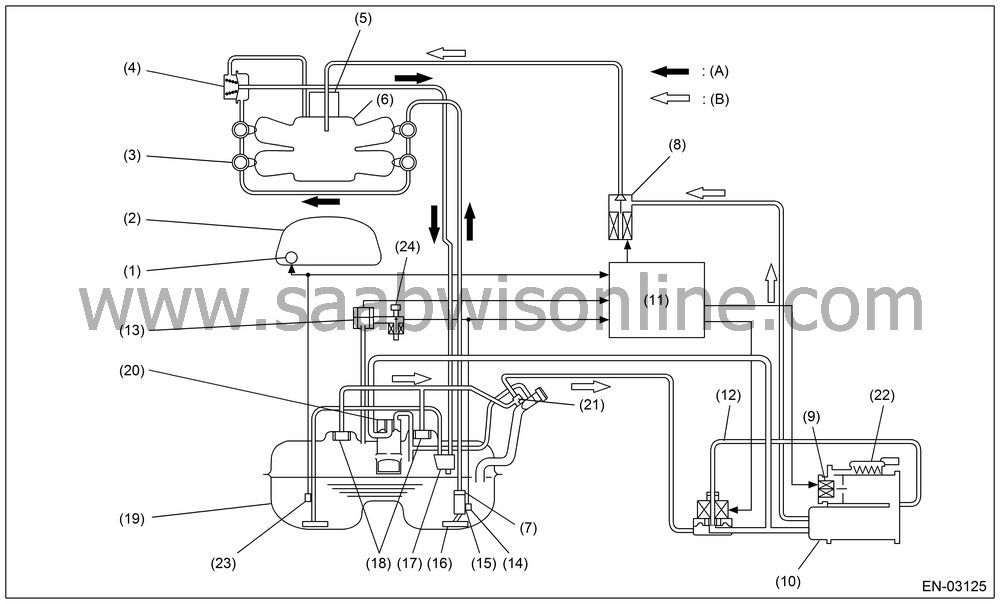
DTC P0442 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LEAK DETECTED (SMALL LEAK)
| DTC P0442 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM LEAK DETECTED (SMALL LEAK) |
|
(1)
|
Fuel gauge
|
(10)
|
Canister
|
(19)
|
Fuel tank
|
|
(2)
|
Combination
meter
|
(11)
|
Engine
control module (ECM)
|
(20)
|
Vent valve
|
|
(3)
|
Fuel injector
|
(12)
|
Pressure
control solenoid valve
|
(21)
|
Shut-off
valve
|
|
(4)
|
Pressure
regulator
|
(13)
|
Fuel tank
pressure sensor
|
(22)
|
Drain filter
|
|
(5)
|
Throttle
body
|
(14)
|
Fuel temperature
sensor
|
(23)
|
Fuel sub
level sensor
|
|
(6)
|
Intake
manifold
|
(15)
|
Fuel level
sensor
|
(24)
|
Fuel tank
sensor control valve
|
|
(7)
|
Fuel filter
|
(16)
|
Fuel pump
|
||
|
(8)
|
Purge control
solenoid valve
|
(17)
|
Jet pump
|
(A)
|
Fuel line
|
|
(9)
|
Drain valve
|
(18)
|
Fuel cut
valve
|
(B)
|
Fuel evaporation
line
|
In this system diagnosis, checking for leakage and valve function is conducted by changing the fuel tank pressure, and monitoring the pressure change using the fuel tank pressure sensor. 0.04 inch diagnosis is performed in the order of mode Z, mode A, mode B, mode C and mode D, and 0.02 inch diagnosis is performed in the order of mode A, mode B, mode C, mode D and mode E.
0.04-inch Diagnosis
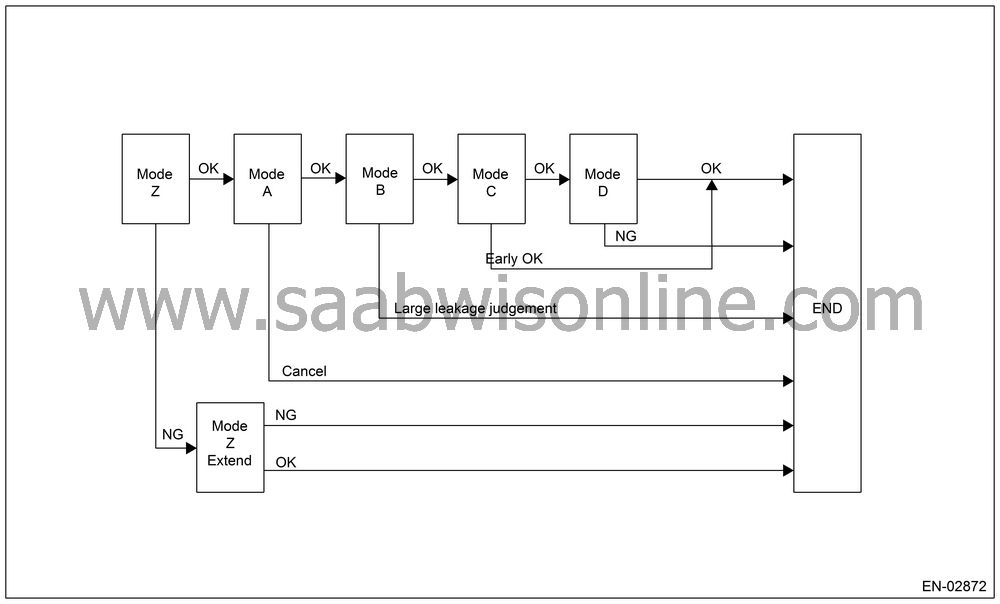
| Mode | Mode Description | Diagnosis Period |
|
Mode
Z
(CPC abnormal open diagnosis) |
Diagnosis
starts when there is a change in fuel tank pressure amount. Purge
control solenoid valve open trouble diagnosis begins.
