Ignition discharge module
| Ignition discharge module |
Ignition
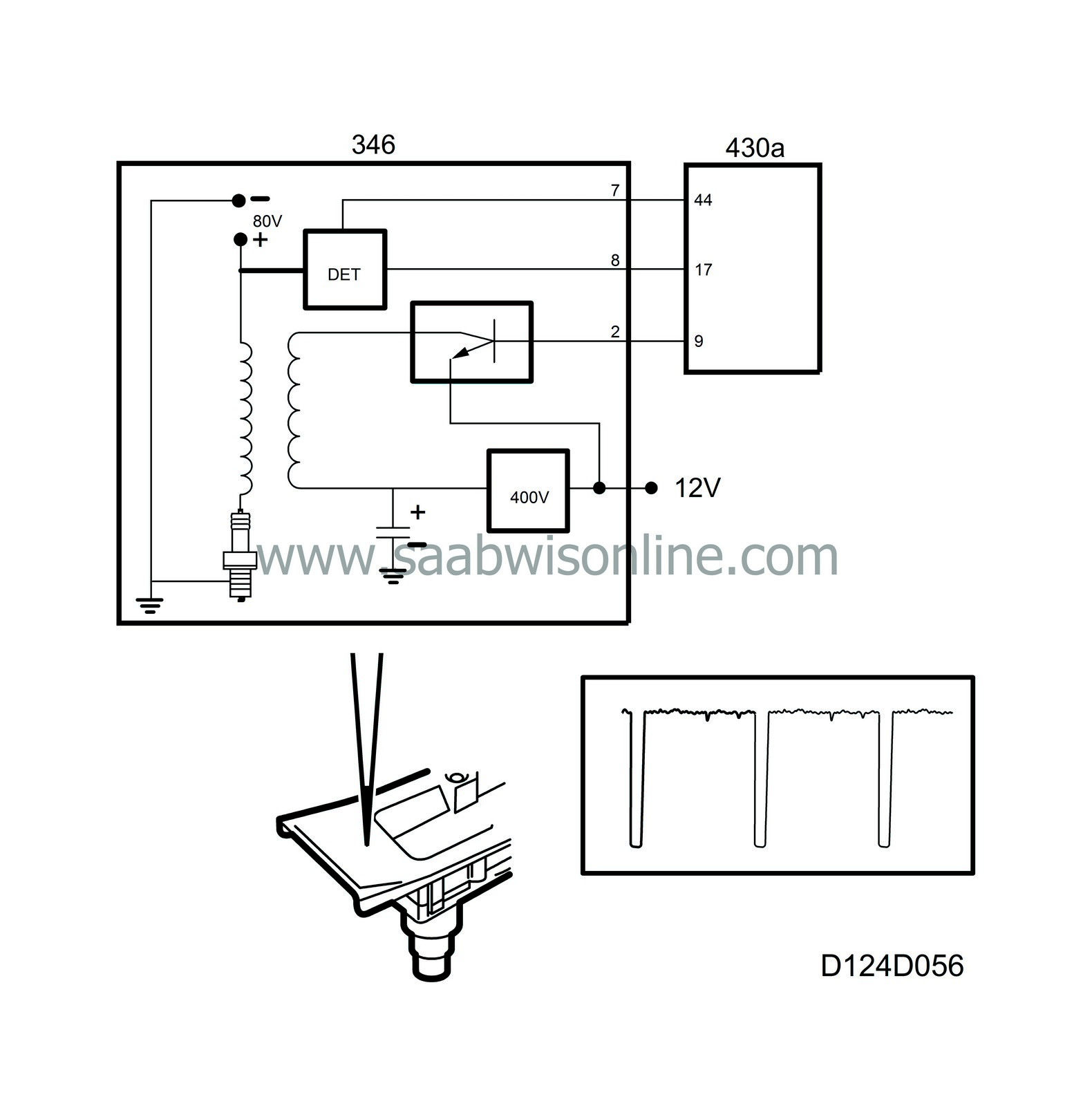
The ignition discharge module is located on the camshaft cover above the spark plugs. It contains 4 ignition coils, the secondary windings of which are connected directly to the spark plugs.The ignition discharge module is powered with B+ from the main relay and grounded to grounding point G7P.
