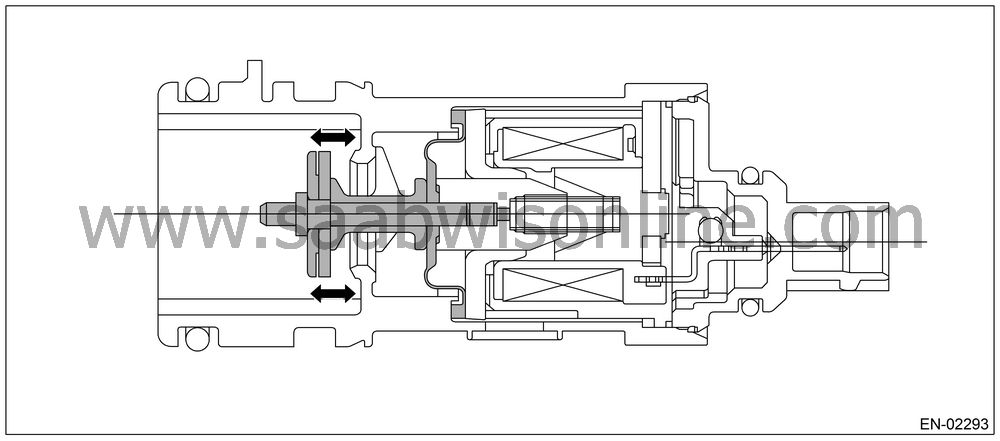
Tank Pressure Switching Solenoid
One of the atmospheric pressure switching solenoid valves is connected to fuel tank pressure sensor and the other is released to atmosphere. The passage to fuel tank pressure sensor is usually released to atmosphere because the solenoid is set to OFF, but the solenoid which is set to ON closes the passage open to atmosphere.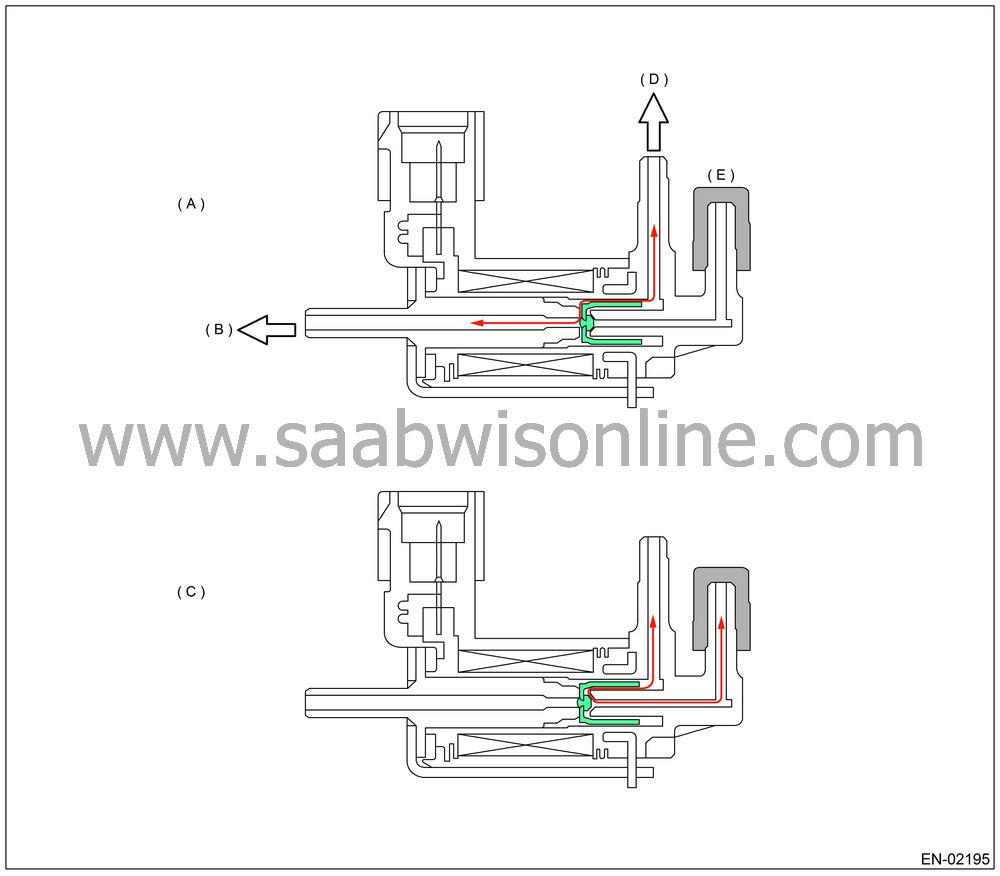
|
(A)
|
Released
to atmosphere (Solenoid OFF)
|
||
|
(B)
|
Ambient
air
|
||
|
(C)
|
During
diagnostics (Solenoid ON)
|
||
|
(D)
|
To pressure
sensor
|
||
|
(E)
|
Plug
|
Purpose of this solenoid
Fuel tank pressure sensor detects the difference between the atmospheric air pressure and the tank pressure, and the ECM monitors the pressure difference.