|
3 — 16
seconds
|
|
Mode
A
(Estimated evaporation amount) |
Calculate
the tank pressure change amount (P1).
|
10
seconds
|
|
Mode
B
(Sealed negative pressure/large leakage judgment) |
Introduce
the intake manifold pressure to the fuel tank and reduce the tank
pressure to the desired value.
If the tank pressure cannot be reduced, it is diagnosed as large leak. |
5 — 25
seconds
|
|
Mode
C
(Pressure increase check/advanced OK judgment) |
Wait until
the tank pressure becomes the desired value (detection starting
pressure of P2). If the tank pressure does not become the value,
make advanced OK judgment.
|
1 — 15
seconds
|
|
Mode
D
(Negative pressure variation measurement/evaporation leakage diagnosis) |
Calculate
the tank pressure variation (P2), and obtain the diagnostic value
using P1 of Mode 1. Perform the evaporation leakage diagnosis using
the diagnostic value.
|
10
seconds
|
Mode Table for Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis
| Mode | Behavior of tank internal pressure under normal conditions | Diagnostic item | DTC |
|
Mode
Z
|
Nearly
same as atmospheric pressure (equivalent pressure of 0 kPa (0 mmHg, 0
inHg))
|
CPC
is judged to be stuck open.
|
P0457
|
|
Mode
A
|
Pressure
is in proportion to amount of evaporative emission.
|
||
|
Mode
B
|
Negative
pressure is formed due to intake manifold negative pressure
|
Large
leakage
|
P0457
|
|
Mode
C
|
Target
pressure is reached.
|
None
|
|
|
Mode
D
|
Pressure
change is small.
|
EVAP
system is judged to have large leak [1.0 mm (0.04 in)].
|
P0442
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
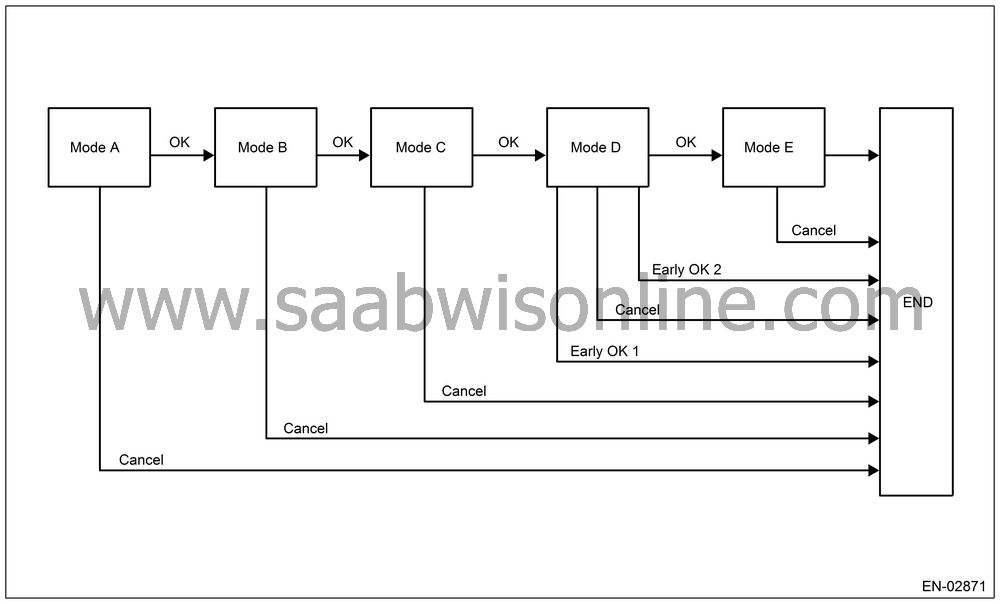
| Mode | Mode Description | Diagnosis Period |
|
Mode
A
(0 point correction) |
Wait until
the tank pressure returns to 0 point (near 0 mm Hg) when tank pressure
is high.
