DTC P0301 CYLINDER 1 MISFIRE DETECTED
|
|
DTC P0301 CYLINDER 1 MISFIRE DETECTED
|
Detect whether the misfire occurred or not.
(Revolution fluctuation method) Monitoring the misfire which influences
exhaust deterioration (1.5 times of FTP) and catalyst damage is
made obligatory by the law. Misfire affecting these two has three
patterns below.
|
•
|
Intermittent misfire (The same cylinder misfires
in random, or different cylinders misfire in random.): FTP 1.5 times
misfire
|
|
•
|
Every time misfire (The same cylinder
misfires every time.): FTP 1.5 times misfire, Catalyst damage misfire
|
The following detecting methods are adopted
for these detection.
Intermittent misfire: FTP 1.5 times misfire
|
•
|
180° Interval Difference Method (MT:
1,800 rpm or less; AT: None)
|
|
•
|
360° Interval Difference Method
(whole range)
|
|
•
|
720° Interval Difference Method
(3,000 rpm or less)
|
Every time misfire: FTP 1.5 times misfire,
Catalyst damage misfire
|
•
|
360° Interval Difference Method
|
|
Secondary
Parameters
|
Enable
Conditions
|
All
secondary parameter enable conditions
|
More
than 1 second
|
Intake
manifold pressure change during 0.5 engine rev.
|
< 13.3
kPa (100 mmHg, 3.94 inHg)
|
Engine
speed change
|
< 700
rpm/32 milliseconds
|
Throttle
position change during 16 milliseconds
|
< 21°
|
Fuel
shut-off function
|
Not
operating
|
Atomospheric
pressure
|
≥ 75.0
kPa (563 mmHg, 22.2 inHg)
|
Fuel
level
|
≥ 9.0 litres (2.38
US gal, 1.98 Imp gal)
|
AT
torque control
|
Not
in operation
|
Evaporative
system leak check
|
Not
in operation
|
Engine
speed
|
460 — 6200
rpm
|
Intake
manifold pressure
|
> Map
3
|
Battery
voltage
|
≥ 8
V
|
Conclusion
of fuel parameter
|
Not supervolatile
|
Map3
MT
(Vehicle Speed < 64.4 km/h (40 MPH))
|
rpm
|
700
|
1000
|
1500
|
2000
|
2500
|
3000
|
3500
|
4000
|
4500
|
5000
|
5500
|
6000
|
6500
|
kPa (mmHg, inHg)
|
24.8 (186, 7.32)
|
21.3 (160, 6.30)
|
20.5 (154, 6.06)
|
20.9 (157, 6.18)
|
20.5 (154, 6.06)
|
21.9 (164, 6.46)
|
24.3 (182, 7.17)
|
26.1 (196, 7.72)
|
28.7 (215, 8.46)
|
30.8 (231, 9.09)
|
34.7 (260, 10.23)
|
38.5 (289, 11.38)
|
40.1 (301, 11.85)
|
MT
(Vehicle Speed ≥ 64.4 km/h (40 MPH))
|
rpm
|
700
|
1000
|
1500
|
2000
|
2500
|
3000
|
3500
|
4000
|
4500
|
5000
|
5500
|
6000
|
6500
|
kPa (mmHg, inHg)
|
40.0 (300, 11.81)
|
40.0 (300, 11.81)
|
33.6 (252, 9.92)
|
34.2 (257, 10.11)
|
33.5 (251, 9.88)
|
35.6 (267, 10.51)
|
34.7 (260, 10.24)
|
27.7 (208, 8.19)
|
28.7 (215, 8.46)
|
30.8 (231, 9.09)
|
34.7 (260, 10.23)
|
38.5 (289, 11.38)
|
40.1 (301, 11.85)
|
AT
|
rpm
|
700
|
1000
|
1500
|
2000
|
2500
|
3000
|
3500
|
4000
|
4500
|
5000
|
5500
|
6000
|
6500
|
kPa (mmHg, inHg)
|
26.0 (195, 7.68)
|
23.3 (175, 6.89)
|
22.3 (167, 6.57)
|
22.8 (171, 6.73)
|
22.7 (170, 6.69)
|
24.0 (180, 7.09)
|
27.9 (209, 8.23)
|
30.0 (225, 8.86)
|
31.7 (238, 9.37)
|
35.2 (264, 10.39)
|
40.0 (300, 11.81)
|
44.4 (333, 13.11)
|
45.7 (343, 13.50)
|
|
•
|
Detecting misfire between idling and high revolution.