Even if the tank pressure is constant, the atmospheric air pressure varies depending on the driving height, and the pressure signal transmitted to ECM will change.
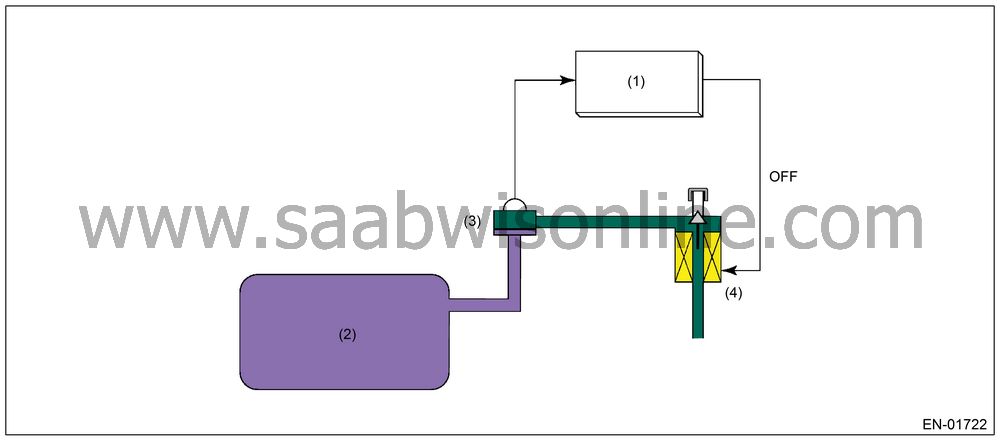
|
(1)
|
Engine
control module (ECM)
|
|
(2)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(3)
|
Fuel tank
pressure sensor
|
|
(4)
|
Atmospheric
pressure switching solenoid
|
Especially, in the small leakage [0.5 mm (0.02 inch)], minute change in the tank pressure has to be detected. This diagnosis period is long (approx. 29 seconds). And if the driving height changes during the diagnosis, the atmospheric air pressure changes. In this case, it becomes difficult to precisely detect the tank pressure variation, causing erroneous diagnosis. Therefore, using the atmospheric pressure switching solenoid, atmospheric air is sealed between the fuel tank pressure sensor and atmospheric pressure switching solenoid, maintaining the air pressure constant and enabling the detection of minute variation of tank pressure.