|
0
s — 12 s
|
|
Mode
B
(Negative pressure Introduction) |
Introduce
the intake manifold pressure into fuel tank to reduce the tank pressure
to the desired value.
|
0
s — 27 s
|
|
Mode
C
(Holding negative pressure) |
Wait until
the tank pressure becomes the desired value (detection starting
pressure of P2).
|
0
s — 20 s
|
|
Mode
D
(Calculation of negative pressure variation) |
Calculate
the time that takes the tank pressure to return to detection completing
pressure of P2. When the tank pressure does not return to the detection
completing pressure of P2, make advanced OK judgment.
|
0
s — 200 s
|
|
Mode
E
(Calculation of yielded evaporation amount) |
Calculate
the yielded evaporation amount (P1).
|
0
s — 280 s
|
| COMPONENT DESCRIPTION |
Pressure Control Solenoid Valve
PCV controls the fuel tank pressure to be equal to the atmospheric air pressure.Normally, the solenoid is set to OFF. And the valve opens and closes mechanically in accordance with the pressure difference between tank and atmospheric air, or tank and canister.
The valve is forcibly opened by setting the solenoid to ON at the time of diagnosis.
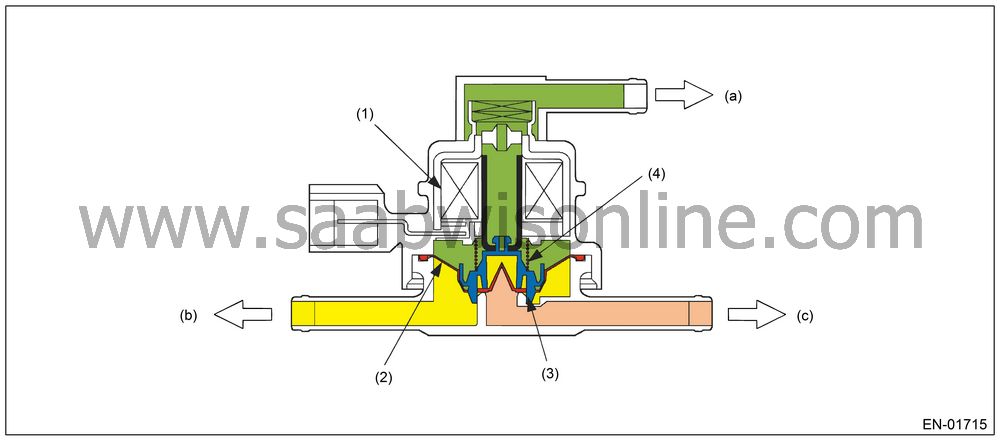
|
(1)
|
Solenoid
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
||
|
(2)
|
Diaphragm
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
||
|
(3)
|
Valve
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
||
|
(4)
|
Spring
|
Valve Operation and Air Flow
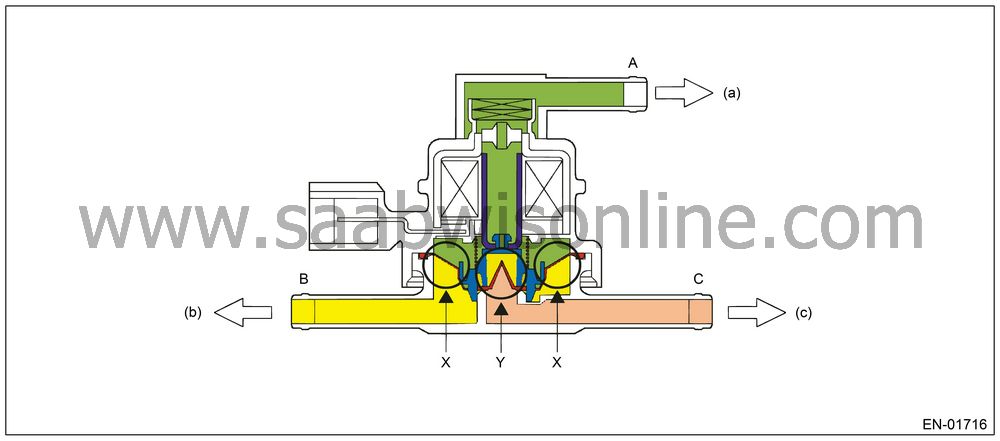
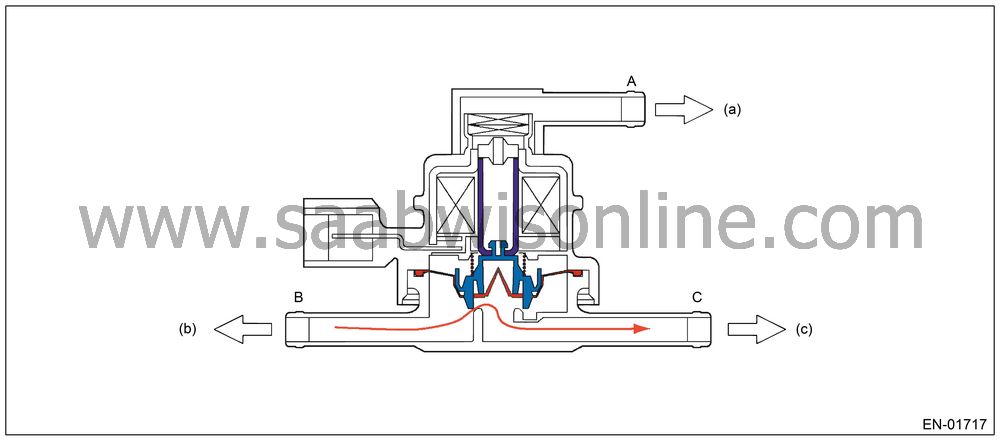
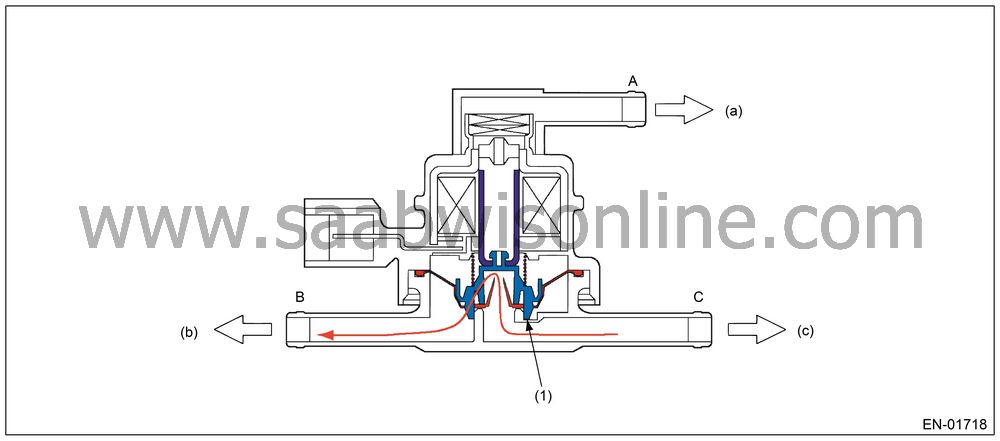
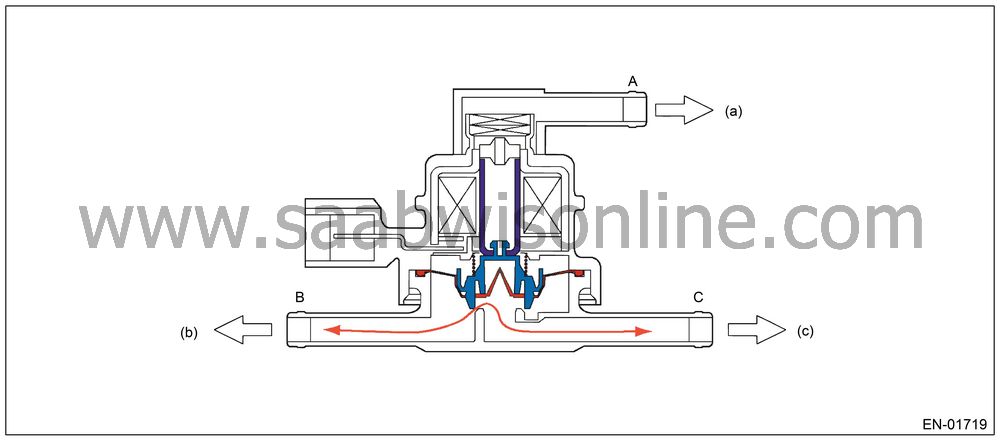
In the figure below, divided by the diaphragm, the part above X is charged with atmospheric air pressure, and the part below X is charged with tank pressure. Also, the part above Y is charged with tank pressure, and the part below Y is charged with canister pressure.If the atmospheric air pressure port is A, tank pressure port is B, and canister pressure port is C, the air flows according to pressure difference from each port as shown in the table below.
