INSPECTION
| INSPECTION |
| ARMATURE |
Check the commutator for any sign of burns of rough surfaces or stepped wear. If wear is of a minor nature, correct it by using sand paper.
Run-out test
Check the commutator run-out, and then replace if it exceeds the limit.
Commutator run-out:
Standard
0.05 mm (0.0020 in)Service limit
Less than 0.10 mm (0.0039 in)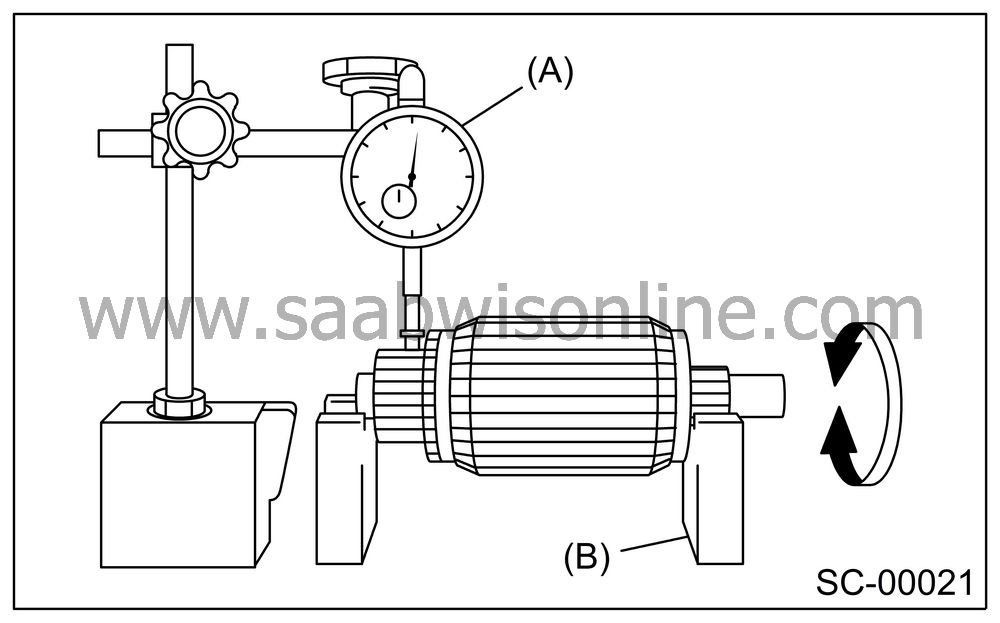
|
(A)
|
Dial gauge
|
|
(B)
|
V-block
|
Depth of segment mold
Check the depth of segment mold.
Depth of segment mold:
0.5 mm (0.020 in)
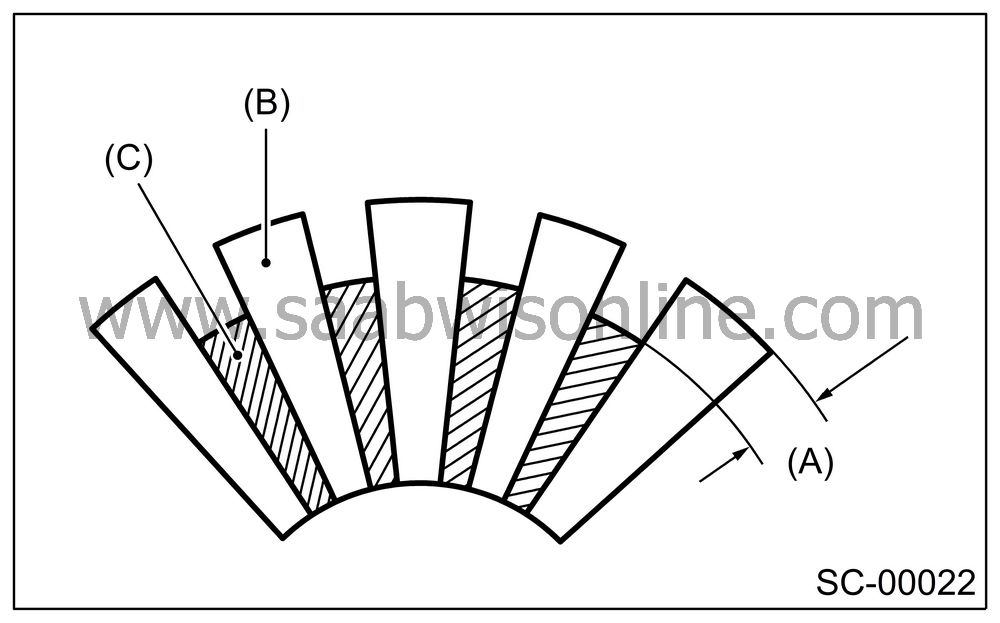
|
(A)
|
Depth of
mold
|
|
(B)
|
Segment
|
|
(C)
|
Mold
|
Armature short-circuit test
Check the armature for short-circuit by placing it on a growler tester. Hold an iron sheet against the armature core while slowly rotating armature. A short-circuited armature will cause the iron sheet to vibrate and to be attracted to core. If the iron sheet is attracted or vibrates, the armature, which is short-circuited, must be replaced or repaired.
