System overview, bus and diagnostics communication
|
|
System overview, bus and diagnostics communication
|
|
System overview, functions, cars with engine management system Trionic T7
|
LHD
 RHD
RHD
|
System overview, functions, cars with engine management system PSG 16
|
LHD

RHD
|
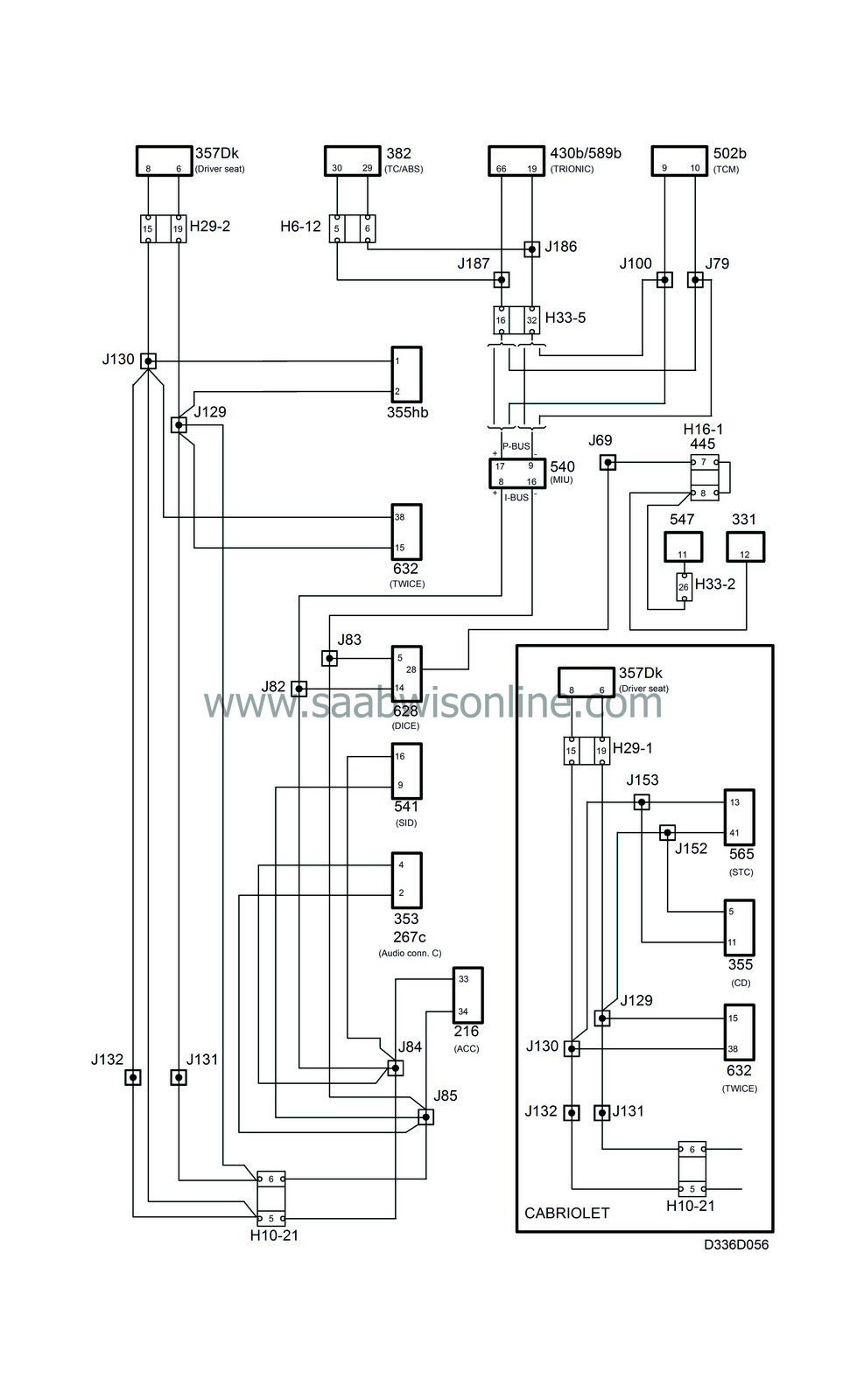
System overview, bus-connected components, cars with engine management system Trionic T7
|
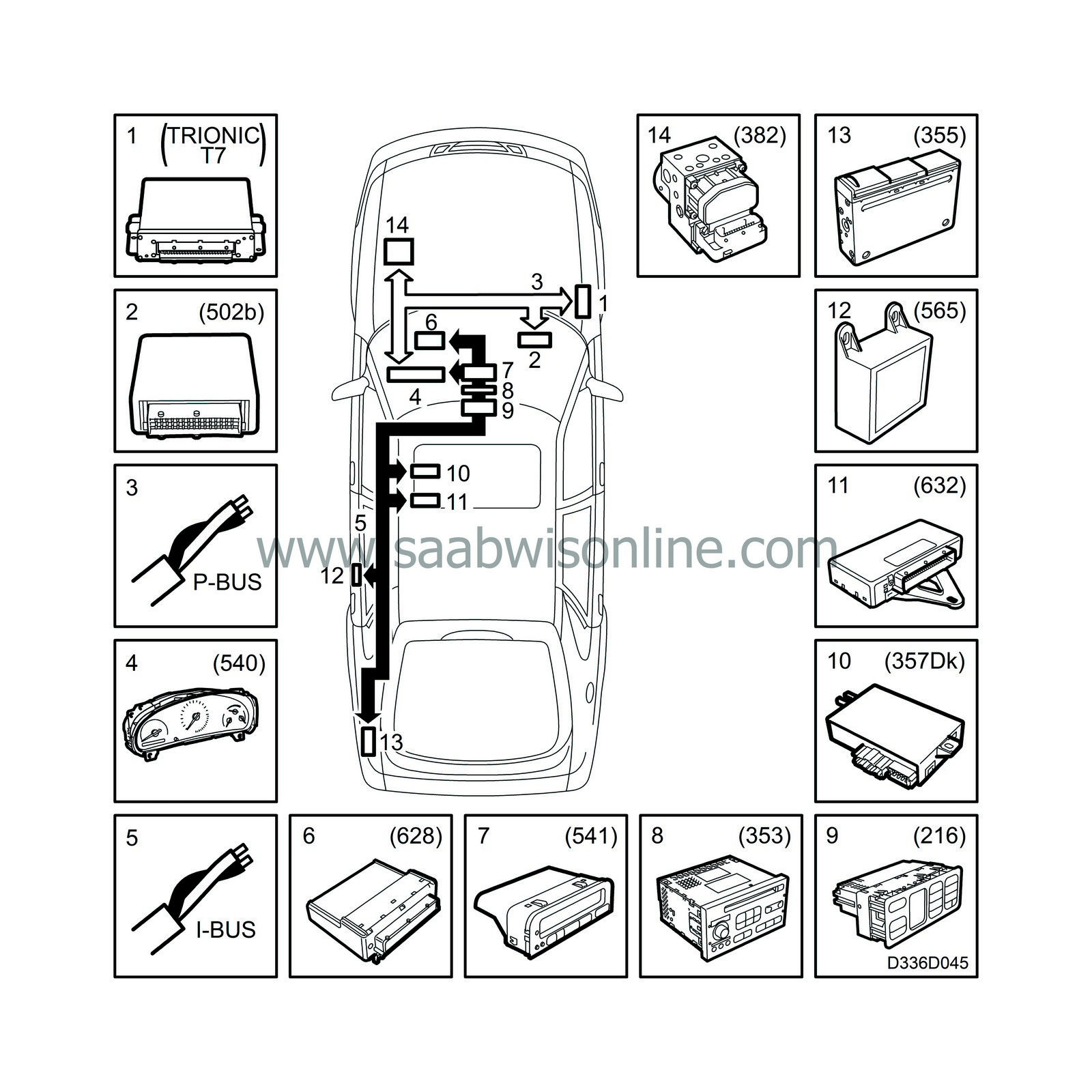
|
1.
|
Trionic, engine management system (430b, 589b)
|
|
2.
|
TCM, (Transmission Control Module) (502b)
|
|
3.
|
P-bus (Powertrain bus)
|
|
4.
|
MIU (Main Instrument Unit) (540)
|
|
5.
|
I-bus (Instrument bus)
|
|
6.
|
DICE (Dashboard Integrated Central Electronics) (628)
|
|
7.
|
SID (Saab Information Display) (541)
|
|
8.
|
Audio system, main unit (353)
|
|
9.
|
ACC, (Automatic Climate Control) (216)
|
|
10.
|
PSM, (Power Seat Memory) (357Dk)
|
|
11.
