P bus and I bus
| P bus and I bus |
Serial means that the information is sent in ”packets” which are transmitted one after the other in rapid succession.
The buses consist of a P bus (Powertrain Bus) and an I bus (Instrument Bus). Both buses are connected to the MIU (Main Instrument Unit). The buses are electrically isolated from each other.
The diagnostics tool is not directly connected to a bus, but communicates with DICE, one of the control modules connected to the I-bus, and thus has access to all control modules connected to a bus.
The data transfer rate of the P bus is ten times faster than that of the I bus. The reason for this is that the powertrain systems need information with the least possible delay.
All the information transmitted by one of the control modules is available to all the other control modules connected to the bus. MIU is responsible for making the information that is available on one bus also available on the other bus.
The control modules send out information on the bus at regular intervals. The time between two transmissions depends on what information is being transmitted and varies between 10 milliseconds (0.010 seconds) and 1 second. Information is also transmitted by the control module whenever the information changes.
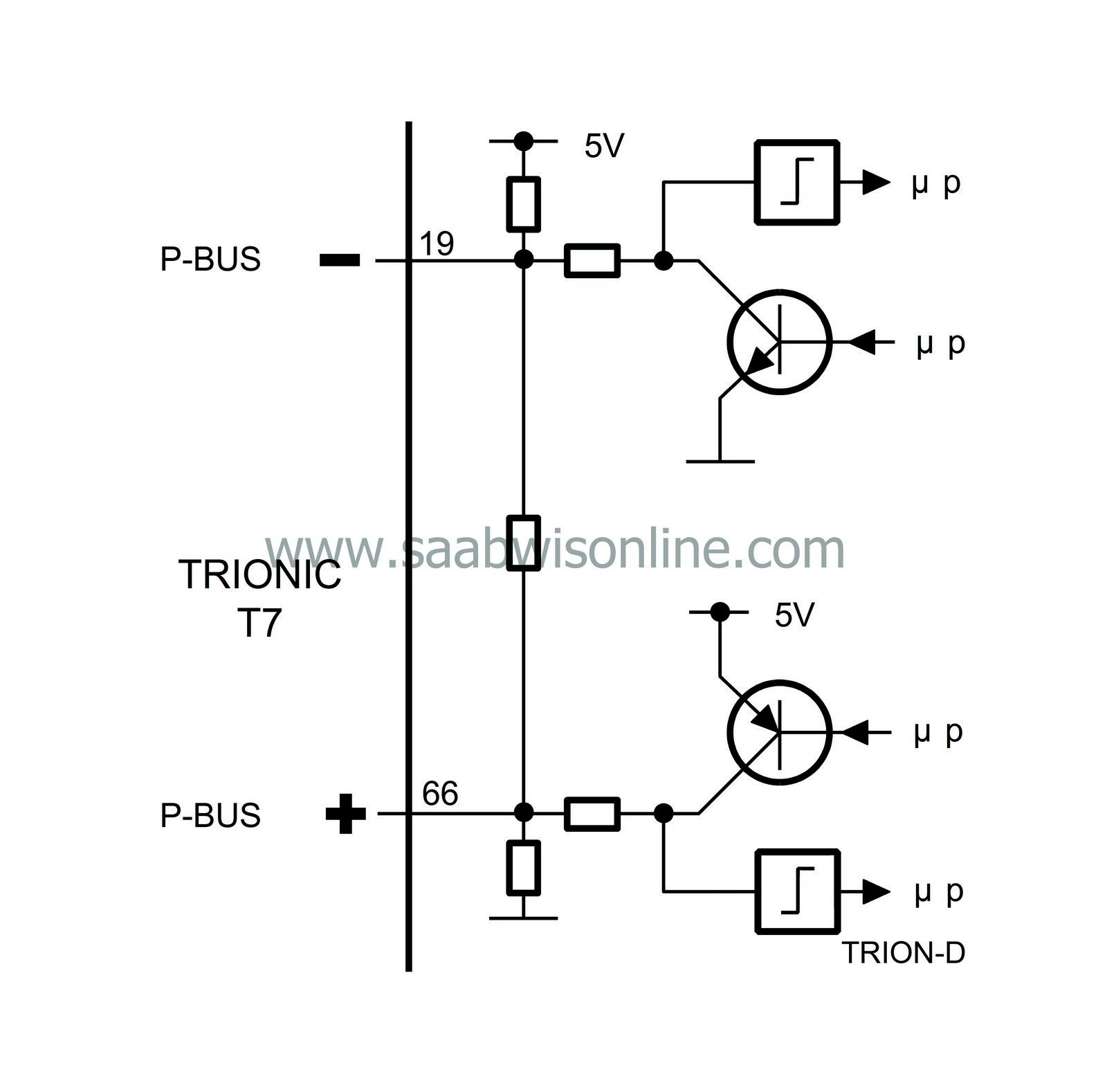
The transfer of information between control modules takes place on two leads, bus+ (green cable) and bus- (white cable). The two bus leads are twisted to increase resistance to electrical interference.