EGR
| EGR |
| - |
Desired value calculation
|
|
| - |
Air mass calculation
|
|
| - |
EGR control and monitoring
|
|
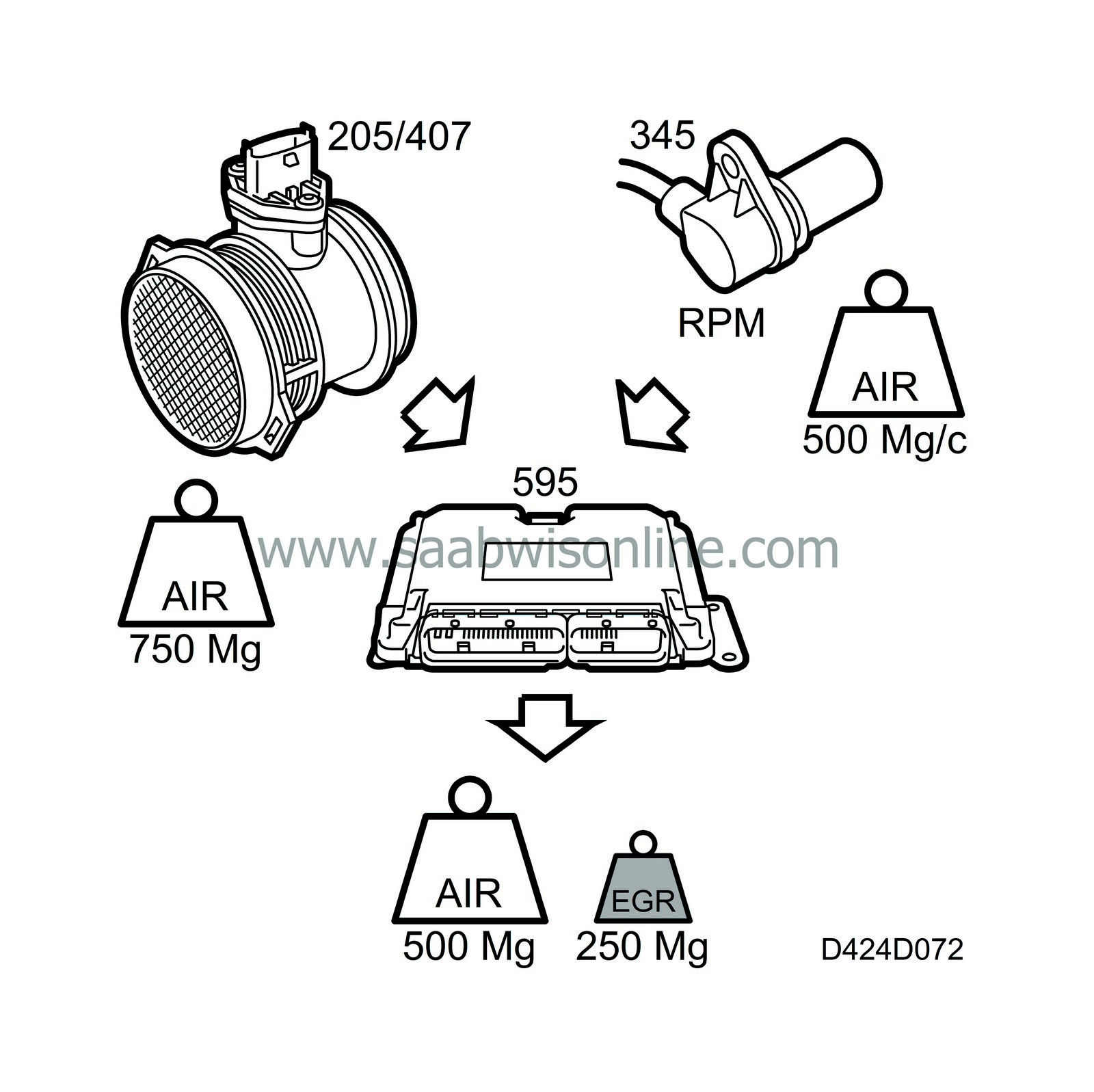
The calculation of the desired value determines the air mass/combustion required by the engine. The EGR control valve is controlled so that the desired quantity of air is obtained. This is achieved by allowing the quantity of recirculated exhaust gas into the intake that is required to reduce the intake air mass/combustion to the value calculated by the function for calculating the desired value.