|
TWICE, (Theft Warning Integrated Central Electronics) (632)
|
|
12.
|
STC, (Soft Top Control) (565)
|
|
13.
|
CDC (CD changer) (355)
|
|
14.
|
TC/ABS (Traction Control) (382)
|
|
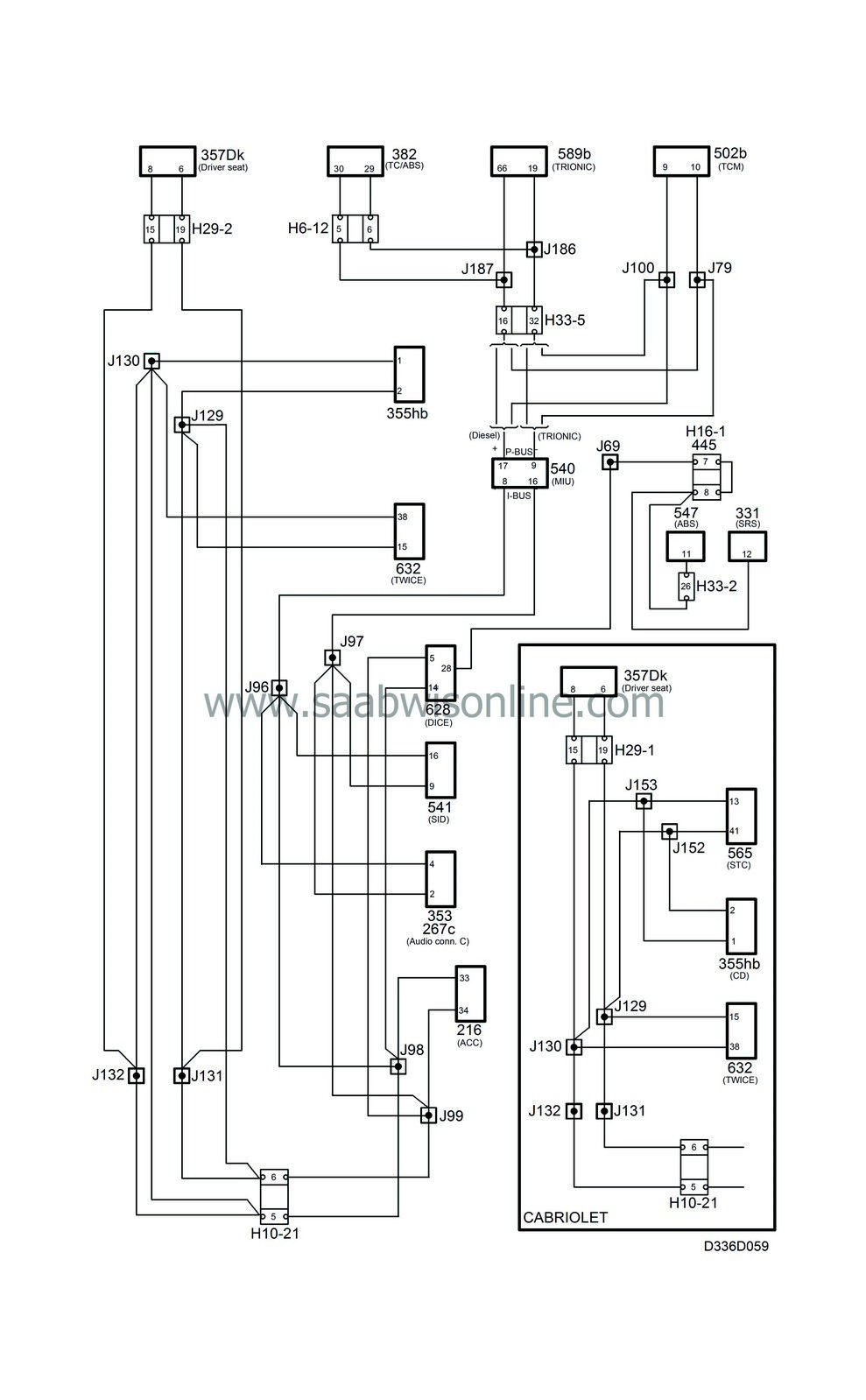
System overview, bus-connected components, cars with engine management system PSG 16
|

|
1.
|
Fuel pump with control module PSG 16 (595)
|
|
2.
|
P-bus (Powertrain bus)
|
|
3.
|
MIU (Main Instrument Unit) (540)
|
|
4.
