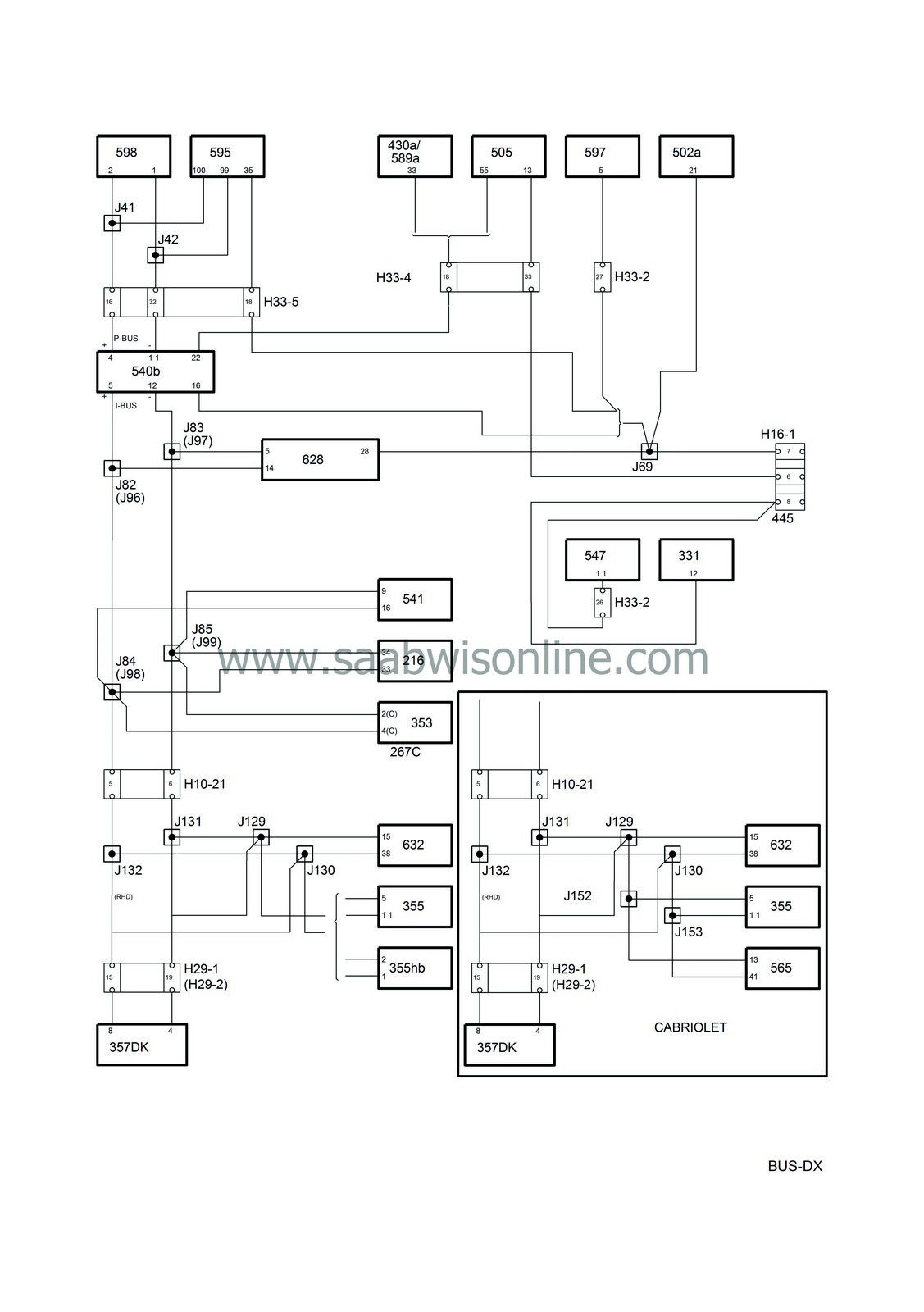
Bus communication
| Bus communication |
| • |
Control module, ACC (216)
|
|
| • |
Radio connector C (267c)
|
|
| • |
Airbag/SRS control module (331)
|
|
| • |
Radio (353)
|
|
| • |
CD changer (355)
|
|
| • |
Connection, bus CD-changer (355hb)
|
|
| • |
PSM control module (357Dk)
|
|
| • |
Control module Trionic (430a)
|
|
| • |
Control module TCM (502a)
|
|
| • |
Control module M2.10.3 (505)
|
|
| • |
MIU (540)
|
|
| • |
SID (541)
|
|
| • |
Control module, (ABS) 547
|
|
| • |
Control module, soft top opening (565)
|
|
| • |
Control module Trionic OBDII (589a)
|
|
| • |
Control module, diesel system (595)
|
|
| • |
Control module, auxiliary heater (597)
|
|
| • |
Diesel pump (598)
|
|
| • |
Control module, DICE (628)
|
|
| • |
Control module, TWICE (632)
|
|
| P bus and I bus |
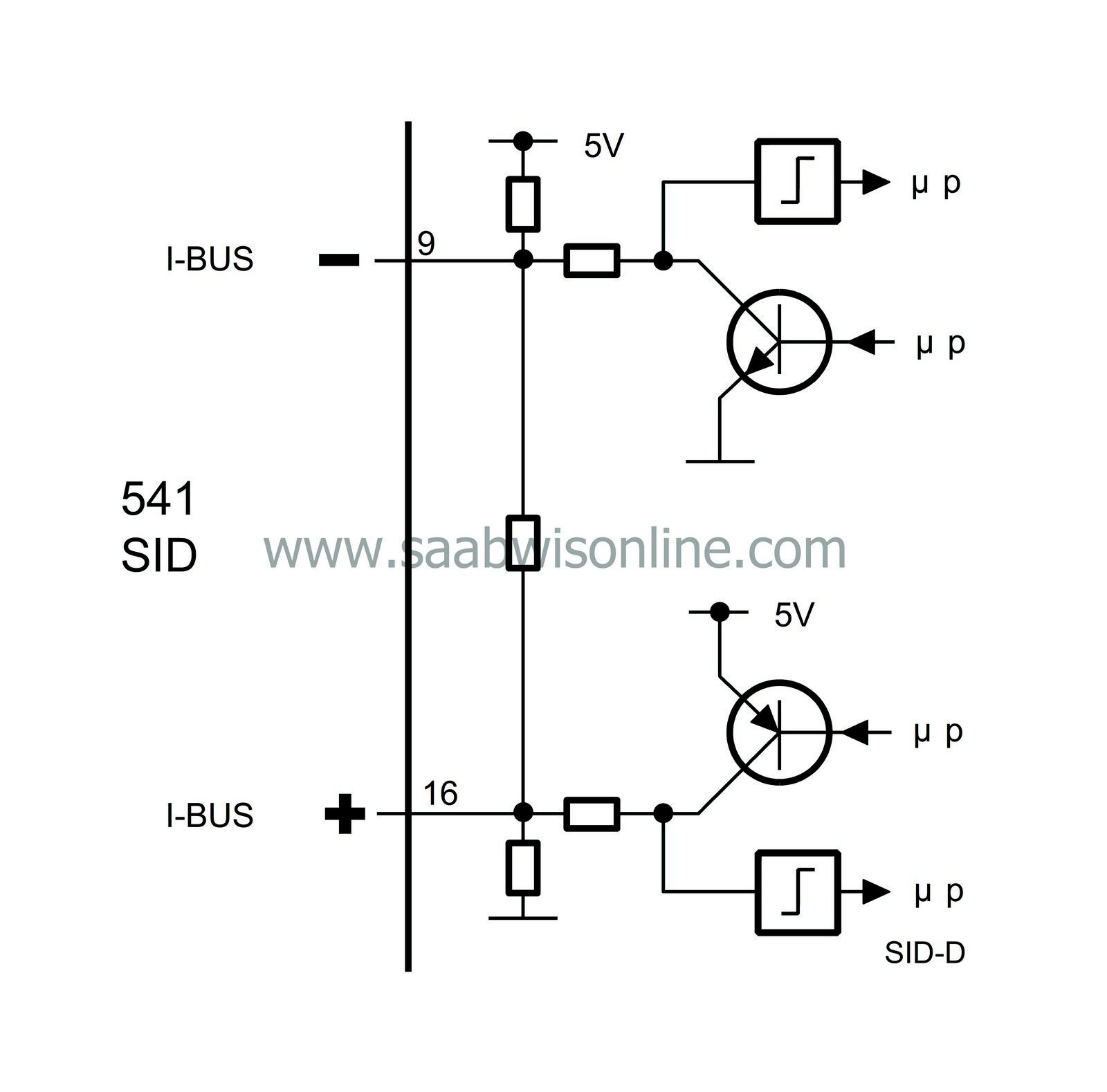
A bus is a number of wires on which information is sent digitally and serially. Digital means that the voltage difference between two wires has only two values, about 0V or 5V. The information is coded so that different combinations of pulses with values 0V and 5V have different meanings.
Serial means that the information is sent in ”packets” which are transmitted one after the other in rapid succession.
Half of the control modules in the Saab 9-3 are connected to the bus.
The buses consist of a P bus (Powertrain Bus) and an I bus (Instrument Bus). Both buses are connected to the MIU (Main Instrument Unit). The buses are electrically isolated from each other.
The diagnostic tool is not connected direct to the bus but communicates via the DICE, one of the control modules connected to the I bus, and so has access to all control modules connected to the bus.
The P-bus has a data transfer rate ten times higher than that of the I-bus. This is because the P-bus requires information with the least possible delay.
All the information sent from one control module is accessible for all other control modules on the bus. The MIU is responsible for ensuring that information available on one bus is also available on the other bus.
The control modules send out information on the bus at regular intervals. The time between two transmissions depends on the information being sent and varies between 10 milliseconds (0.010 seconds) and 1 second. Information is also sent out by the control modules whenever the information changes.
The information is transferred between control modules via two leads, bus+ (green lead) and bus- (white lead). The leads are twisted to reduce their sensitivity to electrical interference.