Brief description of main instrument unit, Trionic T7
|
|
Brief description of main instrument unit, Trionic T7
|
The main instrument unit conveys information to the driver and functions as an information link between the P-bus and the I-bus.
The main instrument unit has its own diagnostics function and sets a diagnostic trouble code when a fault occurs.
The main instrument unit incorporates the following functions:
|
•
|
Coolant temperature gauge
|
|
•
|
Turbo gauge (cars with turbocharger)
|
|
•
|
Selector lever position indicator (cars with automatic transmission)
|
|
•
|
Instrument and display lighting
|
|
•
|
Warning and indicator lamps
|
The main instrument unit's control module receives information from other systems as well as from its own sensors. It processes the information and uses it to control instruments and lamps. Some information is send out on the bus.
The car is equipped with an electronic speedometer which shows the current speed. The left rear wheel sensor sends speed information to the ABS control module which processes it and sends it on to the main instrument unit.
The main instrument unit's control module stores the distance covered and shows the mileage on the odometer display. The odometer display has a six-digit counter which the control unit continuously updates from 000000 to 999999 km (or miles). The trip meter has a four-digit counter which starts at 000.0 and goes up to 999.9 km (or miles).
The electronic tachometer displays the current engine speed. It receives continuous bus information concerning engine speed from Trionic T7. The display of engine speeds below 1100 rpm is damped to provide a more stable reading.
The fuel gauge gives the driver information on how much fuel is left in the tank. It consists of a fuel gauge in the main instrument unit and a level sensor in the tank.
When the fuel level drops below 10 litres, the main instrument control module will switch to measuring fuel consumption. Information arrives on the bus from Trionic T7. This provides a more precise display of the fuel level. The Fuel reserve indicator lamp comes on when the fuel quantity is below 10 litres.
Low fuel level (OBDII)
This function is used only for OBDII diagnostics.
|
Tank venting diagnostics (OBDII)
|
The Trionic sends a signal to the main instrument unit on the diagnostic status of the tank venting system. If there is leakage in the venting system, the main instrument unit sends the information "Tighten fuel filler cap ON" on the bus. The SID unit then displays the requested message.
|
Coolant temperature gauge
|
The coolant temperature gauge provides the driver with information concerning the temperature of the engine coolant. Information arrives on the bus from Trionic T7.
The car is equipped with an electronic turbo gauge that provides information concerning the degree of engine load. Trionic T7 receives information on the current air mass/combustion from the mass air flow sensor located between the air cleaner and the induction side of the turbocharger.
|
Selector lever position indicator
|
Cars with automatic transmission are equipped with an indicator display that presents the selected gear position as an illuminated symbol (PRND321). The information on the selected gear position is sent to the main instrument unit on the bus from TCM.
|
Warning and indicator lamps
|
The main instrument unit contains the following lamps:
|
•
|
Indicator lamp INFO DISPLAY, lights up when a message is shown on the SID unit.
|
|
•
|
Central warning lamp, lights up when a fault occurs in a system having to do with the car's safety.
|
|
•
|
Oil pressure warning lamp, warns the driver when engine oil pressure is too low.
|
|
•
|
Charge warning lamp, indicates to the driver whether or not the generator is charging.
|
|
•
|
AIRBAG warning lamp, warns the driver when a fault has occurred in the airbag system.
|
|
•
|
Brake fluid warning lamp, warns the driver when the fluid level in the reservoir is too low and when a fault has occurred in the anti-lock brake system (ABS).
|
|
•
|
Handbrake warning lamp, informs the driver that the handbrake is applied.
|
|
•
|
ABS warning lamp, the lamp lights up when there is a fault in the ABS system.
|
|
•
|
SPORT indicator lamp, on cars with automatic transmission indicates to the driver that the SPORT mode is active.
|
|
•
|
WINTER indicator lamp, on cars with automatic transmission indicates to the driver that the WINTER mode is active.
|
|
•
|
CHECK GEARBOX indicator lamp, warns the driver when there is a fault in the automatic transmission.
|
|
•
|
Fuel reserve indicator lamp, the lamp lights up when the fuel level is below 10 litres.
|
|
•
|
CHECK ENGINE indicator lamp, warns the driver that there is a fault in the engine management system.
|
|
•
|
Direction indicator repeater lamps, right and left. Show when the direction indicators are on.
|
|
•
|
CRUISE indicator lamp, on cars with cruise control the lamp lights up when cruise control is engaged.
|
|
•
|
SHIFT UP indicator lamp, the lamp lights up when a higher gear should be engaged (certain markets).
|
|
•
|
Lights-on indicator lamp, indicates that the headlamps are on.
|
|
•
|
Rear fog light indicator lamp, indicates that the rear fog light is on.
|
|
•
|
Main beam indicator lamp, indicates that the main beam is on.
|
|
•
|
Selector lever position indicator, indicates the selected gear position on cars with automatic transmission.
|
|
•
|
Door indication, indicates if any of the doors or the tailgate is open.
|
|
Instrument and display lighting
|
The main instrument unit's control module controls the instrument and display lighting according to the light intensity in the cabin in combination with the selected rheostat setting. This gives a good level of lighting for day or night driving and optimum bulb life.