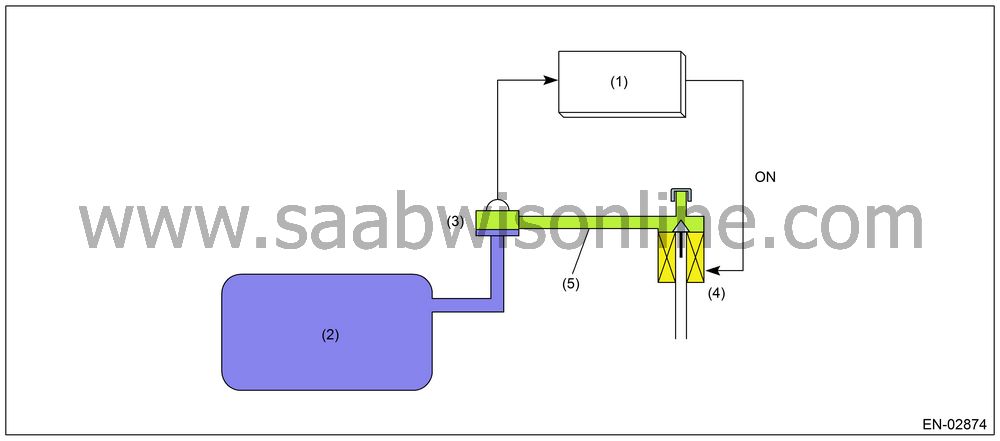
|
(1)
|
Engine
control module (ECM)
|
|
(2)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(3)
|
Fuel tank
pressure sensor
|
|
(4)
|
Atmospheric
pressure switching solenoid
|
|
(5)
|
Constant
pressure
|
| Note | ||
|
ECM also has the atmospheric air pressure sensor, and always monitors atmospheric air. However, as the monitoring range is large, that is, 53.3 to 107 kPa (400 to 800 mmHg, 15.7 to 31.6 inHg), it is not suitable for detection of minute pressure variation. |
||
|
In the case of small leakage diagnosis, the tank pressure variation is very small, that is, 0.13 to 0.26 kPa (1 to 2 mmHg, 0.04 to 0.08 inHg), and the fuel tank pressure sensor is equipped. |
| ENABLE CONDITION |
0.04-inch Diagnosis
| Secondary Parameters | Enable Conditions |
|
Evaporation
diagnosis
|
Incomplete
|
|
Battery
voltage
|
≥ 10.9
V
|
|
Barometric
pressure
|
≥ 75.1
kPa (563 mmHg, 22.2 inHg)
|
|
Total
time of canister purge operation
|
120
seconds or more
|
|
After
engine starting
|
856
seconds or more
|
|
Learning
value of evaporation gas density
|
≤ 0.08
|
|
Engine
speed
|
1,050 ←→ 6,500
rpm
|
|
Fuel
tank pressure
|
< 1.4 kPa
(10.7 mmHg, 0.4 inHg)
|
|
Atmospheric
pressure − Intake manifold vacuum (relative pressure)
|
≥ 13.3
kPa (100 mmHg, 3.92 inHg)
|
|
Vehicle
speed
|
≥ 32
km/h (20 MPH)
|
|
Fuel
level
|
9 ←→ 51 litres (2.38 ←→ 13.5
US gal, 1.98 ←→ 11.2 Imp gal)
|
|
Closed
air/fuel ratio control
|
In
operation
|
|
Fuel
temperature
|
−10 ←→ 45°C
(14 ←→ 113°F)
|
|
Intake
air temperature
|
≥ −10°C
(14°F)
|
|
Pressure
change per second
|
< 0.13
kPa (0.95 mmHg, 0.04 inHg)
|
|
Min.
pressure change per second − Max. pressure change per second
|
< 0.23
kPa (1.75 mmHg, 0.07 inHg)
|
|
Fuel
level change
|
< 3 litres(0.79
US gal, 0.66 Imp gal)/131 milliseconds
|
|
Air fuel
ratio
|
0.76 — 1.25
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
| Secondary Parameters | Enable Conditions |
|
(At
starting a diagnosis)
|
|
|
Engine
speed
|
1,500 — 6,500
rpm
|
|
Battery
voltage
|
≥ 10.9 V
|
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
≥ 75.7 kPa (568 mmHg, 22.4 inHg)
|
|
Since
last incomplete diagnosis event of 0.02-inch leakage
|
≥ 120
seconds
|
|
Total
time of canister purge operation
|
120
second or more
|
|
After
engine starting
|
335 second or more
|
|
Fuel
temperature, or the time after engine start with coolant temperature
of 40°C (104°F) or below
|
−10 ←→ 35°C
(14 ←→ 95°F)
< 2,400 seconds |
|
Fuel
level
|
9 ←→ 51 litres (2.38 ←→ 13.5
US gal, 1.98 ←→ 11.2 Imp gal)
|
|
(Ambient
(estimate) − fuel) temperature
|
< 1°C (34°F)
|
|
Fuel
tank pressure below −3.01 kPa (−22.8 mmHg, −0.88
inHg) (during same driving cycle, Intake manifold vacuum (relative
pressure))
|
Up
to 2 times
|
|
Atmospheric − Intake
manifold vacuum (relative pressure)
|
≥ 13.3
kPa (100 mmHg, 3.92 inHg)
|
|
Fuel
tank pressure
|
−0.67
to 1.20 kPa
(−5 to 9 mmHg, −0.20 to 0.35 inHg)
|
|
Vehicle
speed
|
≥ 68 km/h (42 MPH)
|
|
Closed
air/fuel ratio control
|
In operation
|
|
Ambient
temperature (estimate)
|
≥ −10°C (14°F)
|
|
(During
diagnosis)
|
|
|
P1
|
−0.07 ←→ 0.13 kPa
(−0.5 ←→ 1 mmHg,
−0.02 ←→ 0.04 inHg)
|
|
Pressure
change per second
|
< 0.13
kPa (0.95 mmHg, 0.04 inHg)
|
|
Fuel
level change
|
3litres / 128 milli-seconds
|
|
Min.