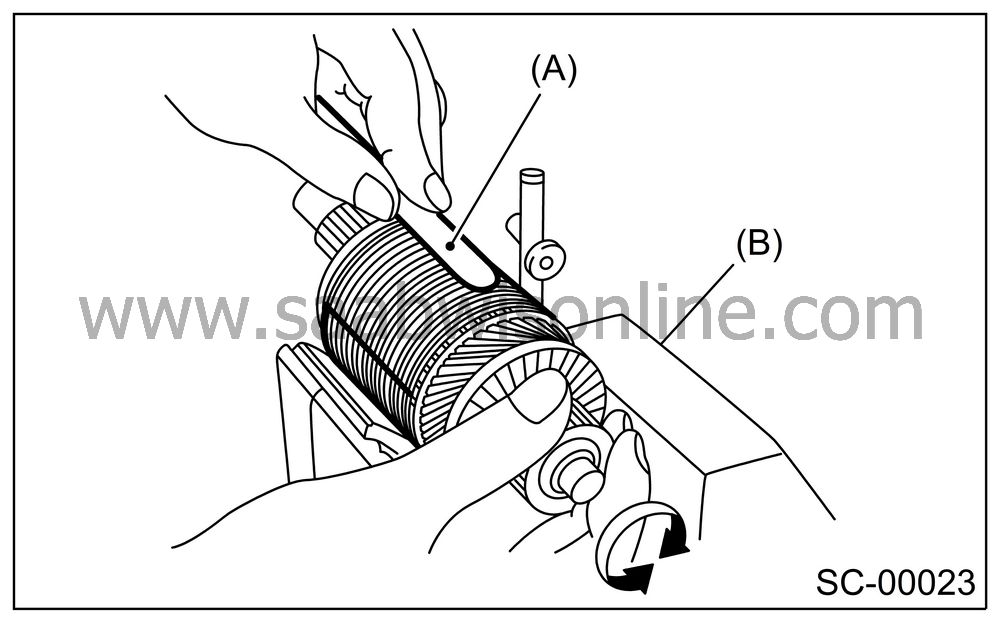
|
(A)
|
Iron sheet
|
|
(B)
|
Grower
tester
|
Armature ground test
Using a circuit tester, touch one probe to the commutator segment and the other to shaft. There should be no continuity. If there is continuity, the armature is grounded.
Replace the armature if it is grounded.