When the main relay operates, B+ is fed to the ignition discharge module, which converts the 12V to 400V DC and stores it in a capacitor. The 400V is connected to one of the poles of the primary winding on each of the 4 ignition coils.
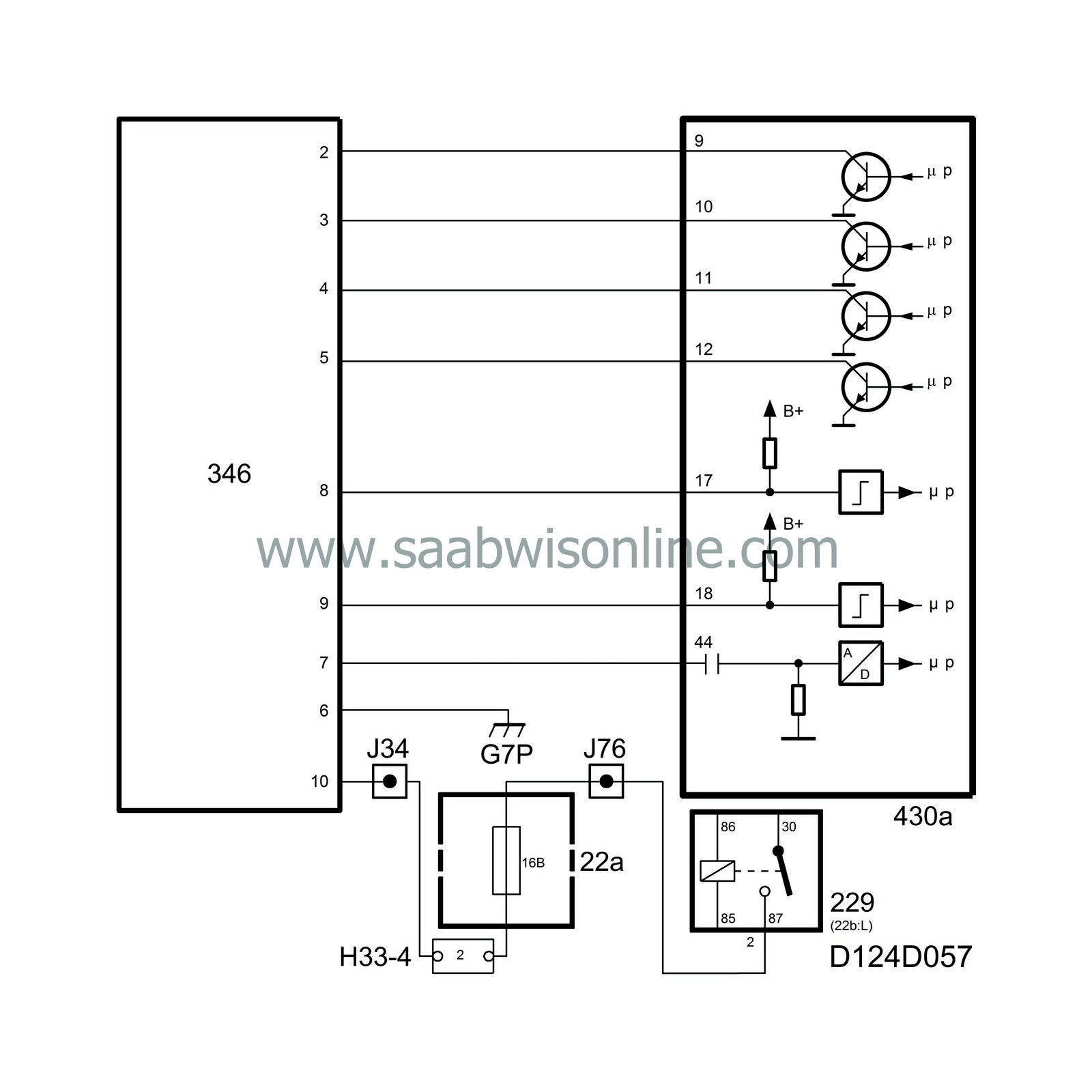
4 ignition leads are connected to the ignition discharge module from Trionic control module pin 9 (cyl. 1), pin 10 (cyl. 2), pin 11 (cyl. 3) and pin 12 (cyl. 4).