Example:
At a certain moment, the engine can pump through 750 mg air/combustion.The desired value calculation says that it should be 500 mg air/combustion for these particular operating conditions. The control function will then open the EGR valve to allow just enough exhaust gas to enter to prevent 250 mg air/combustion from entering the engine.
| Desired value calculation |
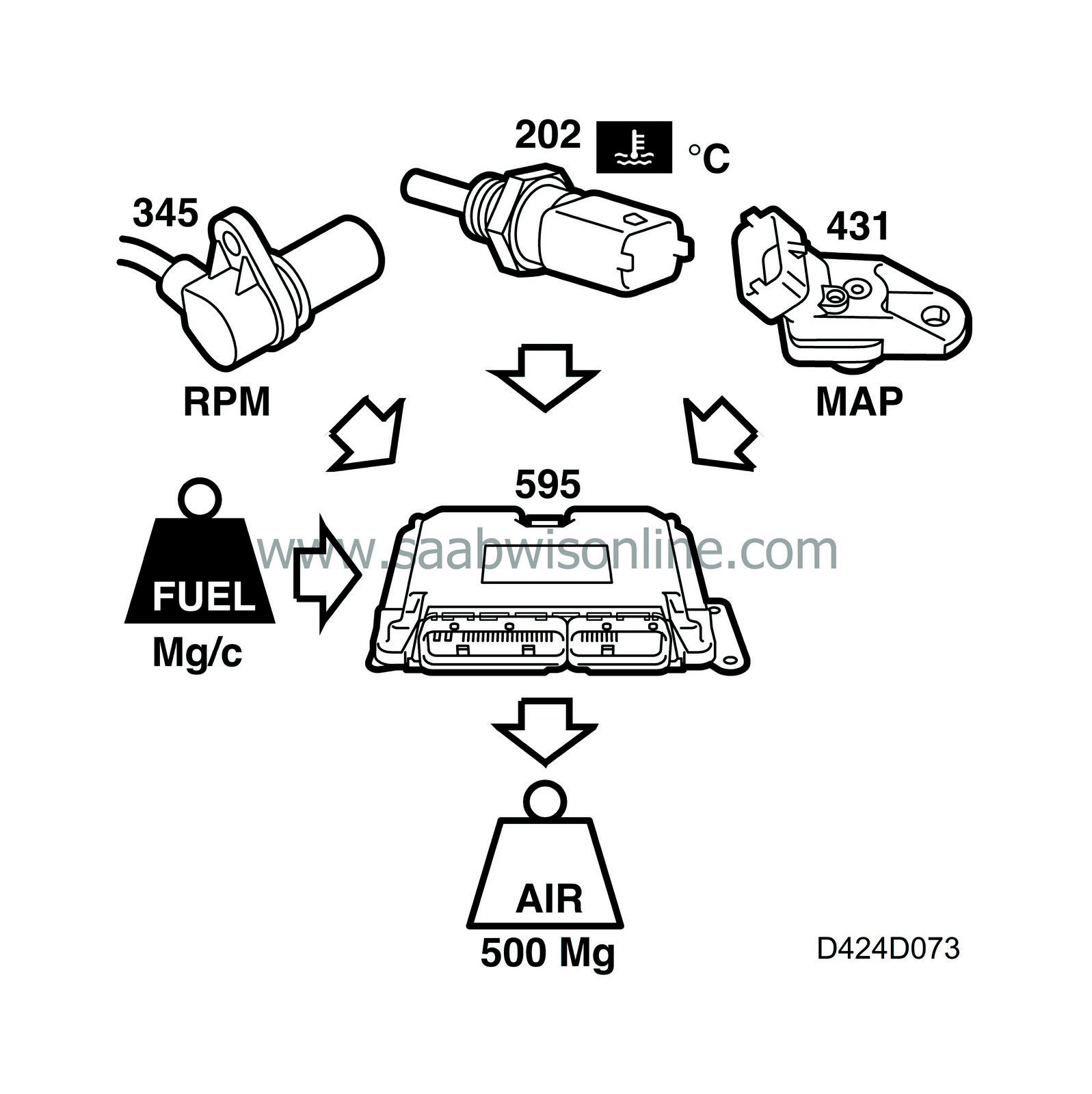
The desired value calculation determines the desired air mass/combustion and makes it available for the other EGR functions. The desired value is a function of
| - |
Engine speed
|
|
| - |
Injected fuel quantity
|
|
| - |
Coolant temperature
|
|
| - |
Atmospheric pressure
|
|
The result of the desired value calculation is carried forward to EGR control.