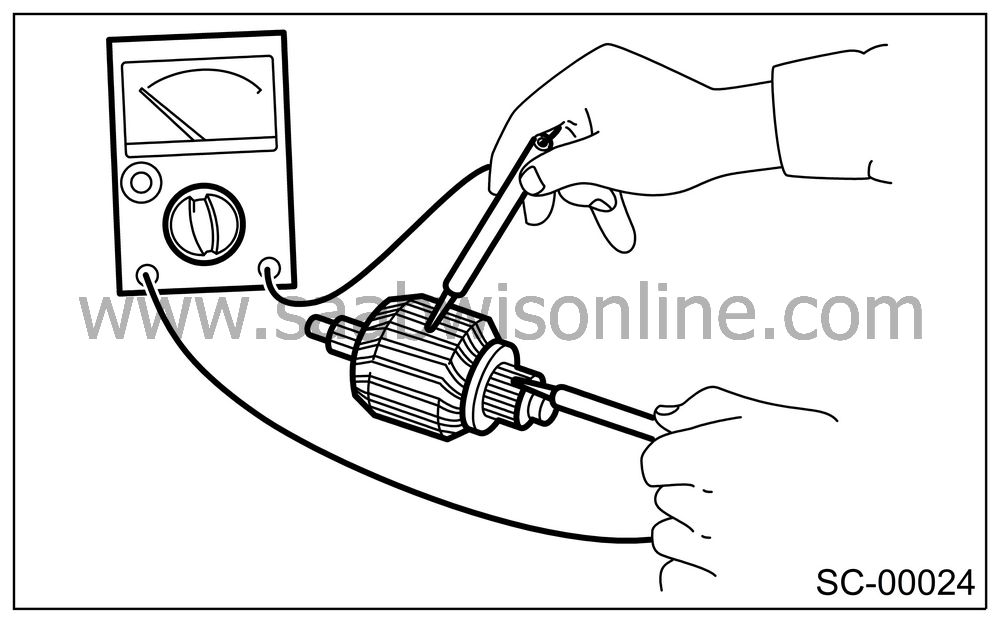
| YOKE |
Make sure the pole is set in position.
| OVERRUNNING CLUTCH |
Inspect the teeth of pinion for wear and damage. Replace if it is damaged. It is normal if the pinion rotates smoothly in direction of rotation (counterclockwise) and does not rotate in the opposite direction.
| Important | ||
|
Do not clean the overrunning clutch with oil to prevent grease from flowing out. |
||
| BRUSH AND BRUSH HOLDER |
Brush length
Measure the brush length, and then replace if it is worn down to under the service limit.
Replace if abnormal wear or cracks are noticed.
Brush length:
Standard
12.3 mm (0.484 in)Service limit
7.0 mm (0.276 in)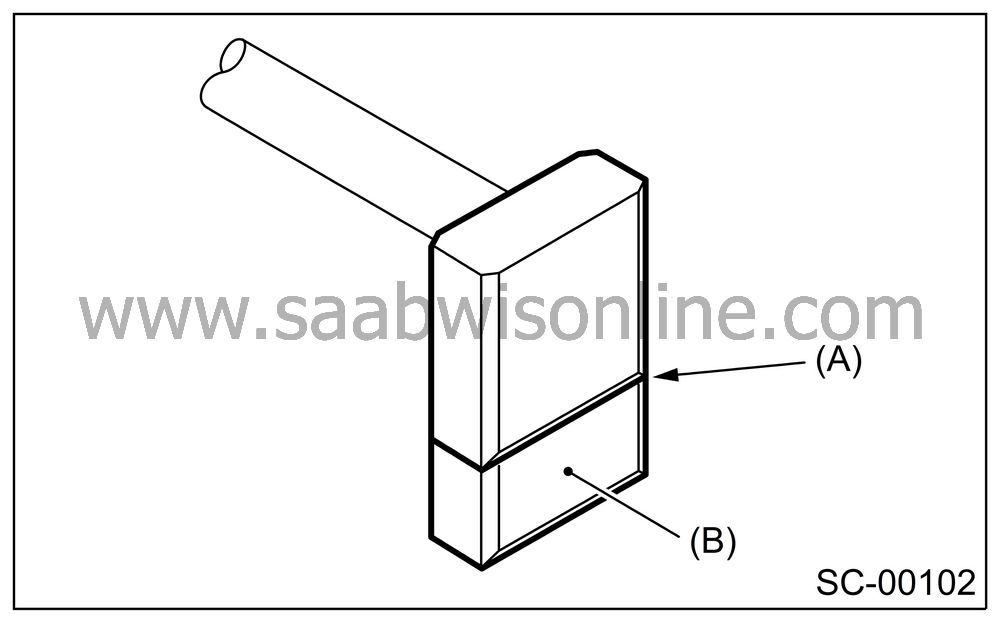
|
(A)
|
Service
limit line
|
|
(B)
|
Brush
|
Brush movement
Be sure the brush moves smoothly inside brush holder.
