Boost pressure control
| Boost pressure control |
| - |
Desired value calculation
|
|
| - |
Current boost pressure and atmospheric pressure
|
|
| - |
Boost pressure control
|
|
| Desired value calculation |
The desired value calculation uses the parameters
| - |
Engine speed
|
|
| - |
Desired fuel quantity
|
|
| - |
Atmospheric pressure from atmospheric pressure sensor
|
|
To determine the desired value for the boost pressure, a value is taken from a file that is dependent on the engine speed and the injected fuel quantity. This value is corrected for air pressure.
| Current boost pressure and current atmospheric pressure |

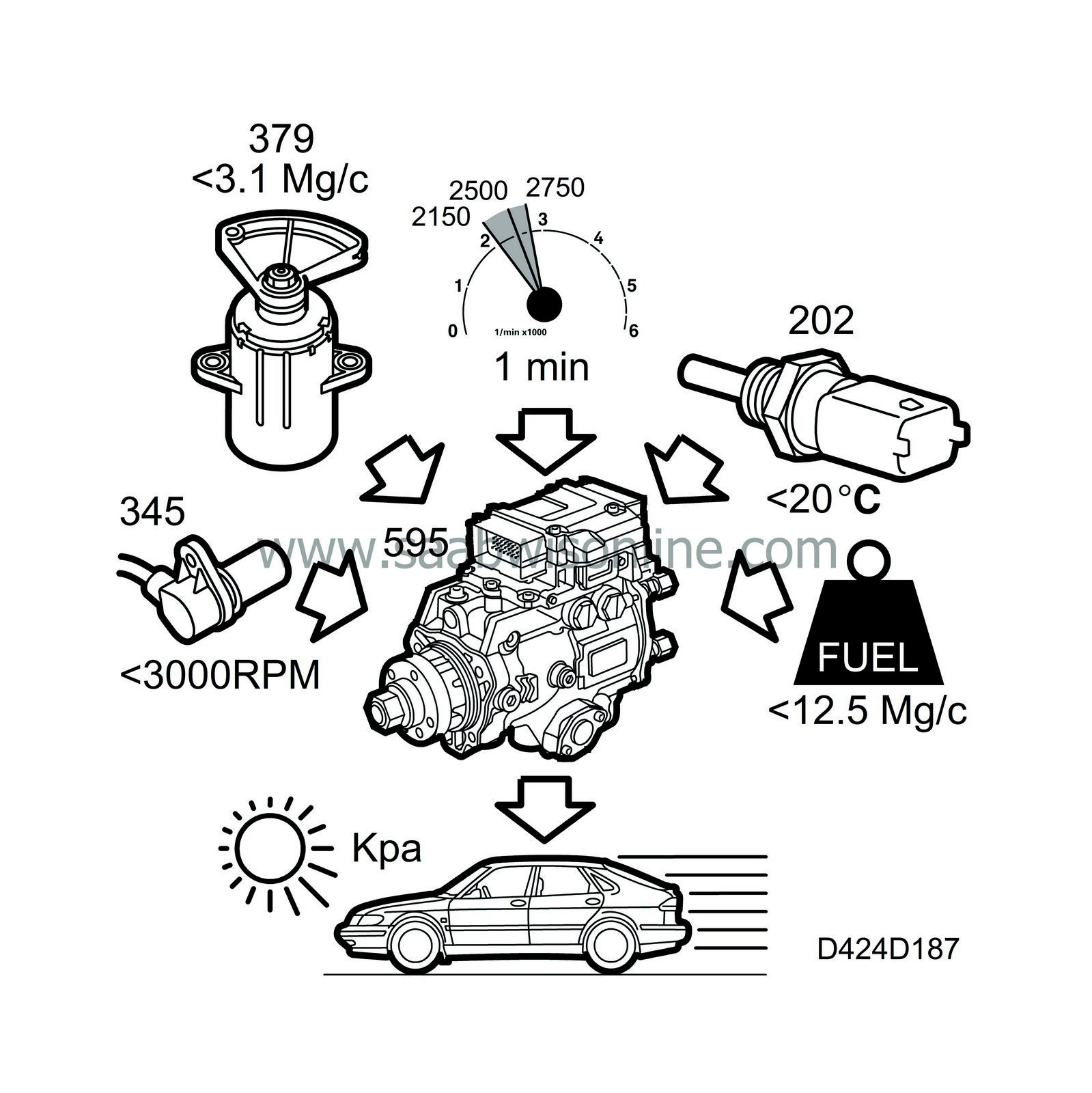
The boost pressure is measured by the intake pressure sensor (407/603) in the intake manifold and filtered before being sent on to the control module.
