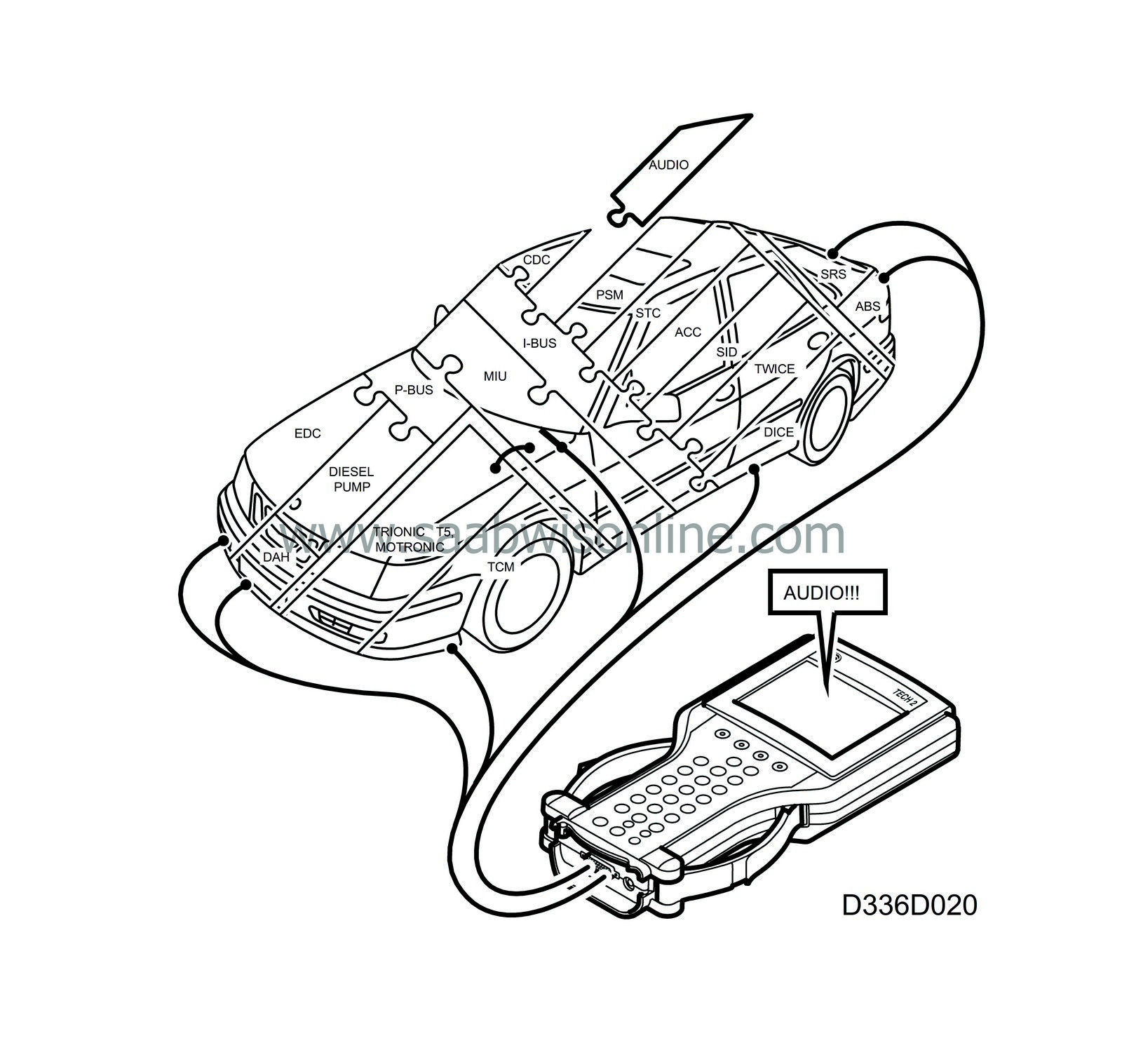
Bus diagnosis
| Bus diagnosis |
In a bus system, it is necessary for all the units to be able to communicate with each other. For example, the engine cannot be started unless the engine management system can receive the immobilizer information sent by TWICE (not OBDII).
Bus faults can be caused by a bus lead breaking. This could result in one or more systems disappearing from the bus concerned (I or P), depending on where the break in the wiring harness occurred.
If a short circuit occurs in a bus lead, all systems will disappear from the bus concerned (I or P).