When the control module grounds pin 9, the other pole of the primary winding on cyl. 1 coil will be grounded (via the ignition discharge module B+ input) and 400 V will be transformed up to max. 40 kV in cyl. 1 coil. Ignition in cyl. 2, 3 and 4 is carried out in the same way.
| Diagnosis |
| • |
The engine will not start if there is a break in the power supply or ground to the ignition discharge module.
|
|
| • |
The cylinder in question will not fire if there is a break on its ignition lead.
|
|
Ignition control, start
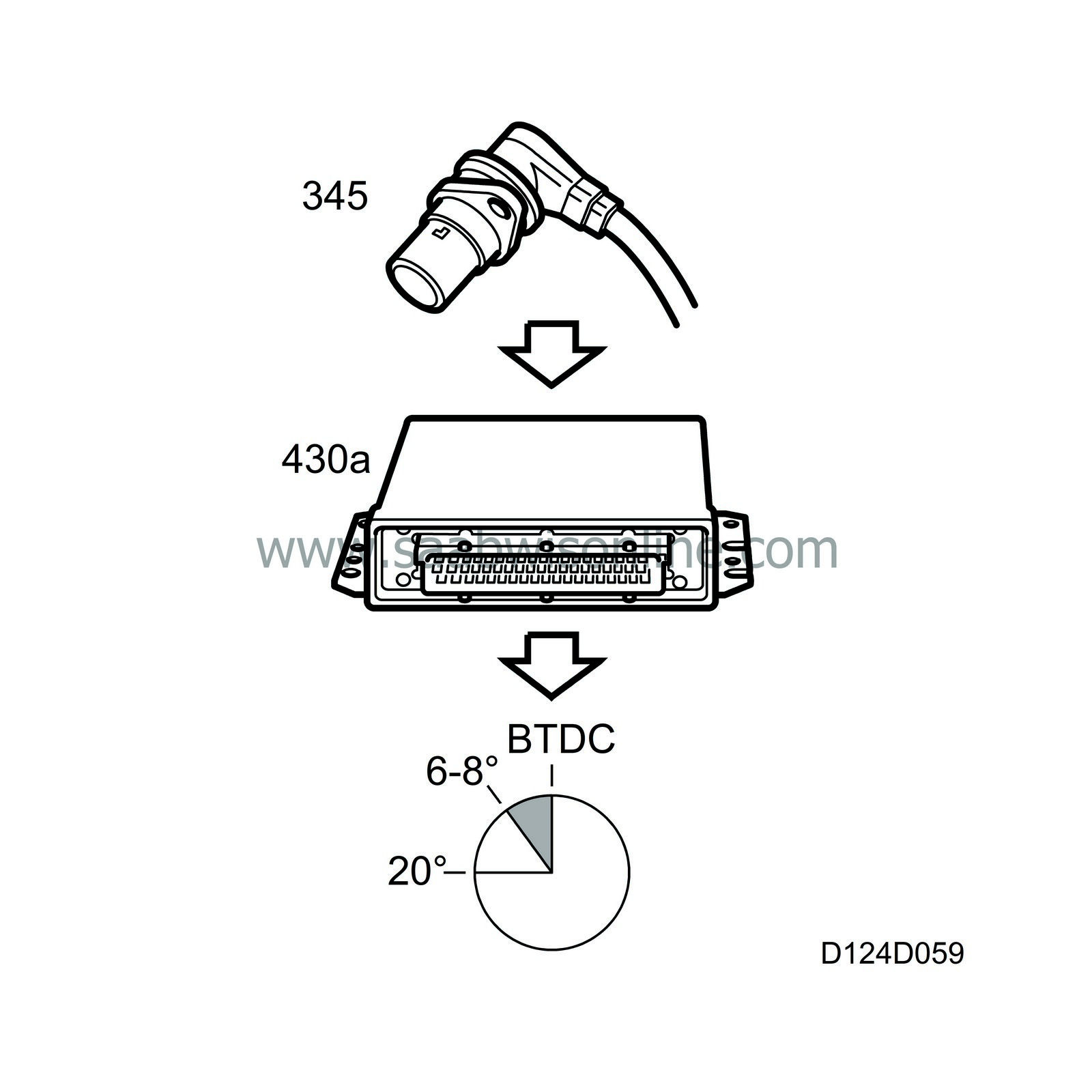