Brush spring force
Measure the brush spring force with a spring scale. If it is less than the service limit, replace the brush holder.
Brush spring force:
Standard
Except Saab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT MODEL
15.9 — 19.5 N (1.62 — 1.99 kgf, 3.57 — 4.38 lb) (when new)Saab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT MODEL
21.6 N (2.2 kgf, 4.9 lb) (when new)Service limit
Except Saab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT MODEL
2.5 N (0.25 kgf, 0.56 lb)Saab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT MODEL
5.9 N (0.6 kgf, 1.3 lb)| SWITCH ASSEMBLY |
Using a circuit tester (set in “ohm”), check that there is continuity between terminals S and M, and between terminal S and ground.
Also check to be sure there is no continuity between terminals M and B.
Terminal/Specified resistance:
S — M/Less than 1 Ω
S — Ground/Less than 1 Ω
M — B/More than 1 MΩ
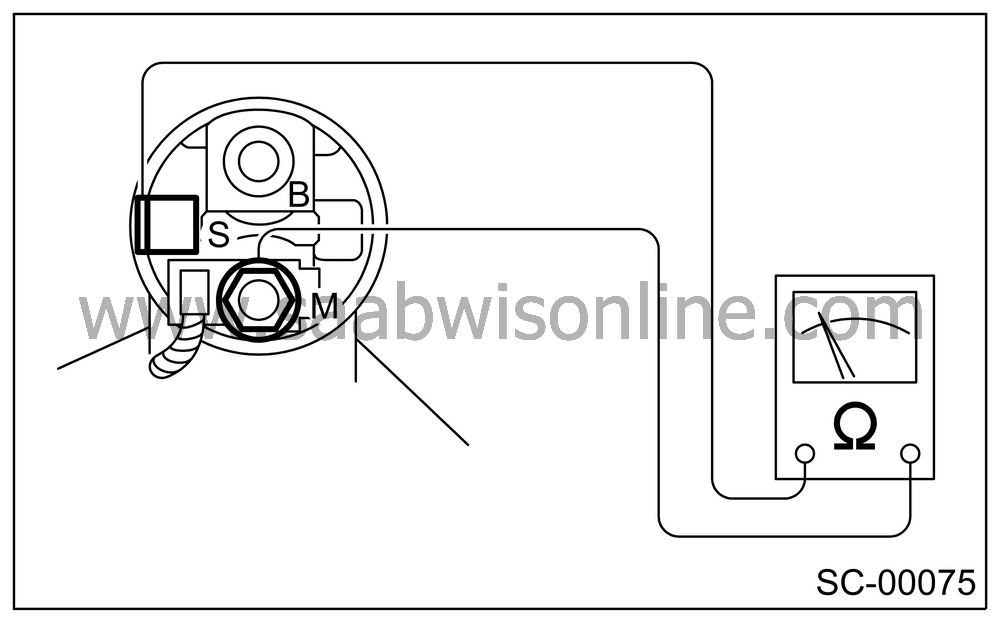
| SWITCH ASSEMBLY OPERATION |
Connect the terminal S of switch assembly to positive terminal of battery with a lead wire, and starter body to ground terminal of battery. The pinion should be forced endwise on shaft.
| Important | ||
|
With the pinion forced endwise on shaft, the starter motor may rotate because current flows through the pull-in coil to motor, however, this is not a problem. |
||
Disconnect the connector from terminal M, and then connect the positive terminal of battery and terminal M using a lead wire and ground terminal to starter body.
In this test set up, the pinion should return to its original position even when it is pulled out with a screwdriver.
