Fault criteria, catalytic converter
|
|
Fault criteria, catalytic converter
|
The catalytic converter is diagnosed once per trip.
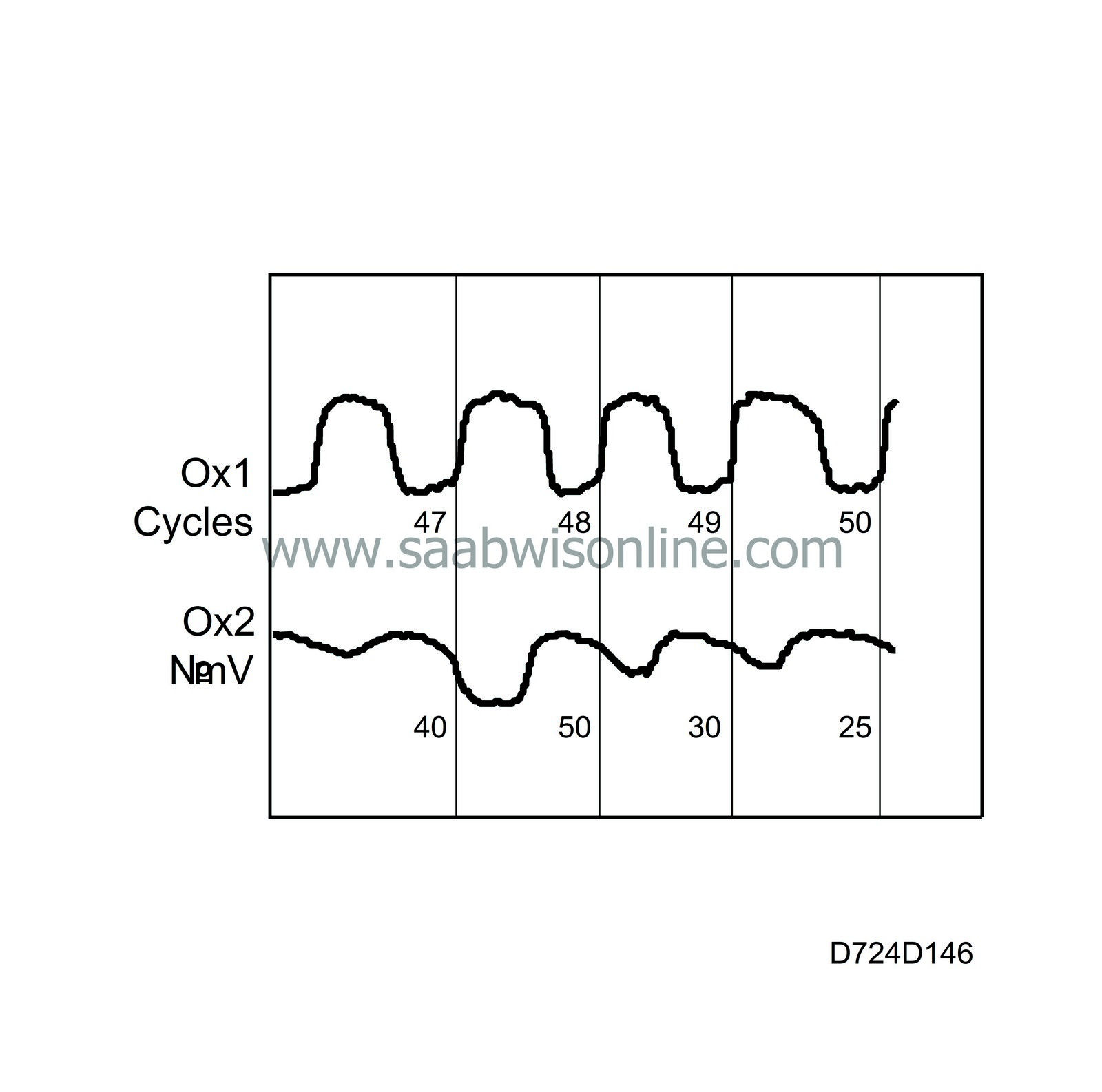
The ability of the catalytic converter to store oxygen is proportional to its efficiency. If the oxygen storage capacity of the catalytic converter is poor, the natural fluctuation of closed loop in the fuel/air ratio will be noticeable even after the catalyst. There is also an oxygen sensor after the catalytic converter (oxygen sensor 2).
Once the conditions for the diagnosis have been fulfilled, the voltage changes from oxygen sensor 2 will be analysed. The catalytic converter is defective if the voltage changes are too great with regard to engine load and speed.
Voltage changes from oxygen sensor 2 are corrected with respect to load and engine speed and totalled for 50 individual, approved periods for oxygen sensor 1 *). Fault criteria are fulfilled if the total exceeds a calibrated value.
*) An approved period means that the sensor voltage pulse ratio is 30-80 % (+).