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
| Condition of pressure | Flow |
|
A < B
(solenoid OFF)
|
B → C
|
|
B < C
(solenoid OFF)
|
C → B
|
|
Solenoid
ON
|
B ←→ C
|
When A < B (Solenoid OFF)
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
When B < C (Solenoid OFF)
|
(1)
|
Valve
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
||
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
||||
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
When Solenoid is ON
|
(a)
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
(b)
|
Fuel tank
|
(c)
|
Canister
|
CCV
CCV controls the ambient air to be introduced to the canister.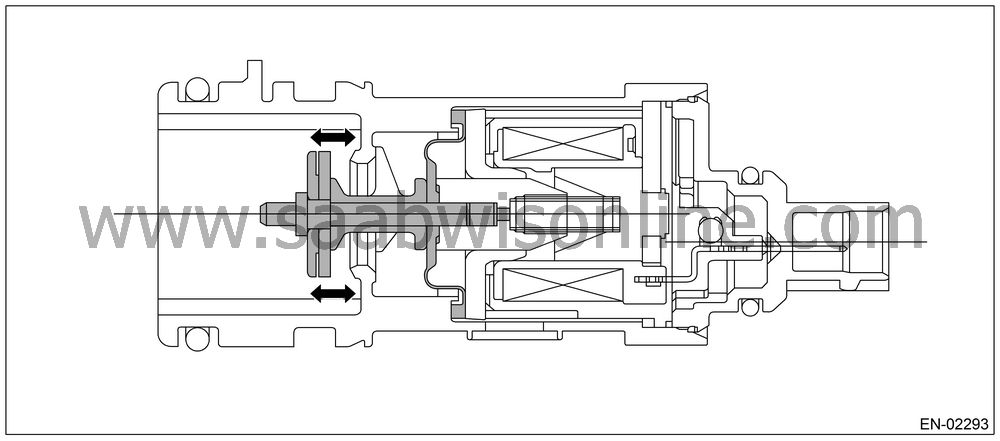
| ENABLE CONDITION |
0.04-inch Diagnosis
| Secondary Parameters | Enable Conditions |
|
Battery
voltage
|
≥ 10.9
V
|
|
Barometric
pressure
|
≥ 75.1
kPa (563 mmHg, 22.17 inHg)
|
|
Cumulative time of canister
purge
|
120 seconds or more
|
|
After
engine starting
|
856
seconds or more
|
|
Learning
value of evaporation gas density
|
≤ 0.08
|
|
Engine
speed
|
1050 ←→ 6000
rpm
|
|
Fuel
tank pressure
|
≥ −4.00
kPa (−30 mmHg, −1.18 inHg)
|
|
Intake
manifold vacuum (relative pressure)
|
< −26.7
kPa (−200 mmHg, −7.87 inHg)
|
|
Vehicle
speed
|
≥ 32
km/h (20 MPH)
|
|
Fuel
level
|
9 ←→ 51 litres (2.38 ←→ 13.47
US gal, 1.98 ←→ 11.22 Imp gal)
|
|
Closed
air/fuel ratio control
|
In
operation
|
|
Fuel
temperature
|
−10 ←→ 45°C
(14 ←→ 113°F)
|
|
Intake
air temperature
|
≥ −10°C
(14°F)
|
|
Pressure
change per second
|
< 0.13
kPa (0.95 mmHg, 0.04 inHg)
|
|
Min.
pressure change per second − Max. pressure change per second
|
< 0.23
kPa (1.7 mmHg, 0.07 inHg)
|
|
Fuel
level change
|
< 2.5 litres(2.1
US qt, 1.8 Imp gal)/128 milliseconds
|
|
Air fuel
ratio
|
> 0.76 — 1.25
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
| Secondary Parameters | Enable Conditions |
|
(At
starting a diagnosis)
|
|
|
Evaporation
diagnosis
|
Not completed
|
|
Battery
voltage
|
≥ 10.9 V
|
|
Atmospheric
pressure
|
≥ 75.1 kPa (563 mmHg, 22.2 inHg)
|
|
Since
last incomplete diagnosis event of 0.02-inch leakage
|
> 600
seconds
|
|
Cumulative
time of canister purge
|
120 seconds or more
|
|
After
engine starting
|
770 second or more
|
|
Fuel
temperature
|
−10 ←→ 70°C
(14 ←→ 158°F)
|
|
Fuel
level
|
9 ←→ 51 litres (2.38 ←→ 13.47
US gal, 1.98 ←→ 11.22 Imp gal)
|
|
Intake
manifold vacuum (relative pressure)
|
< −8.0
kPa (−60 mmHg, −2.36 inHg)
|
|
Fuel
tank pressure
|
−0.67 — 1.43 kPa (−5 — 10.7
mmHg, −0.20 — 0.42 inHg)
|
|
Vehicle
speed
|
≥ 68 km/h (42 MPH)
|
|
Closed
air/fuel ratio control
|
In operation
|
|
Engine
speed
|
550 ←→ 6,000 rpm
|
|
(During
diagnosis)
|
|
|
Fuel
level change
|
≤ 4.2litres (4.4
US qt,
3.7 Imp qt)
|
|
Pressure
change per second
|
< 0.06
kPa (0.44 mmHg, 0.02 inHg)
|
|
Min.