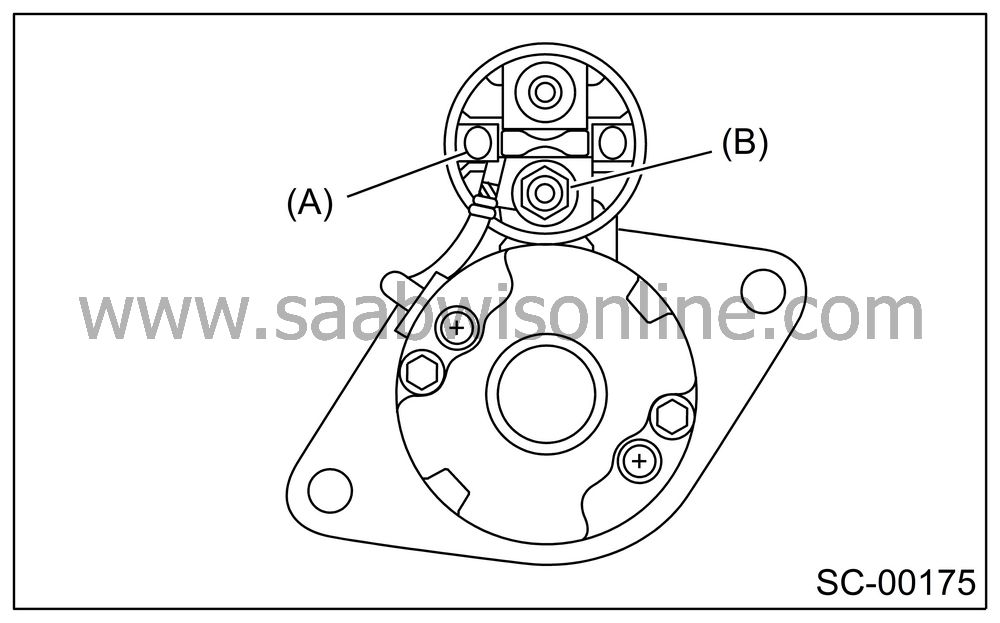
|
(A)
|
Terminal
S
|
|
(B)
|
Terminal
M
|
| PINION GAP |
Measure the pinion gap while the pinion is pulled out as shown in the figure.
Pinion gap:
0.5 — 2.0 mm (0.020 — 0.079 in)
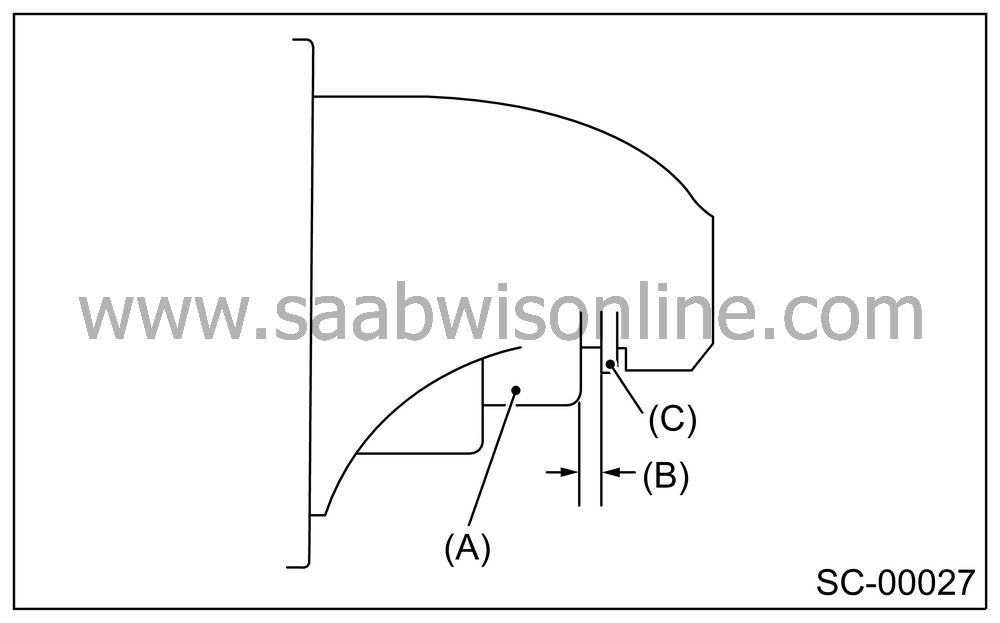
|
(A)
|
Pinion
|
|
(B)
|
Gap
|
|
(C)
|
Stopper
|
If the motor is running with the pinion forced endwise on shaft, disconnect the connector from terminal M of switch assembly, and then connect terminal M to ground terminal (−) of battery with a lead wire. Next, gently push the pinion back with your fingertips, and then measure the pinion gap.
| PERFORMANCE TEST |
The starter should be submitted to performance tests whenever it has been overhauled, to assure its satisfactory performance when installed on the engine.