|
|
•
|
Perform the diagnosis continuously.
|
When the misfire occurred, the engine speed
is decreased and the crankshaft position speed will change. Calculate
the interval difference value (diagnostic value) from crankshaft
position speed by the following formula, and judge whether the misfire
occurs or not comparing the calculated result with judgment value. Counting
the number of misfire up, and if the misfire ratio is higher during
1000 rev. or 200 rev., judge NG for the corresponding cylinder.
Calculate
the diagnostic value (from crankshaft position speed)
|
→
|
Misfire
detection every single ignition (Compare diagnostic value with judgment
value)
|
•
|
180° Interval
Difference Method
|
|
•
|
360° Interval Difference Method
|
|
•
|
720° Interval Difference Method
|
|
→
|
NG judgment
(Judge misfire occurrence required by the law) (Compare number of misfire
with judgment)
|
•
|
FTP1.5
times misfire NG judgment
|
|
•
|
Catalyst damage misfire NG judgment
|
|
As the following figure, pick out a random
cylinder as the standard and name it omg 0. And the former crankshaft
position speed is named omg 1, the second former crankshaft position
speed is named omg 2, the third is named omg 3, and the following
is the same.
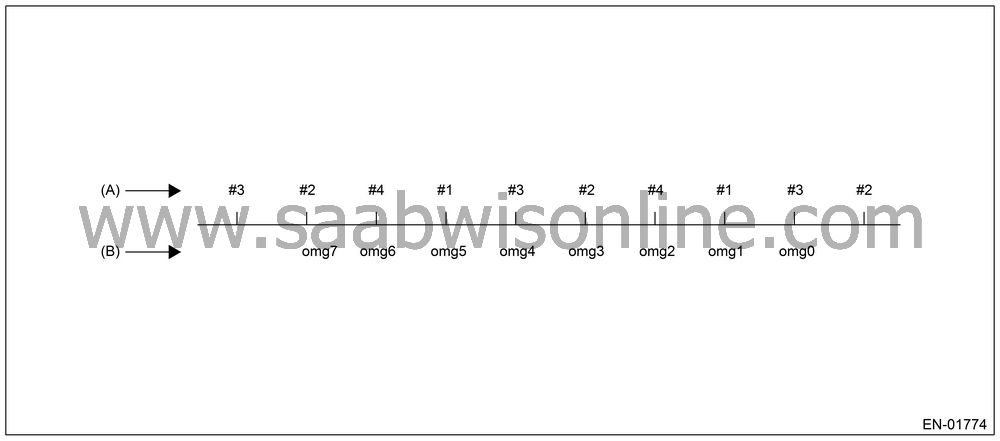
(A)
|
Ignition
order
|
(B)
|
Crankshaft
position speed
|
|
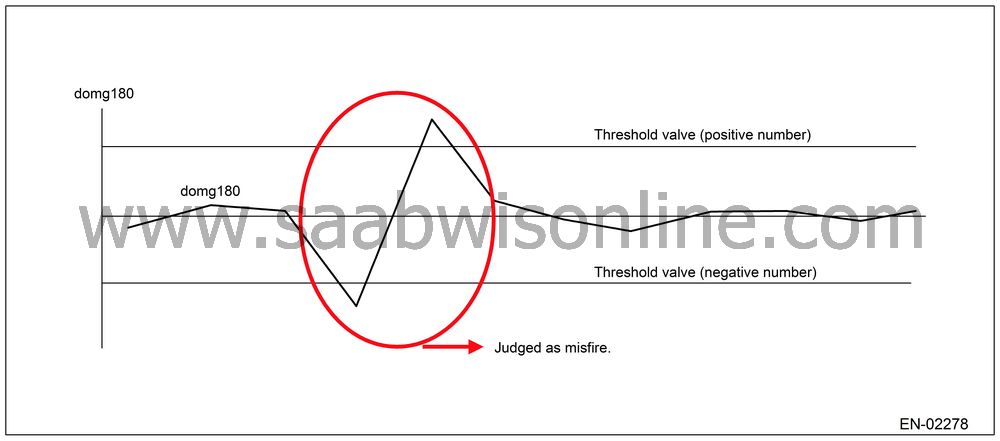
|
180° Interval Difference
Method
Diagnosis value
|
domg
180 = (omg −1 omg 0) − (omg 5 − omg
1)/4
|
Judge misfire occurs in the following cases.