tank pressure change per second − Max. tank pressure change
per second
|
< 0.07
kPa (0.51 mmHg, 0.02 inHg)
|
|
|Tank
pressure change per second|
|
≤ 0.1
kPa (0.75 mmHg, 0.03 inHg)
|
|
Pressure
change (Mode D)
|
−0.47 ←→ 0.32
kPa
(−3.5 ←→ 2.4 mmHg, −0.14 ←→ 0.09
inHg)
|
|
Pressure
change (Mode E)
|
−0.32 ←→ 0.32
kPa
(−2.4 ←→ 2.4 mmHg, −0.09 ←→ 0.09
inHg)
|
| GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE |
0.04-inch Diagnosis
| • |
Perform the diagnosis only once in more than
856 seconds after the engine start at the constant driving speed
of 32 km/h (20 MPH) or more.
|
|
| • |
Pay attention to the fuel temperature
and fuel level.
|
|
0.02-inch Diagnosis
| • |
Perform diagnosis in more than 770 seconds
after engine start at the constant speed of 68 km/h (42
MPH) or more, and judged OK or NG.
|
|
| • |
If not judged OK or NG, repeat the
diagnosis.
|
|
| • |
Pay attention to the fuel level.
|
|
| DIAGNOSTIC METHOD |
Purge control solenoid valve open malfunction diagnosis
DTCP0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (fuel cap loose/off)
Purpose of Mode Z
When performing the leakage diagnosis of EVAP system, CPC has to operate normally. Therefore, mode Z is used to diagnose the CPC open fixation.
If the CPC open fixation trouble is detected, the EVAP system leakage diagnosis is cancelled.
Diagnostic method
CPC functional diagnosis is performed by monitoring the tank pressure in Mode Z.
Normality Judgment
Judge OK when the following criteria are satisfied in 3 seconds after Mode Z started, and change to Mode A.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
(Tank pressure
when Mode Z started) — (Tank pressure when Mode Z finished)
|
≤ 0.4
kPa (3 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
P0457
|
Normal Operation

|
(1)
|
Mode Z
|
(3)
|
Fuel tank
pressure
|
(5)
|
OK judgement
|
|
(2)
|
3 seconds
|
(4)
|
0.4 kPa
(3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
| • |
evptez − evptezha ≤ 0.4 kPa
(3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
|
| • |
evptezini − evptezha ≤ 0.4
kPa (3.0 mmHg, 0.12 inHg)
|
|
Judge normal when both calculations are completed.
Abnormality Judgment
If OK judgment cannot be made, extend Mode Z 16 seconds more, and judge NG when all the criteria below are completed in 16 seconds.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
(Tank
pressure when Mode Z started) − (Tank pressure when Mode
Z finished)
|
> 0.6
kPa (4.5 mmHg, 0.18 inHg)
|
P0457
|
|
Tank
pressure when Mode Z started
|
≤ 1.43
kPa (10.7 mmHg, 0.42 inHg)
|
|
|
TIme for
no fuel rolling of 2litres or more
|
≥ 40
seconds
|
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 16 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunction occurs in 2 continuous driving cycles.
Finish the Evap. diagnosis when making NG judgment for purge control solenoid valve open fixation.
Cancel the Evap. diagnosis when the OK/NG judgment for purge control solenoid valve open fixation cannot be made in Mode Z.
Purge Control Solenoid Valve Open Fixation

|
(1)
|
Mode Z
|
(4)
|
Fuel tank
pressure
|
(7)
|
No fuel rolling for more than 40 seconds
|
|
(2)
|
Extended
mode Z
|
(5)
|
0.87 kPa
(6.5 mmHg, 0.26 inHg)
|
||
|
(3)
|
16 seconds
|
(6)
|
1.43 kPa
(10.7 mmHg, 0.42 inHg)
|
(8)
|
NG judgement
|
| • |
evptezini, evptez ≤ 1.43 kPa (10.7
mmHg, 0.42 inHg)
|
|
| • |
evptez − evptezha ≤ 0.87
kPa (6.5 mmHg, 0.26 inHg)
|
|
| • |
evptezini − evptezha ≤ 0.87
kPa (6.5 mmHg, 0.26 inHg)
|
|
| • |
No fuel rolling of above 2litres(0.79
US gal, 0.67 Imp gal) for more than 40 seconds.
|
|
Judge normal when all the calculations are completed.
Leak Diagnosis
DTCP0442 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (small leak)
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (fuel cap loose/off)
Diagnostic method
| • |
The diagnostic method consists of creating
a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the presence
of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns
to atmospheric pressure.
|
|
| • |
The diagnosis is divided into the following
five phases.
|
|
Mode A: (Estimation of evaporation gas yield)
The amount of change of tank pressure (P1) in Mode A is calculated. After calculating P1, change to Mode B.