tank pressure change per second − Max. tank pressure change
per second
|
< 0.23
kPa (1.75 mmHg, 0.07 inHg)
|
|
Change
of atmospheric pressure during P1 calculation
|
−0.07 ←→ 0.15 kPa
(−0.5 ←→ 1.125 mmHg, −0.02 ←→ 0.04
inHg)
|
|
Change
of atmospheric pressure during P2 calculation
|
−0.15 ←→ 0.15
kPa
(−1.125 ←→ 1.125 mmHg, −0.04 ←→ 0.04
inHg)
|
| GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE |
0.04-inch Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis only once in 856 seconds or more after starting the engine constantly at 32 km/h (20 MPH) or more.
Pay attention to the fuel temperature and fuel level.
0.02-inch Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis in 335 seconds after starting the engine constantly at 68 km/h (42 MPH) or more, and perform OK/NG judgment.
If OK/NG judgment is not possible, repeat the diagnosis.
Pay attention to the fuel temperature and fuel level.
| DIAGNOSTIC METHOD |
Diagnosing Function of Drain Valve and Purge Control Solenoid Valve
DTCP0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Purpose of Mode Z
When performing the leakage diagnosis of EVAP system, purge control solenoid valve have to operate normally. Therefore, mode Z is used to diagnose the purge control solenoid valve open fixation.
If purge control solenoid valve open fixation trouble is detected, the evaporation system leakage diagnosis is cancelled.
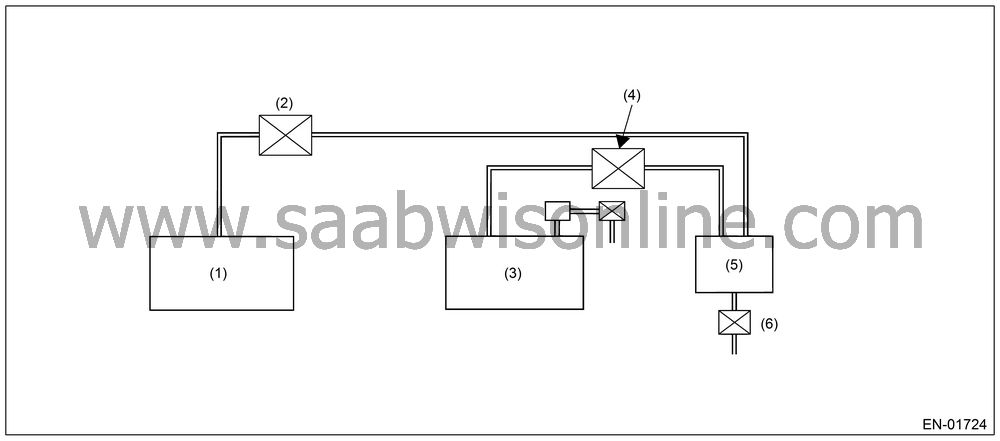
|
(1)
|
Engine
|
(4)
|
Pressure
control solenoid valve (Close)
|
|
(2)
|
Purge control
solenoid valve (Open)
|
(5)
|
Canister
|
|
(3)
|
Fuel tank
|
(6)
|
Drain valve
(Stuck close)
|
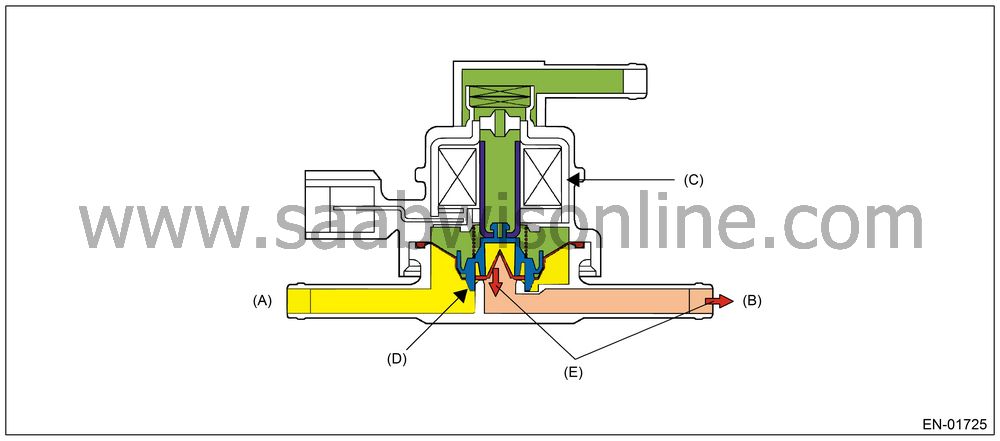
|
(A)
|
To fuel
tank
|
|
(B)
|
To canister
(Negative pressure)
|
|
(C)
|
Solenoid
ON
|
|
(D)
|
Valve cannot
be open.