|
|
•
|
domg 180 > judgment
value of positive side
|
|
•
|
domg 180 ≤ judgment
value of negative side
(judgment value before 180°CA)
|
|
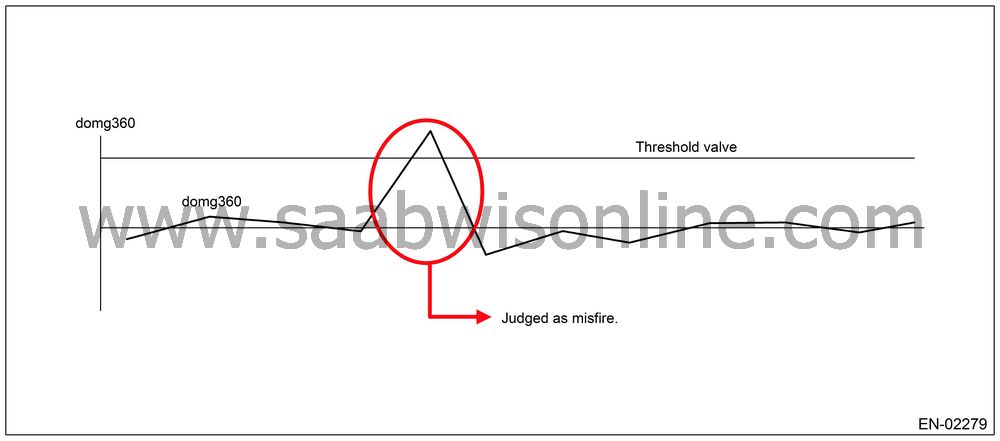
360° Interval Difference
Method
|
Diagnosis
value
|
domg
360 = (omg 1 − omg 0) − (omg 3 − omg
2)
|
Misfire
judgment
|
domg 360 > judgment value
|
→
|
Misfire
occurs
|
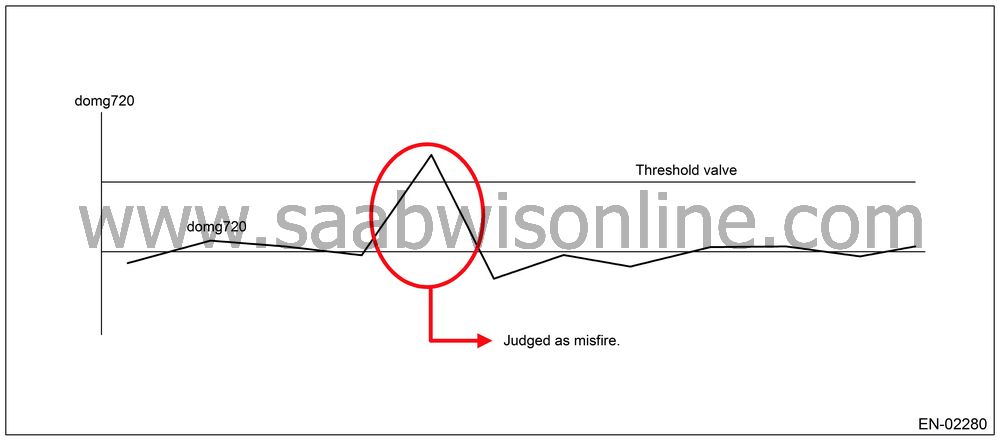
720° Interval Difference
Method
|
Diagnosis
value
|
domg
720 = (omg 1 − omg 0) − (omg 5 − omg
4)
|
Misfire
judgment
|
domg 720 > judgment value
|
→
|
Misfire
occurs
|
FTP 1.5 times misfire (Misfire occurrence
level affecting exhaust gas)
Judgment
Value (Judge that malfunction occurs when the misfire ratio is high
in 1000 engine revs.)