Mode B: (Seal negative pressure)
Introduce the negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → −1.4 kPa (0 → −10.5 mmHg, 0 → −0.41 inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, Mode C is entered.
In this case, if the tank pressure does not become the desired negative pressure, judge that there is a large leakage in the system, finish the Evap. diagnosis when judging large leak (10 or 25 seconds).
Abnormality Judgment
Judge NG (large leak) when the criteria below are completed in the specified time.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
P0457
|
||
|
Time
before reaching desired negative pressure
|
≥ 25
seconds
|
|
|
Or
time for Mode B
|
≥ 10
seconds
|
|
|
(Min.
value of tank pressure during Mode B) − (Tank pressure
when Mode B started)
|
< −0.3
kPa (−4 mmHg, −0.16 inHg)
|
Mode C: (Check increasing pressure)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure. (Wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation.)
Change to Mode D when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation.
Judge immediate OK and change to Mode E when it does not return in spite of spending the specified time.
| Tank pressure when P2 calculation started | Time for immediate OK judgment |
|
−1.3
kPa (−9.75 mmHg, −0.38 inHg)
|
15 seconds
|
Mode D: (Measurement of negative pressure changes)
Monitor the pressure variation in the tank in Mode Z. In this case, the tank pressure increases, that is, the pressure becomes as high as the atmospheric air pressure, because evaporator is generated. However, if any leakage exists, the pressure increases additionally in proportion to this leakage. The pressure variation of this tank is P2.
After calculating P2, perform following small leak diagnosis.
After Mode D
Assigning P1 and P2, which are tank variations measured in Mode A and Mode B, to the formula below, judge the small leakage of the system. If the measured judgment value exceeds the threshold value, it is judged to be malfunction.
Abnormality Judgment
Judge NG when the criteria below are completed. Judge OK when not completed and clear the NG.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value | DTC |
|
P2 − 1.5 × P1
|
> Value on map 7. *Threshold value: Map (Fuel
level vs Tank temperature)
|
P0442
|
|
P2: Change of tank pressure within 10 seconds on Mode D
|
||
|
P1:
Change of tank pressure within 10 seconds on Mode A
|
*1.5:
Compensation
value of the amount of evaporator occurrence. (Because evaporator
increases more when becoming negative pressure.)
Map 7 Limit of malfunction criteria as Evap. diagnosis.
| Fuel temperature vs Fuel level | 5°C (41°F) | 15°C (59°F) | 25°C (77°F) | 35°C (95°F) | 45°C (113°F) |
|
10 L
(2.6 US gal, 2.2 Imp gal)
|
0.49
kPa
(3.68 mmHg, 0.145 inHg) |
0.49
kPa
(3.68 mmHg, 0.145 inHg) |
0.50
kPa (3.75 mmHg, 0.148 inHg)
|
0.54
kPa
(4.07 mmHg, 0.160 inHg) |
0.56
kPa
(4.17 mmHg, 0.164 inHg) |
|
20 L
(5.3 US gal, 4.4 Imp gal)
|
0.50
kPa (3.77 mmHg, 0.148 inHg)
|
0.51
kPa (3.79 mmHg, 0.149 inHg)
|
0.53
kPa
(4.01 mmHg, 0.158 inHg) |
0.56
kPa
(4.17 mmHg, 0.164 inHg) |
0.57
kPa
(4.27 mmHg, 0.168 inHg) |
|
30 L
(7.9 US gal, 6.6 Imp gal)
|
0.51
kPa (3.85 mmHg, 0.152 inHg)
|
0.51
kPa (3.79 mmHg, 0.149 inHg)
|
0.54
kPa
(4.06 mmHg, 0.160 inHg) |
0.57
kPa
(4.27 mmHg, 0.168 inHg) |
0.60
kPa
(4.48 mmHg, 0.176 inHg) |
|
40 L
(10.6 US gal, 8.8 Imp gal)
|
0.65
kPa (4.88 mmHg, 0.192 inHg)
|
0.65
kPa (4.90 mmHg, 0.193 inHg)
|
0.66
kPa (4.98 mmHg, 0.196 inHg)
|
0.71
kPa (5.32 mmHg, 0.209 inHg)
|
0.76
kPa (5.73 mmHg, 0.226 inHg)
|
|
50 L
(13.2 US gal, 11.0 Imp gal)
|
0.79
kPa
(5.90 mmHg, 0.232 inHg) |
0.79
kPa
(5.90 mmHg, 0.232 inHg) |
0.79
kPa
(5.90 mmHg, 0.232 inHg) |
0.85
kPa
(6.38 mmHg, 0.251 inHg) |
0.88
kPa
(6.60 mmHg, 0.260 inHg) |
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 30 — 100 Seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunction occurs in 2 continuous drive cycles.