| Air mass calculation |
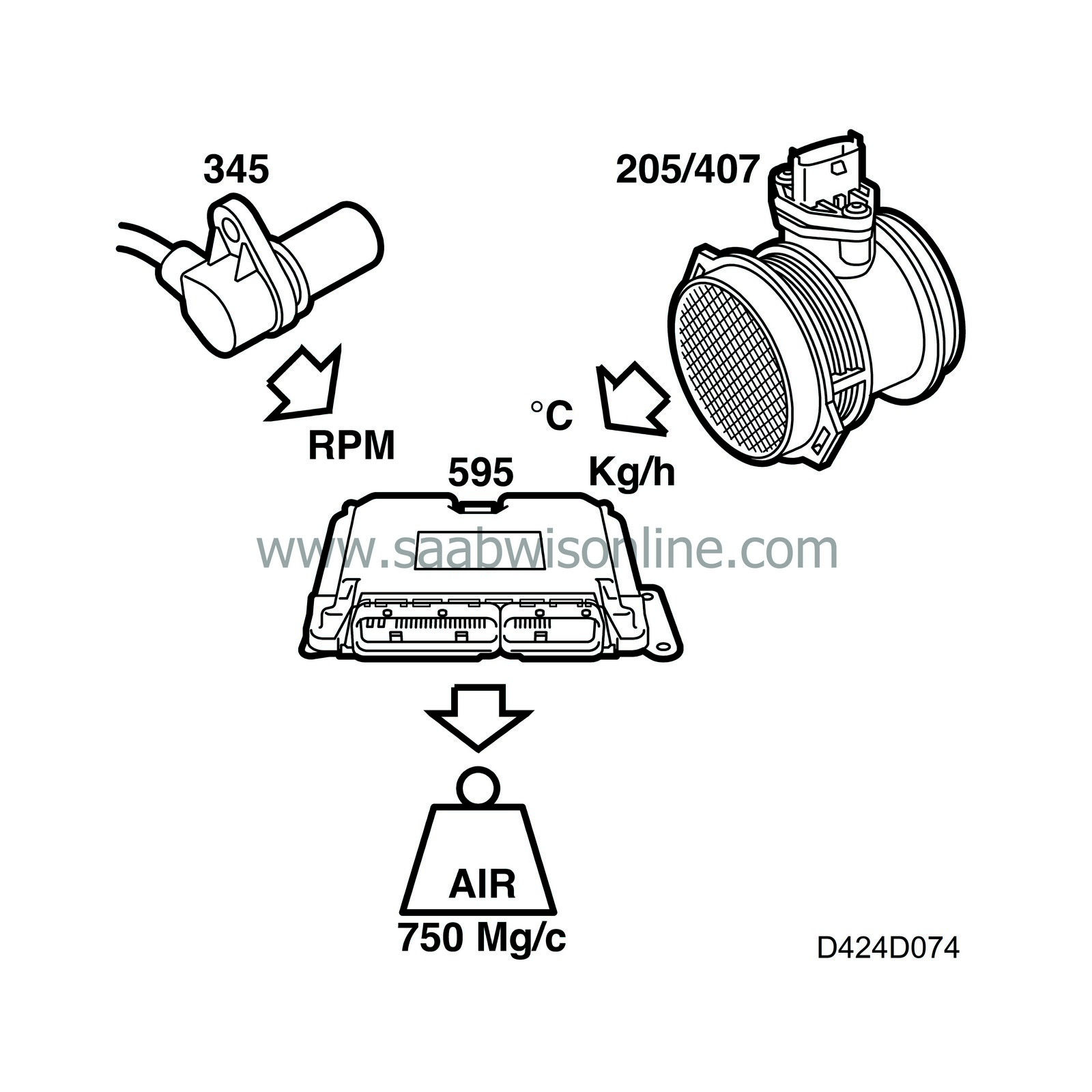
The current air mass/combustion is calculated using the variables engine speed, intake air mass from the mass air flow sensor and air temperature in the mass air flow sensor.
The signal from the mass air flow sensor is filtered and the reading converted from kg/h to mg/combustion. When the air mass has been converted to mg/combustion, a plausibility check is performed by comparing the engine speed with the intake air mass.