Diagnosis not yet performed during this trip
Catalytic converter heating:
|
•
|
Engine speed (rpm) x load (kPa) = >60 000
|
|
•
|
Total acceleration >15 sec.
|
|
•
|
Above conditions fulfilled for 120 sec.
|
|
•
|
No period at idling speed >40 sec.
|
|
•
|
No fuel shut-off >10 sec.
|
Evaluation of catalytic converter
|
•
|
Vehicle speed 30-100 km/h.
|
|
•
|
Engine speed (rpm) x load (kPa) = 60 000 - 260 000
|
|
•
|
Engine coolant temperature >60C (>140F)
|
|
•
|
Oxygen sensor 2 >0.4 V on some occasion during this driving cycle
|
|
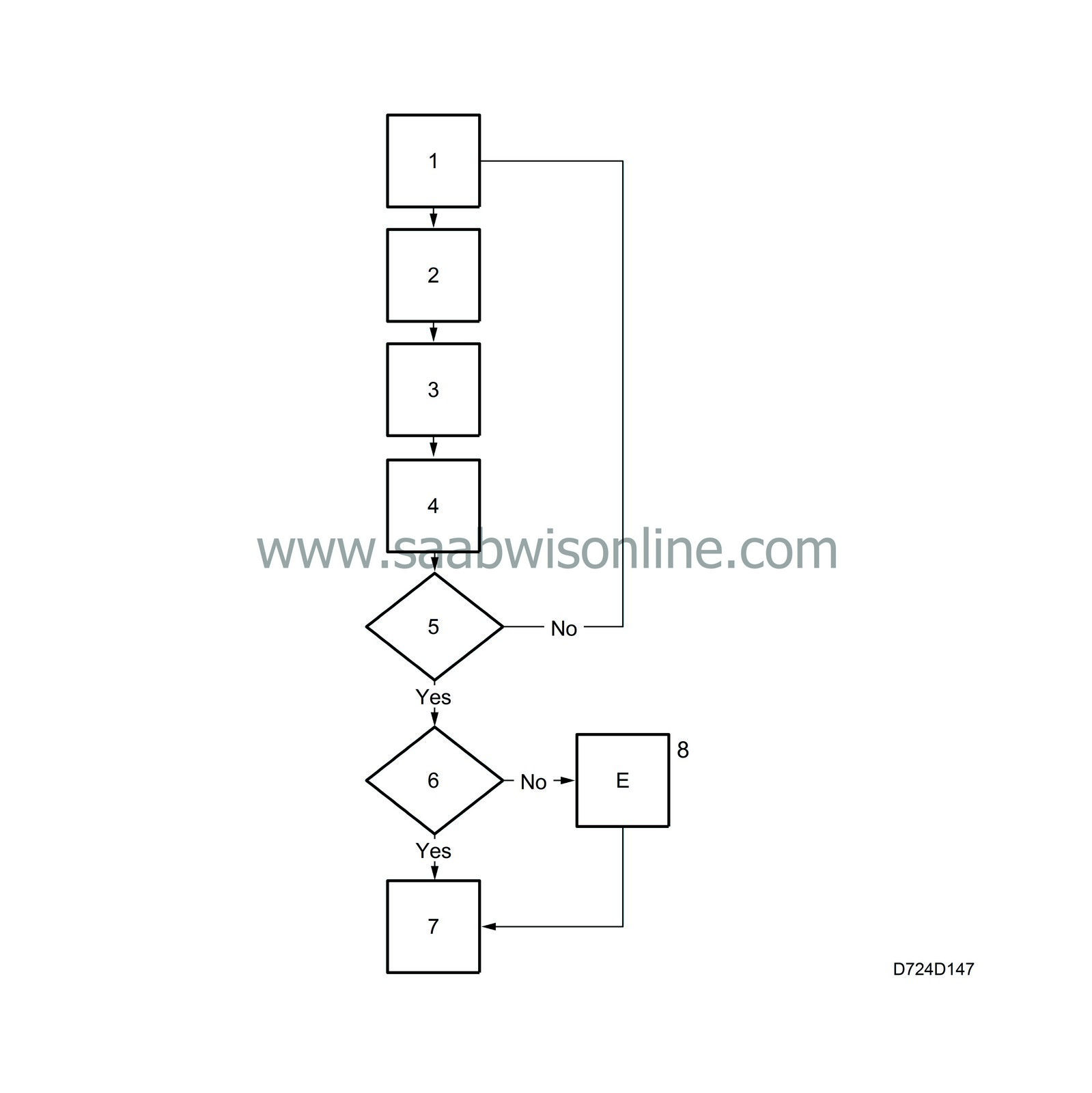
1.
|
Measure:
- oxygen sensor 1, voltage
- oxygen sensor 2, voltage
|
|
2.
|
The voltage change in the rear sensor is registered during one oxygen sensor 1 period with a pulse ratio that is 30-80% (+)
|
|
3.
|
Correct the voltage change with respect to load and engine speed
|
|
4.
|
Add the voltage change in memory
|
|
7.
|
Diagnosis performed during this trip
|
|
8.
|
Fault criteria for catalytic converter fulfilled
|