|
|
(E)
|
Negative
pressure
|
Diagnostic method
Purge control solenoid valve open fixation diagnosis is performed in mode Z as shown in the figure below.
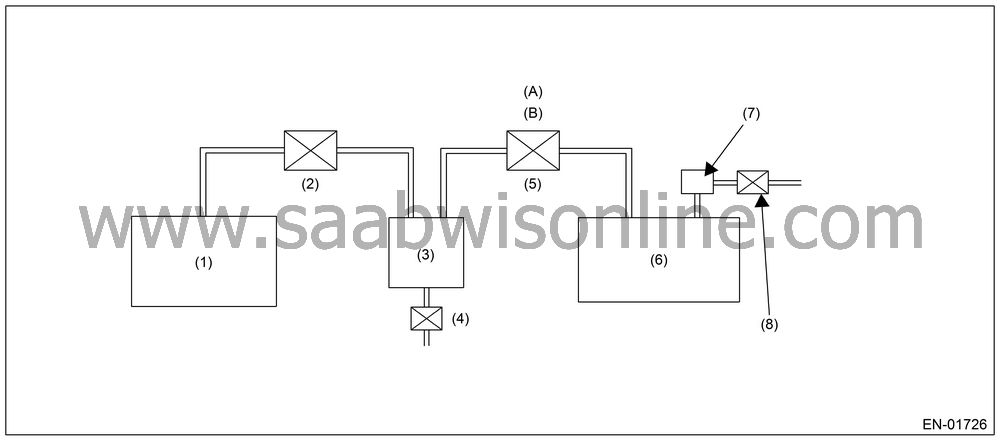
|
(1)
|
Engine
|
(5)
|
Pressure
control solenoid valve
|
|
(2)
|
Purge control
solenoid valve
|
(6)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(3)
|
Canister
|
(7)
|
Fuel tank
pressure sensor
|
|
(4)
|
Drain valve
|
(8)
|
Atmospheric
pressure switching solenoid
|
Diagnosing function of purge control solenoid valve [P0457]
Purge control solenoid valve functional diagnosis is performed by monitoring the tank pressure in Mode Z.Normality Judgment
Judge OK when the following criteria are satisfied in 3 seconds after Mode Z started, and change to Mode A.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
(Tank pressure
when Mode Z started) — (Tank pressure when Mode Z finished)
|
≤ 0.4
kPa (3 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
P0457
|
Normal
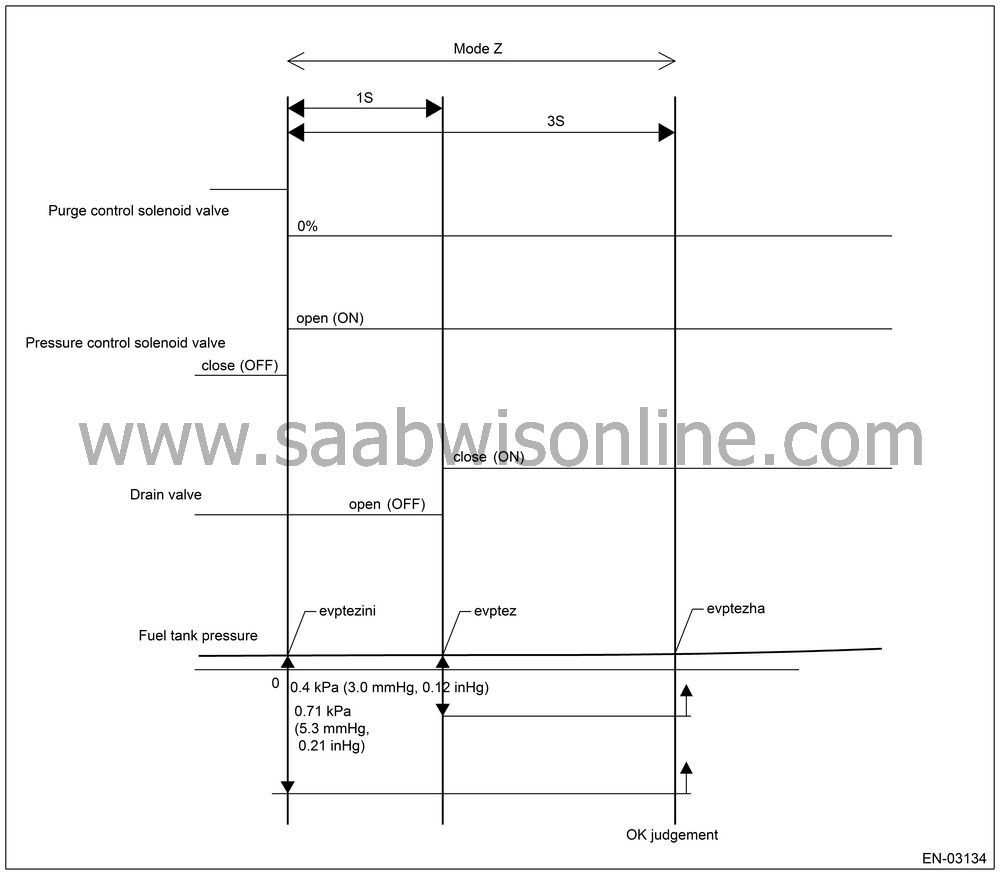
Judge normal when the following conditions are completed at once.
| • |
evptez − evptezha ≤ 0.4 kPa