Leak diagnosis
DTCP0456 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (very small leak)
Diagnostic method
| • |
The diagnostic method consists of creating
a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the presence
of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns
to atmospheric pressure.
|
|
| • |
The diagnosis is divided into the following
five phases.
|
|
Mode A: (0 point correction)
Wait until the tank pressure returns to 0 point (near 0 mmHg) when tank pressure is high. Then change to Mode B. If the tank pressure does not return to 0 point in the specified time, cancel the diagnosis.
Mode B: (Negative pressure introduction)
Introduce the negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → −2.0 kPa (0 → −15 mmHg, 0 → −0.59 inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, Mode C is entered.
In this case, if the tank pressure does not become the desired negative pressure, cancel the diagnosis.
Mode C: (Holding negative pressure)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure. (Wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation.)
Change to Mode D when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation, or when spending the specified time.
Mode D: (Calculation of negative pressure variation)
By monitoring the tank pressure at Mode D, calculate the pressure variation (P2) and measure the time (evpdset) it takes the tank pressure to return to the detection completing pressure of P2. Then change to Mode E. When the tank pressure does not return to the detection completing pressure of P2 in the specified time, make advanced OK judgment or cancel the diagnosis according to P2 value.
Normality judgment
Judge OK when the following criteria are satisfied.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value |
|
Advanced OK judgment 1
|
|
|
Mode D holding
time
|
≥ 30 seconds
|
|
Tank pressure
|
≤ −1.8
kPa (−13.4 mmHg, −0.53 inHg)
|
|
Advanced OK judgment 2
|
|
|
Mode D holding
time
|
≥ 200 seconds
|
|
P2
|
≤ 0.9 — 1.3 kPa
(7 — 9.6 mmHg, 0.28 — 0.38 inHg) |
Mode E (Calculation of yielded evaporation amount)
Calculate the pressure variation (P1) at the time (evpdset), and make NG/OK judgment according to P1 value (ambiguous determination acceptable).
Abnormality Judgment
Judge NG when the following criteria are satisfied.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value |
|
P1
|
< Value from Map 7
|
|
* Threshold value: Map (Fuel
level vs evpdset)
|
Map 7 Limit of malfunction criteria as Evap. diagnosis
| Time (evpdset) vs Fuel level | 0 seconds | 30 seconds | 80 seconds | 100 seconds | 150 seconds | 200 seconds |
|
10 L
(2.6 US gal, 2.2 Imp gal)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
0.21
kPa (1.6 mmHg, 0.063 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
|
30 L
(7.9 US gal, 6.6 Imp gal)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
0.21
kPa (1.6 mmHg, 0.063 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
|
50 L
(13.2 US gal, 11.0 Imp gal)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
0.24
kPa
(1.8 mmHg,
0.071 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0.29
kPa (2.2 mmHg, 0.087 inHg)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
0
kPa
(0 mmHg,
0 inHg)
|
Normality judgment
Judge OK when the following criteria are satisfied.
Judgment Value
| Malfunction Criteria | Threshold Value |
|
P1
|
> Value from Map
8
|
|
* Threshold value: Map (Fuel
level vs evpdset)
|
Map 8 Limit of malfunction criteria as Evap. diagnosis
| Time (evpdset) vs Fuel level | 0 seconds | 30 seconds | 80 seconds | 100 seconds | 150 seconds | 200 seconds |
|
10 L
(2.6 US gal, 2.2 Imp gal)
|
0.16
kPa (1.2 mmHg, 0.047 inHg)
|
0.37
kPa (2.8 mmHg, 0.110 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
|
30 L
(7.9 US gal, 6.6 Imp gal)
|
0.16
kPa (1.2 mmHg, 0.047 inHg)
|
0.37
kPa (2.8 mmHg, 0.110 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
|
50 L
(13.2 US gal, 11.0 Imp gal)
|
0.16
kPa (1.2 mmHg, 0.047 inHg)
|
0.40
kPa
(3 mmHg, 0.118 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
0.45
kPa (3.4 mmHg, 0.134 inHg)
|
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 540 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunction occurs in 2 continuous drive cycles.
| DTC CLEAR CONDITION |
| • |
When the OK idling cycle was completed 40 times
in a row
|
|
| • |
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
|
| MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT CLEAR CONDITION |
| • |
When the OK driving cycle was completed 3 times
in a row
|
|
| • |
When “Clear Memory” was
performed
|
|
| FAIL SAFE |
None
| ECM OPERATION AT DTC SETTING |
| • |
Memorize the freeze frame data. (For test mode $02)
|
|
| • |
Memorize the diagnostic value and trouble
standard value. (For test mode $06)
|
|