The ignition timing during start is 10 BTDC. For easier starting when the coolant temperature is below 0 C, the control module will ground each ignition lead 210 times per second from 10 BTDC to 20 ATDC, whereby a so-called "multispark" is generated. This function ceases at engine speeds above 900 rpm.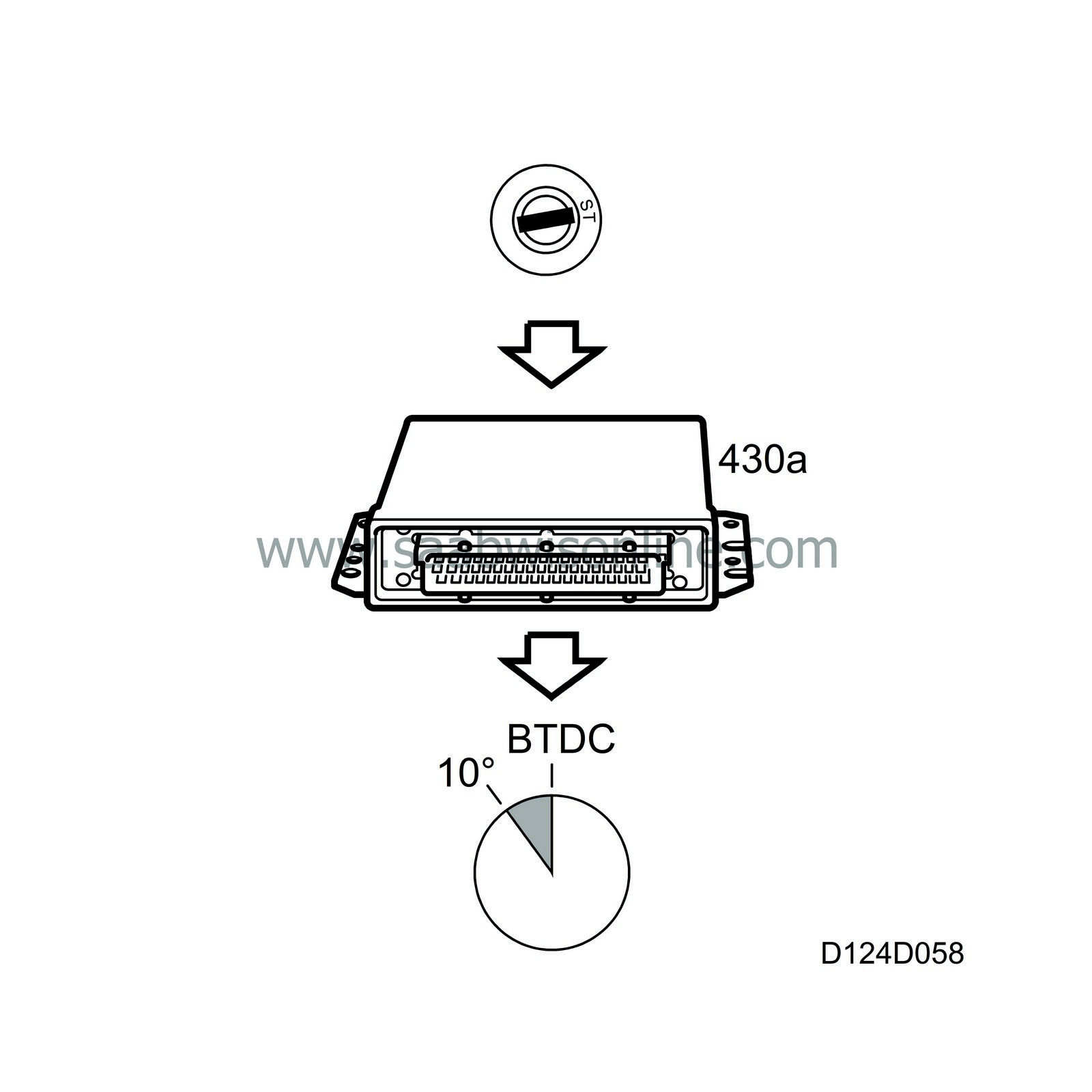
Idling speed
At idling speed, a special ignition control curve is used. Normal advanced ignition is approx. 6-8.If the engine speed drops, e.g. when the radiator fan is engaged, the ignition will be advanced up to max. 20 BTDC to increase the engine torque and maintain engine speed. Correspondingly, the ignition is retarded if the engine speed increases.