(3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
|
| • |
evptezini − evptezha ≤ 0.71
kPa (5.3 mmHg, 0.21 inHg)
|
|
Abnormality Judgment
If OK judgment cannot be made, extend Mode Z 16 seconds more, and judge NG when all the criteria below are completed in 16 seconds.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
(Tank
pressure 1 second after Mode Z started) − (Tank pressure
when Mode Z finished)
|
> 0.6
kPa (4.5 mmHg, 0.18 inHg)
|
P0457
|
|
Tank
pressure when Mode Z started
|
≤ 0.91
kPa (6.8 mmHg, 0.27 inHg)
|
|
|
TIme for
no fuel rolling of 3litres or more
|
≥ 35
seconds
|
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 16 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunction occurs in 2 continuous driving cycles.
Finish the Evap. diagnosis when making NG judgment for purge control solenoid valve open fixation.
Cancel the Evap. diagnosis when the OK/NG judgment for purge control solenoid valve open fixation cannot be made in Mode Z.
Purge control solenoid valve open fixation
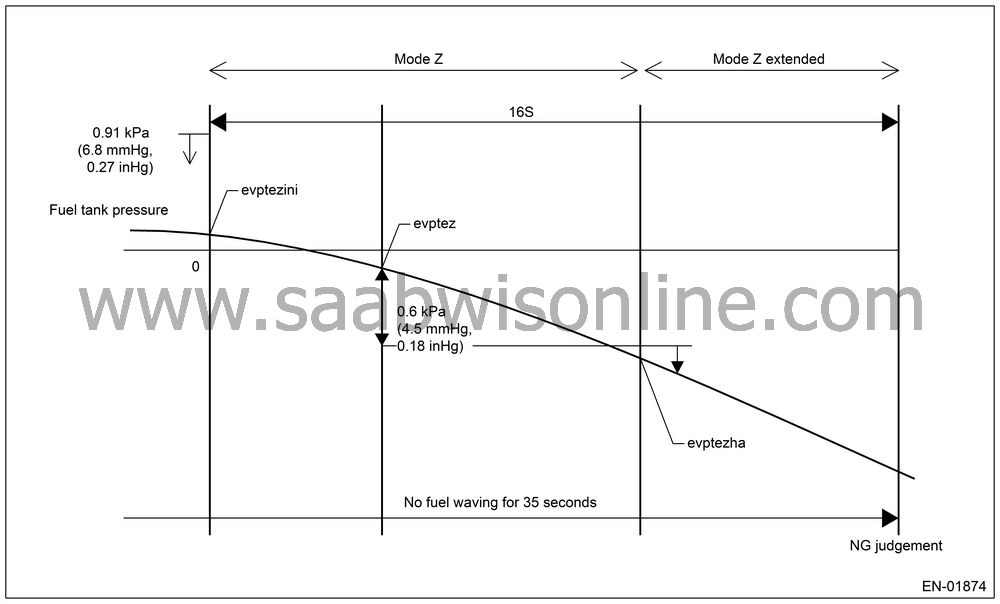
Judge NG when the following conditions are completed at once.