|
Malfunction
Criteria
|
Threshold
Value
|
FTP emission
judgment value
|
> 1.0% in
1000 revs.
|
Time Needed for Diagnosis:
1000
engine revs.
Malfunction Indicator
Light Illumination:
Illuminates when malfunction occurs in
2 continuous driving cycles.
Catalyst damage misfire (Misfire
occurrence level damaging catalyst)
Judgment
Value (Judge that malfunction occurs when the misfire ratio is high
in 200 engine revs. (400 ignitions))
|
Malfunction
Criteria
|
Threshold
Value
|
Catalyst
damage misfire judgment value
|
See Map
1
|
Map 1 Fault criteria
threshold for misfire which would result in catalyst damage
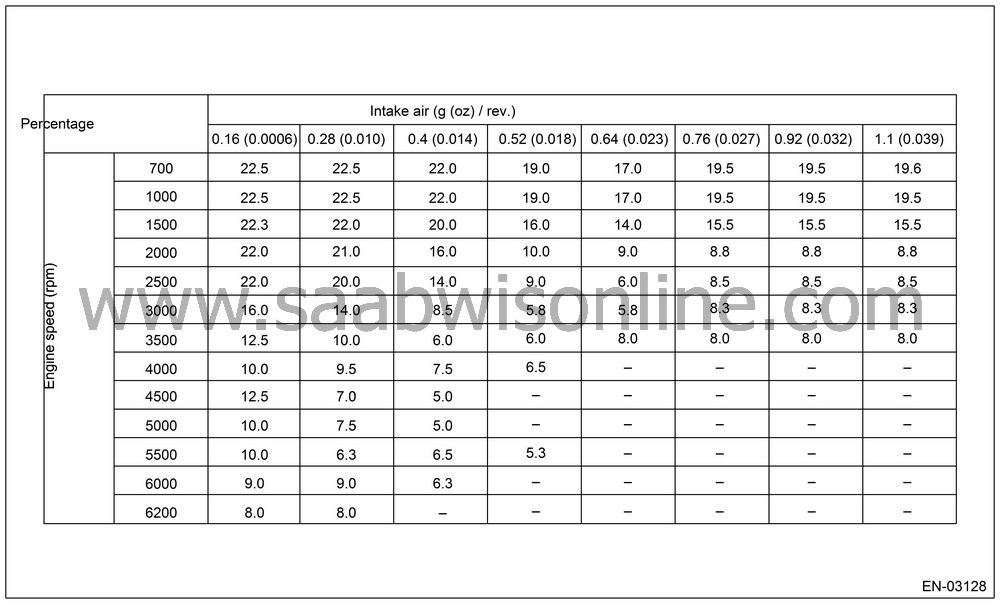
These figures mean the misfire ratio (%)
in 400 ignitions; for example, 22.5 (%) means 400 (ignition) × 22.5 (%) = 90
(ignition) or more, so this case is judged misfire.
Time Needed for Diagnosis:
200
engine revs.
Malfunction Indicator
Light Illumination:
Illuminates as soon as the malfunction
occurs.
|
•
|
When the OK idling cycle was completed 40 times
in a row
|
|
•
|
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
|
MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR LIGHT CLEAR CONDITION
|
|
•
|
When the OK driving cycle was completed 3 times
in a row
|
|
•
|
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
None
|
ECM OPERATING
AT DTC SETTING
|
Memorize the freeze frame data. (For test
mode $02)