Driving
Ignition control at idling speed attends to rapid changes in the engine idling speed.Ignition control will revert to normal control depending on load and engine speed when the throttle moves from idling position.
Combustion signals
The Trionic system does not include a camshaft position sensor, which is usually a precondition for sequential knock control and fuel injection.Saab Trionic must determine whether ignition takes place in cyl. 1 or cyl. 4 when the crankshaft position sensor indicates that cyl. 1 and cyl. 4 are at TDC.
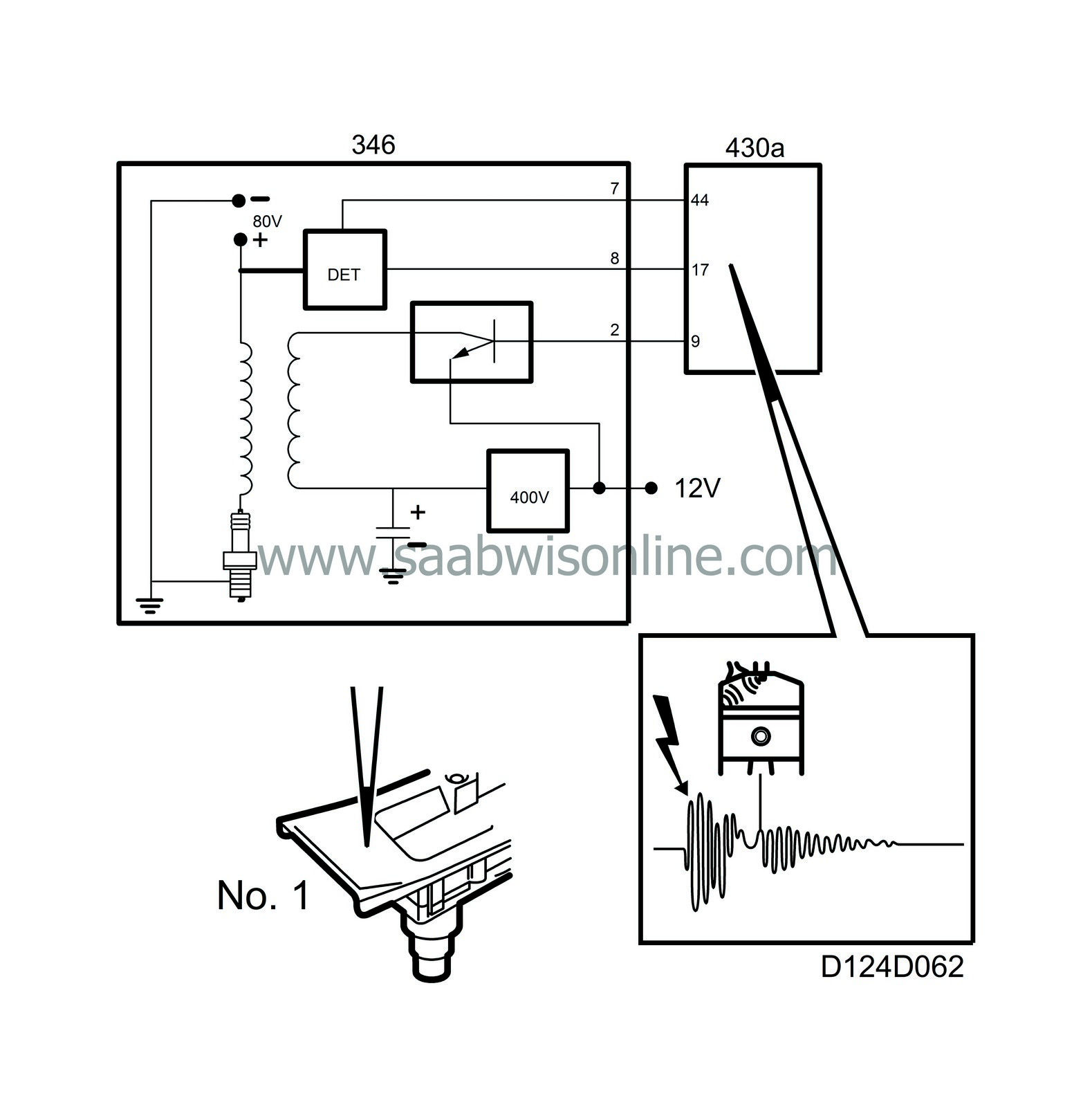
This is achieved in the following way: One pole of the 4 ignition coil secondary windings is connected to respective spark plug in the usual way. The other pole is not grounded directly but is connected to 80 V. This means that 80 V is always applied across the spark plug gap except just as the spark is generated.
Once combustion has taken place, the temperature in the combustion chamber is extremely high. The gases ionize and start conducting current. This results in current crossing the spark plug gap (without generating a spark).
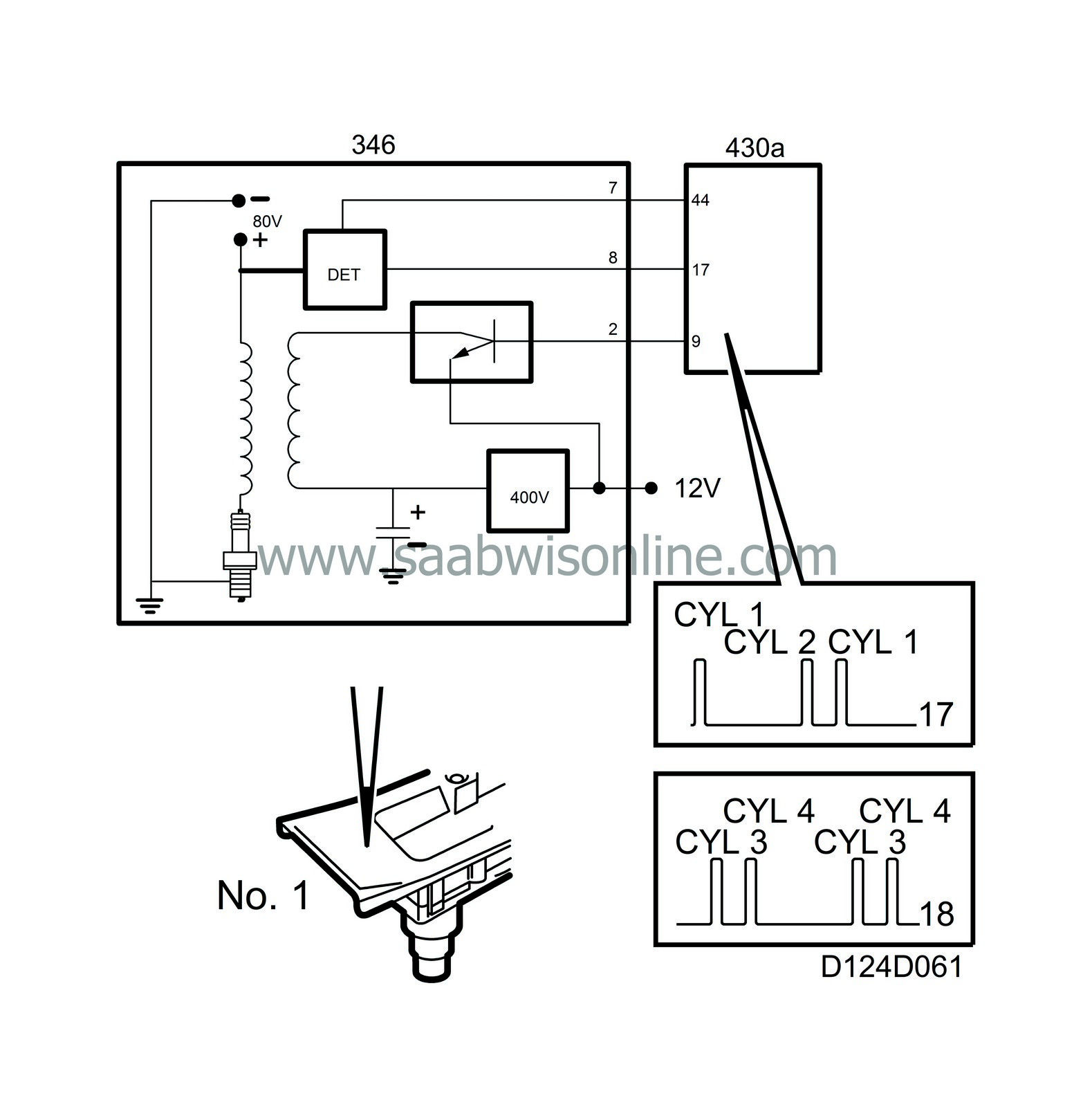