| • |
evptez − evptezha > 0.6 kPa
(4.5 mmHg, 0.18 inHg)
|
|
| • |
evptezini ≤ 0.91 kPa (6.8
mmHg, 0.27 inHg)
|
|
| • |
Period without 3litres(0.79 US
gal, 0.67 Imp gal) or more fuel waving is 35 seconds or more.
|
|
Leakage Diagnosis
DTCP0442 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
P0456 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Very Small Leak)
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Diagnostic Method
| • |
The diagnostic method consists of creating
a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the presence
of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns
to atmospheric pressure.
|
|
| • |
The diagnosis is devided into the following
five phases.
|
|
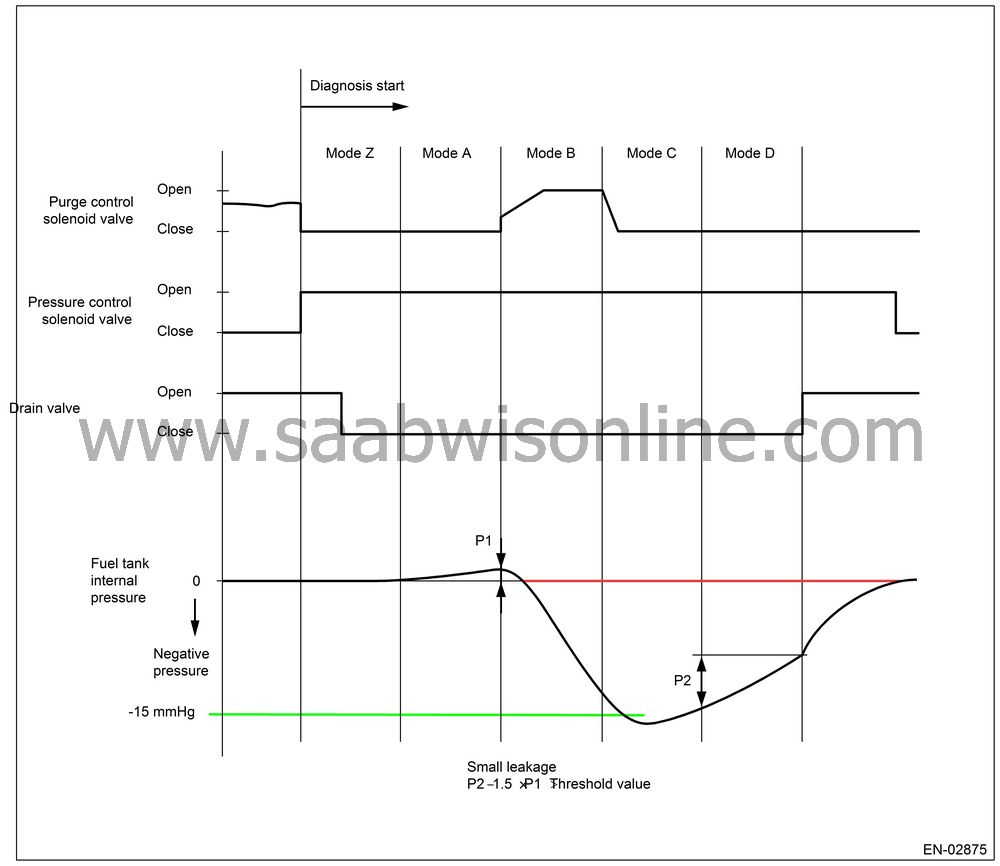
Mode A; (Estimation of evaporation abundance)
Calculate the tank pressure variation amount (P1) at Mode A. Move to Mode B after calculating P1.