Three performance tests, no-load test, load test, and lock test, are presented here; however, if the load test and lock test cannot be performed, carry out at least the no-load test.
For these performance tests, use the circuit shown in figure.
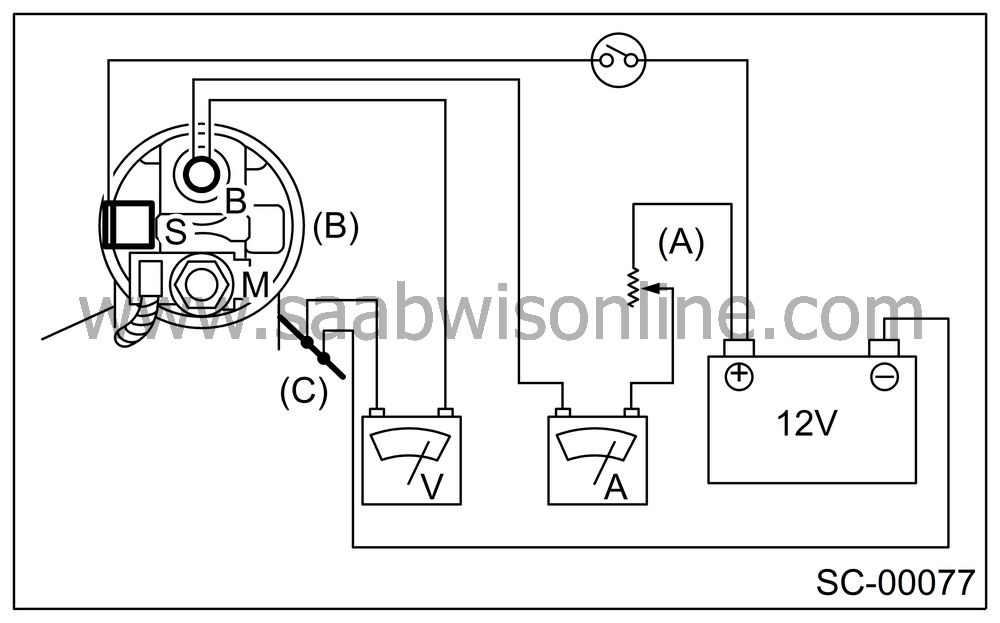
|
(A)
|
Variable
resistor
|
|
(B)
|
Magnetic
switch
|
|
(C)
|
Starter
body
|
No-load test
With switch on, adjust the variable resistor to obtain 11 V, take the ammeter reading, and then measure the starter speed. Compare these values with the specifications.
No-load test (standards):
Voltage/Current
Saab 9-2X 2.5i Linear MT
MAX. 11 V/95 ASaab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT
MAX. 11 V/90 AAT
MAX. 11 V/90 ARotating speed
Saab 9-2X 2.5i Linear MT
More than 2,500 rpmSaab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT
More than 2,860 rpmAT
More than 2,000 rpmLoad test
Apply the specified braking torque to starter. The condition is satisfactory if the current draw and starter speed are within the specifications.
Load test (standards):
Voltage/Load
Saab 9-2X 2.5i Linear MT
8 V/8.5 Nm (0.87 kgf-m, 6.3 ft-lb)Saab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT
8 V/9.3 Nm (0.95 kgf-m, 6.9 ft-lb)AT
8 V/9.8 Nm (1.0 kgf-m, 7.2 ft-lb)Current/Speed
Saab 9-2X 2.5i Linear MT
More than 280 A/870 rpmSaab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT
More than 280 A/860 rpmAT
More than 280 A/1000 rpmLock test
With the starter stalled, or not rotating, measure the torque developed and current draw when the voltage is adjusted to the specified voltage.
Lock test (standards):
Voltage/Current
Saab 9-2X 2.5i Linear MT
Less than 4 V/680 ASaab 9-2X 2.0T Aero MT
Less than 4 V/515 AAT
Less than 3.5 V/960 ATorque