Ionization current is measured in pairs, cyl. 1+2 and cyl. 3+4. If combustion takes place in cyl. 1 or 2, the ignition discharge module sends a B+ pulse to Trionic control module pin 17. Correspondingly, the ignition discharge module sends a B+ pulse to control module pin 18 if combustion has taken place in cyl. 3 or 4.
If the crankshaft position sensor indicates that cyl. 1 and 4 are at TDC at the same time as a B+ pulse arrives at control module pin 17, the control module will know that cyl. 1 has fired.
When starting, the control module cannot determine which of the cylinders 1 and 4 is on its compression stroke and consequently ignition will take place in cylinders 1 and 4 simultaneously. Correspondingly, ignition takes place in cylinders 2 and 3 in the same way. The ignition and fuel injection will be synchronized to the firing order of the engine as soon as combustion signals arrive at control module pins 17 and 18.
Combustion signals are also used to detect misfiring.
| Diagnosis |
Combustion signals
| • |
The ignition and fuel injection will not be synchronized if there is a break on any of the leads to control module pins 17 and 18.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
If synchronization has not taken place, knock control will be performed in parallel on cylinders 1+4 and 2+3.
|
|
Knock control
Saab Trionic does not have a conventional knock sensor. Instead, the ignition discharge module analyses the ionization current in all cylinders and sends signals to Trionic control module pin 44. This function is adaptive with regard to troublesome fuel additives.From the combustion signals, the control module is made aware of which cylinder has fired and if the signal on the knock lead is also above a certain level, the control module will register knocking on that cylinder. Ignition in the cylinder will then be retarded 1.5.
Ignition will be retarded even further if the knocking persists, but only to max. 12. The amount injected will be increased slightly if the retardation is above a certain level on all cylinders.
Knock control will be performed differently if knocking occurs when the intake manifold pressure exceeds approx. 140 kPa: the fuel injection and ignition matrices are changed first and if this does not help, the boost pressure is reduced.
This is to attain good performance even when knocking occurs.