Mode B; (Seal negative pressure)
Introduce the negative pressure of the intake manifold into the tank.
Approx. 0 → −1.4 kPa (0 → −10.5 mmHg, 0 → −0.41 inHg) (0.04-inch diagnosis)
Approx. 0 → −3.05 kPa (0 → −22.875 mmHg, 0 → −0.9 inHg) (0.02-inch diagnosis)
Move to Mode C when reaching the pressure above (target pressure).
Then, if the tank pressure does not become negative, judge that there is large leakage in the system. In 0.04-inch diagnosis, judge that there is large leakage (10 seconds or 25 seconds) and terminate the EVAP. diagnosis. In 0.02-inch diagnosis, cancel the diagnosis (20 seconds).
Abnormality Judgment
Judge NG (large leakage) when the malfunction criteria below is completed.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
(0.04-inch
diagnosis)
|
P0457
|
|
|
Period
until reaching target negative pressure
|
≥ 25
seconds
|
|
|
OR,
Mode B period
|
≥ 10
seconds
|
|
|
(Tank Pressure
Min. Value in Mode B) − (Tank Pressure when starting Mode
B)
|
> −0.53
kPa (−4 mmHg, −0.16 inHg)
|
Mode C; (Check increasing pressure)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure. (Wait until returning to the start level of P2 calculation)
When returning to the start level of P2 calculation, move to Mode D.
Judge premature OK and move to Mode E when not returning in the determined period of time.
| Tank pressure when P2 calculation started | Premature OK Judgment Period | |
|
0.04-inch
Diagnosis
|
−1.30 kPa (−9.75 mmHg, −0.38 inHg)
|
15
seconds
|
|
0.02-inch
Diagnosis
|
−3.00
kPa (−22.5 mmHg, −0.89 inHg)
|
20 seconds
|
Mode D; (Measurement of negative pressure variation)
Monitor the tank pressure variation in Mode D. In this case, the tank pressure increases (close to atmospheric pressure) because the evaporator is generated. However, if there is leakage, the pressure increases additionally. P2 means the variation amount of this tank pressure. After calculating P2, perform the small leakage diagnosis.
When Terminating Mode D
By assigning the variation values of tank pressure, P1 and P2, in the following formula, judge the system small leakage. If the calculated judgment value is larger than the threshold value, judge that there is a failure.
0.04-inch Diagnosis
Judge NG when the malfunction criteria below is completed.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
P2 − 1.5 × P1
P2 = Change of tank pressure in 16 seconds at mode D. P1 = Change of tank pressure in 16 seconds at mode A. |
> 0.38 ←→ 0.81
kPa (2.86 ←→ 6.08 mmHg, 0.11 ←→ 0.24 inHg)
*Threshold value: Map (fuel level vs tank temperature) |
P0442
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
Abnormality Judgment
Judge NG when the malfunction criteria below is completed.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
P2 − 1.5 × P1
P2 = Change of tank pressure in 22 seconds at mode D. P1 = Change of tank pressure in 22 seconds at mode A. |
≥ 0.40 ←→ 0.97
kPa (3 ←→ 7.3 mmHg, 0.12 ←→ 0.29
inHg)
*Threshold value: Map (fuel level vs tank temperature) |
P0456
|
Normality Judgment
Judge OK when the malfunction criteria below is not completed.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
P2 − 1.5 × P1
|
< 0.31 ←→ 0.60
kPa (2.3 ←→ 4.5 mmHg, 0.09 ←→ 0.18
inHg)
|
P0456
|
If OK/NG judgment is not possible, repeat the diagnosis.
Time Needed for Diagnosis:
|
0.04
inches:
|
30 to
100 seconds
|
|
0.02
inches:
|
30 to
100 seconds
|
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Detect when malfunction occurs in two continuous drive cycles.
| DTC CLEAR CONDITION |
| • |
When the OK idling cycle was completed 40 times
in a row
|
|
| • |
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
|
| MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT CLEAR CONDITION |
| • |
When the OK driving cycle was completed 3 times
in a row
|
|
| • |
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
|
| FAIL SAFE |
None
| ECM OPERATION AT DTC SETTING |
| • |
Memorize the freeze frame data. (For test mode $02)
|
|
| • |
Memorize the diagnostic value and trouble
standard value. (For test mode $06)
|
|