Information on the intake air mass/combustion is made available to the fuel quantity calculation.
| EGR control and monitoring |
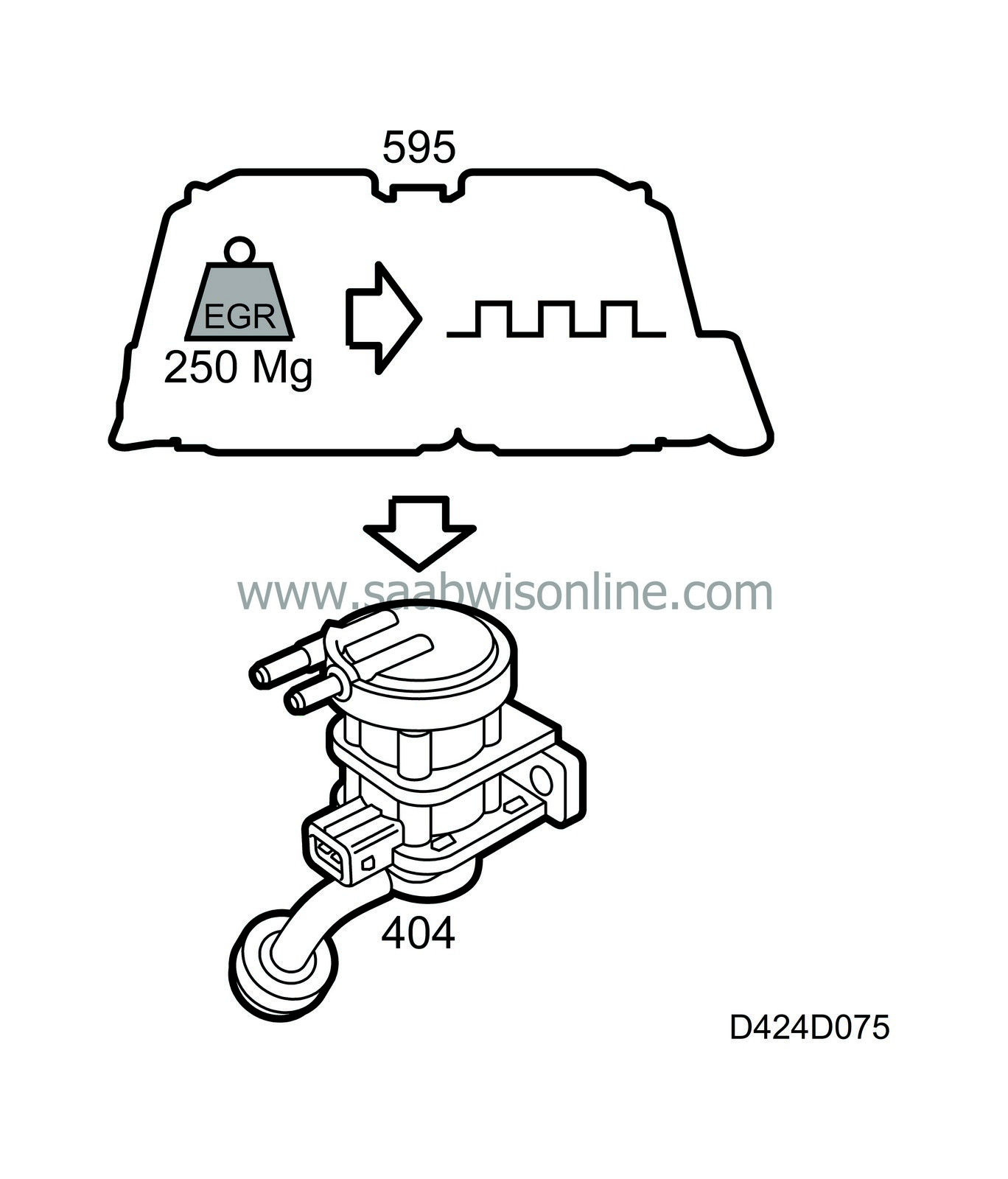
The EGR desired value is converted into a timing ratio using pre-programmed parameters. The value is then conveyed to the final stage control, where the signal is amplified and compensated for the battery voltage, see table. The compensation value is multiplied with the current timing ratio.
|
Voltage (V)
|
Compensation value
|
|
9
|
1.4
|
|
14.2
|
1.0
|
|
16
|
0.775
|
This is done to compensate for a higher or lower voltage than 14.2 V resulting in a different valve lift and consequently an incorrect control of the valve.
The timing ratio is then available on the control module pin to be connected to the EGR control valve.