Basic charging pressure is obtained if there is a break in the lead to control module pin 44 and the ignition will be retarded by 12 when the engine load is so high that there is a risk of knocking occurring.
| Diagnosis |
| • |
If there is an open circuit to control module pin 44, diagnostic trouble code P0327 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Ignition is retarded by 12 when the engine load is so high there is risk of knocking.
|
|
| • |
Basic charging pressure
|
|
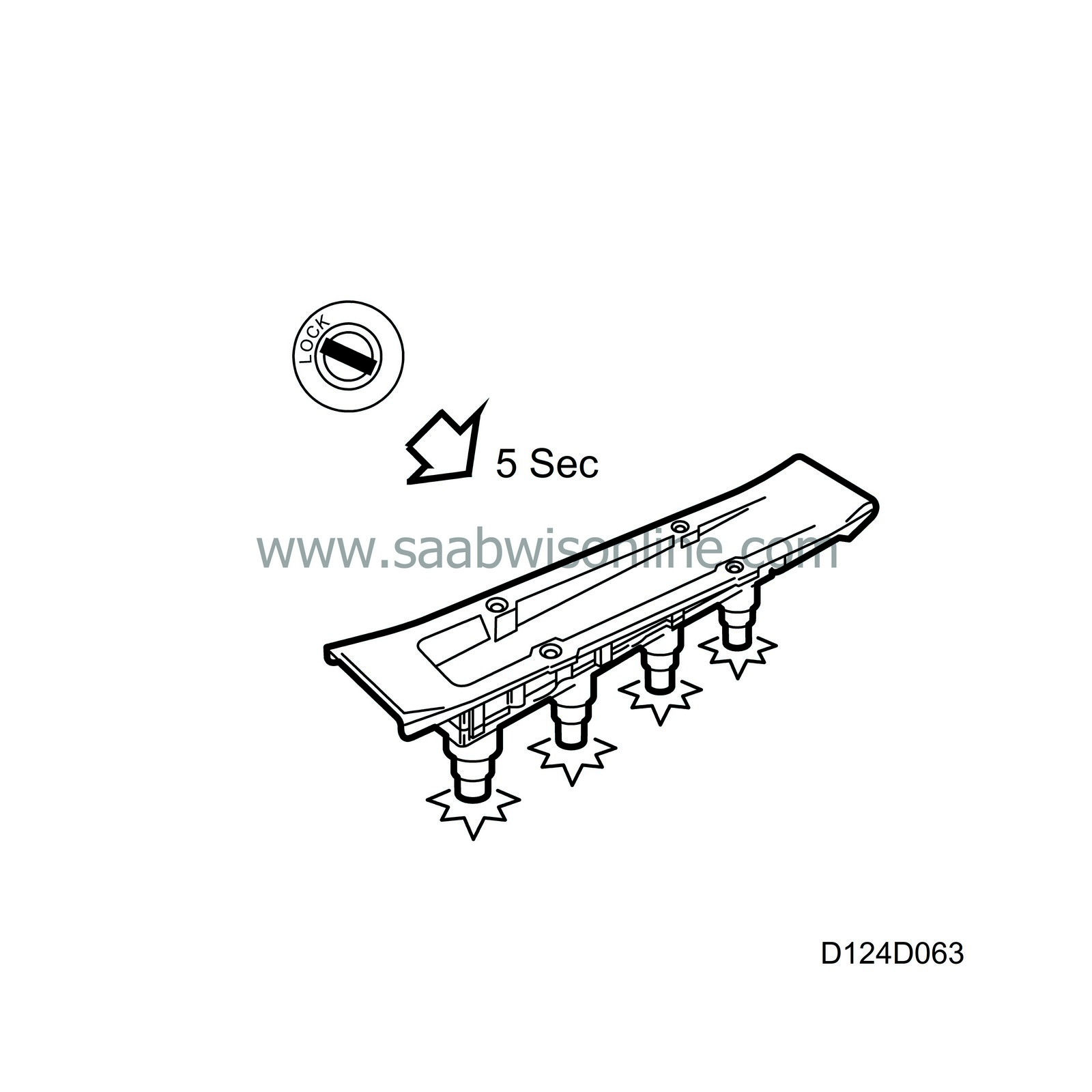
Burn-off
After turning off the ignition and the engine has stopped, the main relay will be operative for a further 6 seconds. The Trionic control module will then ground all the ignition leads 210 times per second for 5 seconds. Any fouling present on each electrode gap will then be burned away by more than 1000 sparks.