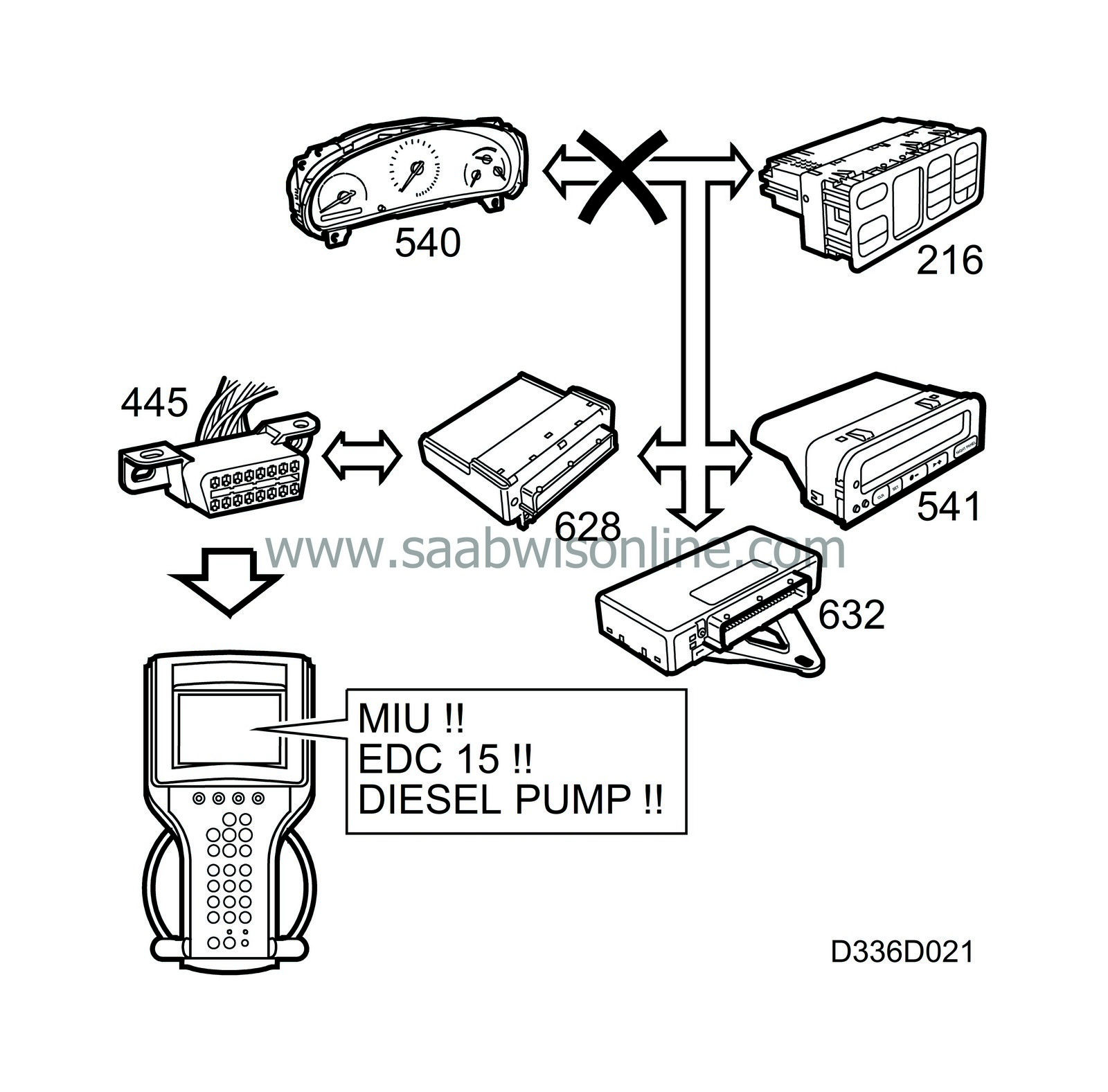
Note that if there is a short circuit on the I bus, DICE will be the only bus system that can be contacted with the diagnostic tool with the exception of EDC 15.
In the event of a grounding or power supply fault in one or more systems, these systems will no longer be able to communicate.
| Permanent bus faults |
Irrespective of which system is contacted, the diagnostic tool will first check with the aid of the DICE that all systems in the car connected to a bus are awake and in communication.
If any control module connected to a bus is missing, the diagnostic tool will show this. This means that all control modules connected to a bus are communicating correctly unless the diagnostic tool indicates otherwise with a warning.
In the case of a permanent bus fault, the text on the diagnostic tool's display will refer to a fault diagnosis procedure described in the ”Bus and diagnostics communication” category.