The atmospheric pressure is measured by the atmospheric pressure sensor (539), which is located on the left-hand side of the radiator.
| Boost pressure control |
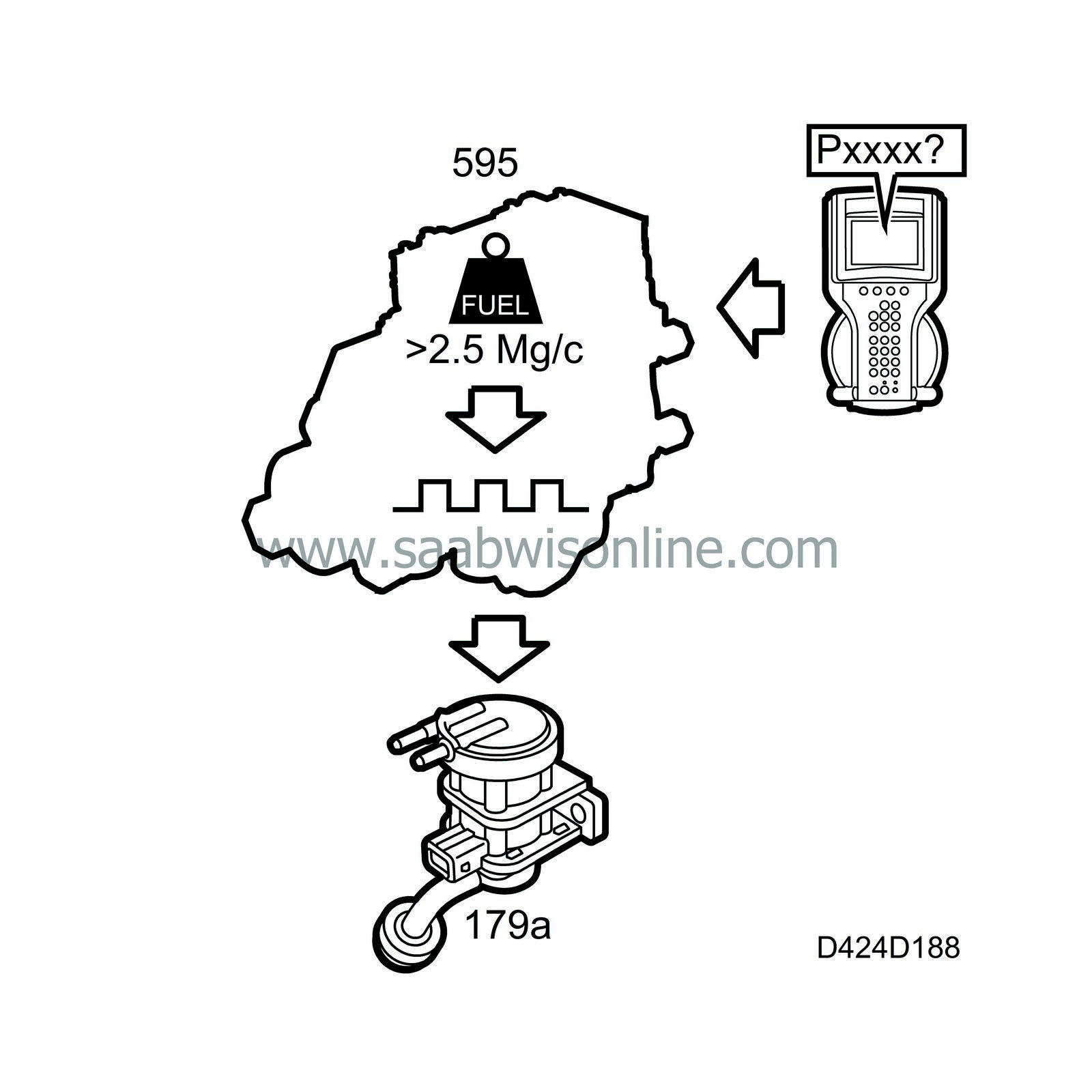
The timing ratio is regulated when the following conditions are met:
| - |
No system error (DTC) related to the mass air flow sensor EGR or wastegate
|
|
| - |
Injected fuel quantity exceeds 2.5 mg/combustion
|
|
The desired boost pressure value is converted to a timing ratio using pre-programmed tables. The timing ratio is then conveyed to the final stage control, where the signal is amplified and compensated for the battery voltage, see table.
|
Voltage (V)
|
Compensation value
|
|
9
|
1.4
|
|
14.2
|
1.0
|
|
16
|
0.775
|
This is done to compensate for a higher or lower voltage than 14.2 V resulting in a different valve lift and consequently an incorrect control of the valve.
The timing ratio is then available on control module pin 13 to be connected to the control valve for the turbocharger wastegate.
The charge air control reading in % is displayed on the diagnostic tool, 65% PWM means that charge air control is inactive.
PSG 16 will limit the engine torque when a DTC related to the wastegate is generated.