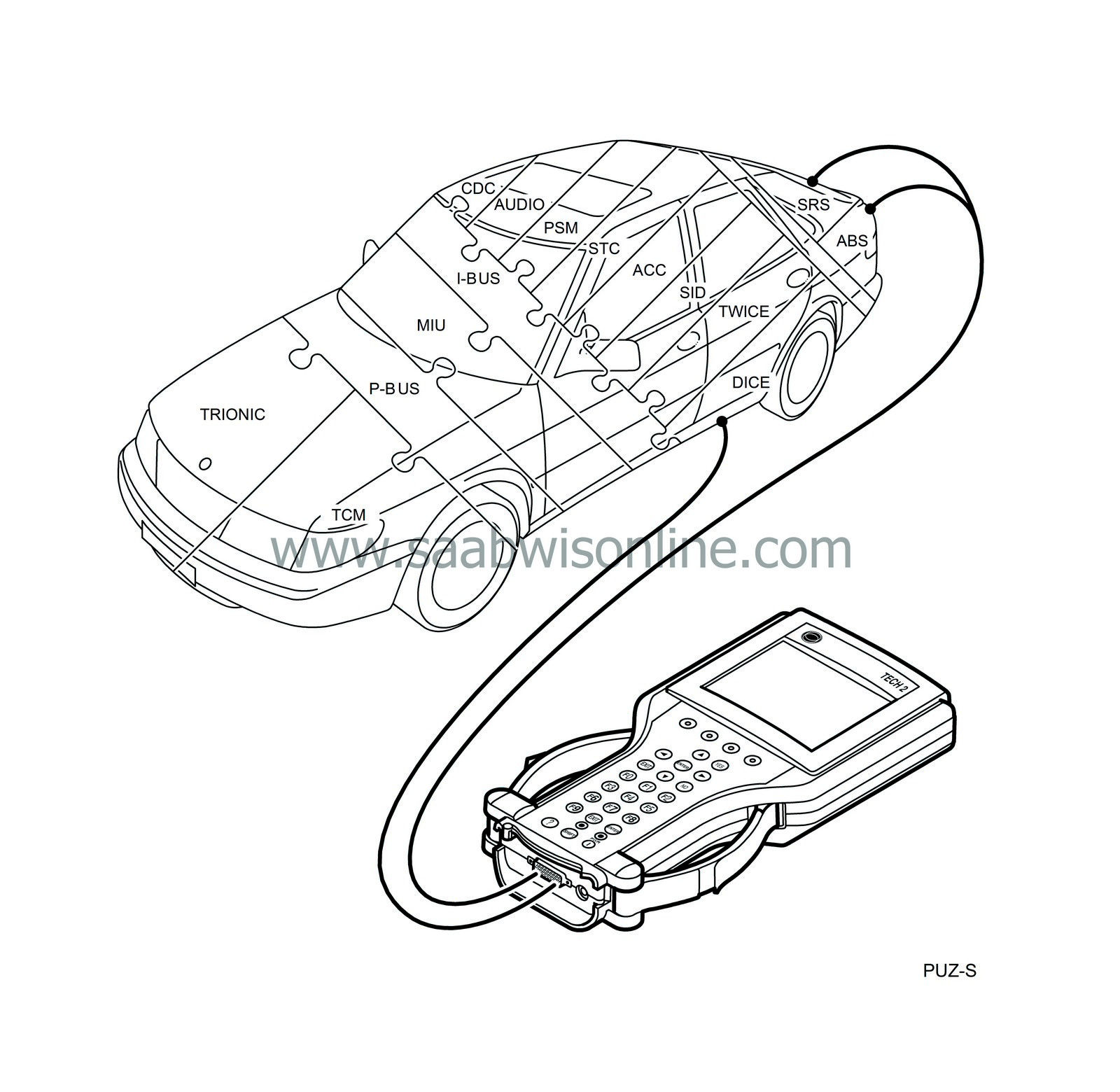
P-bus and I-bus in the Saab 9-3
On the Saab 9-3, not as many control modules as on the Saab 9-5 are connected to a bus system.
Trionic T7, on the other hand, is not connected to the I-bus. This system requires
considerably faster
communication to avoid noticeable delays, e.g. when Trionic T7 requests a certain fuel mass for injection.
Trionic T7 is therefore connected to a separate bus called the P-bus (Powertrain Bus). Communication on the P-bus is ten times faster than on the I-bus.
In addition, the P-bus is connected to the MIU. The MIU ensures that information which is available on one bus is also available on the other.