|
I-bus (Instrument bus)
|
|
5.
|
DICE (Dashboard Integrated Central Electronics) (628)
|
|
6.
|
SID (Saab Information Display) (541)
|
|
7.
|
Audio system, main unit (353)
|
|
8.
|
ACC, (Automatic Climate Control) (216)
|
|
9.
|
PSM, (Power Seat Memory), (357Dk)
|
|
10.
|
TWICE, (Theft Warning & Integrated Central Electronics) (632)
|
|
11.
|
CDC (CD changer) (355)
|
|
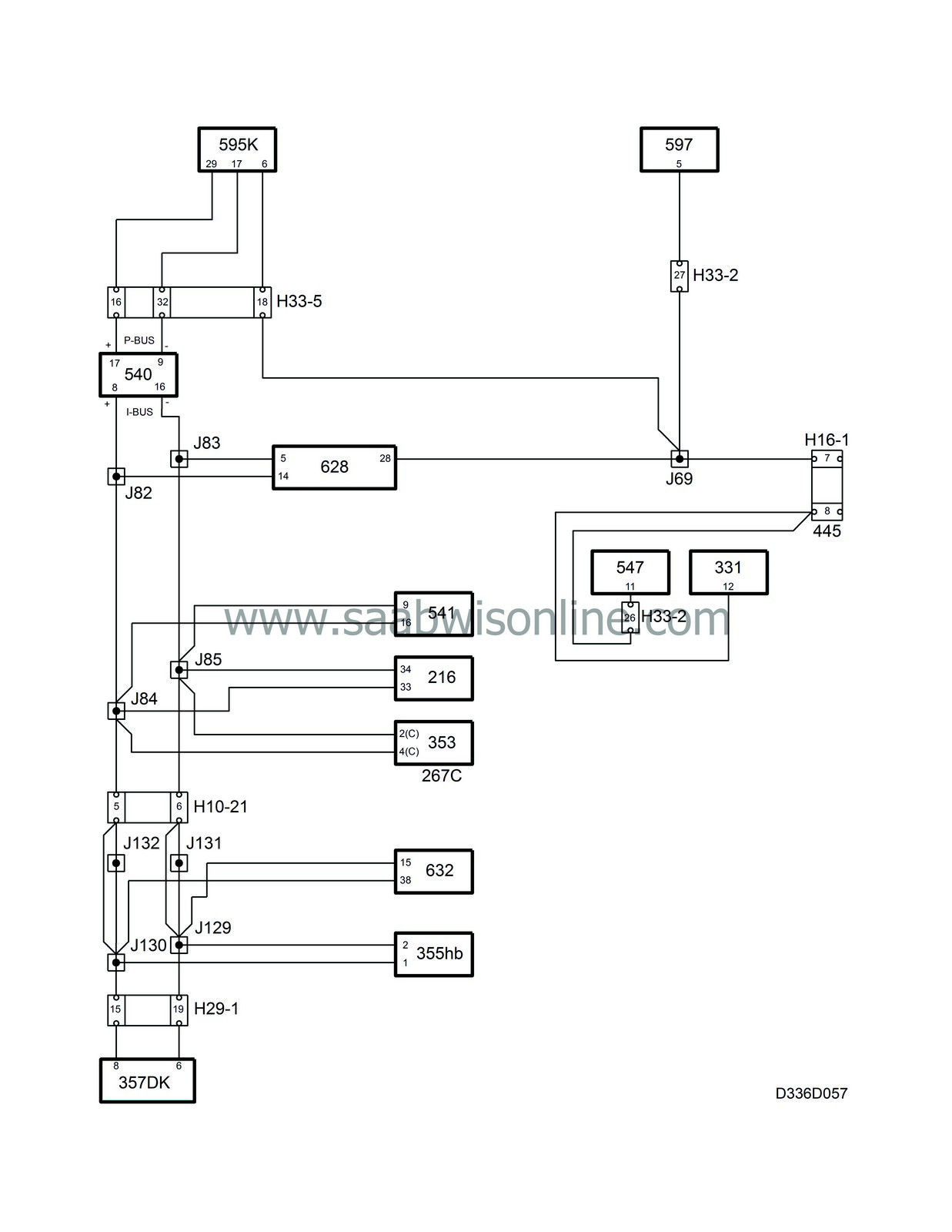
System overview, components connected to K lead, PSG 16
|
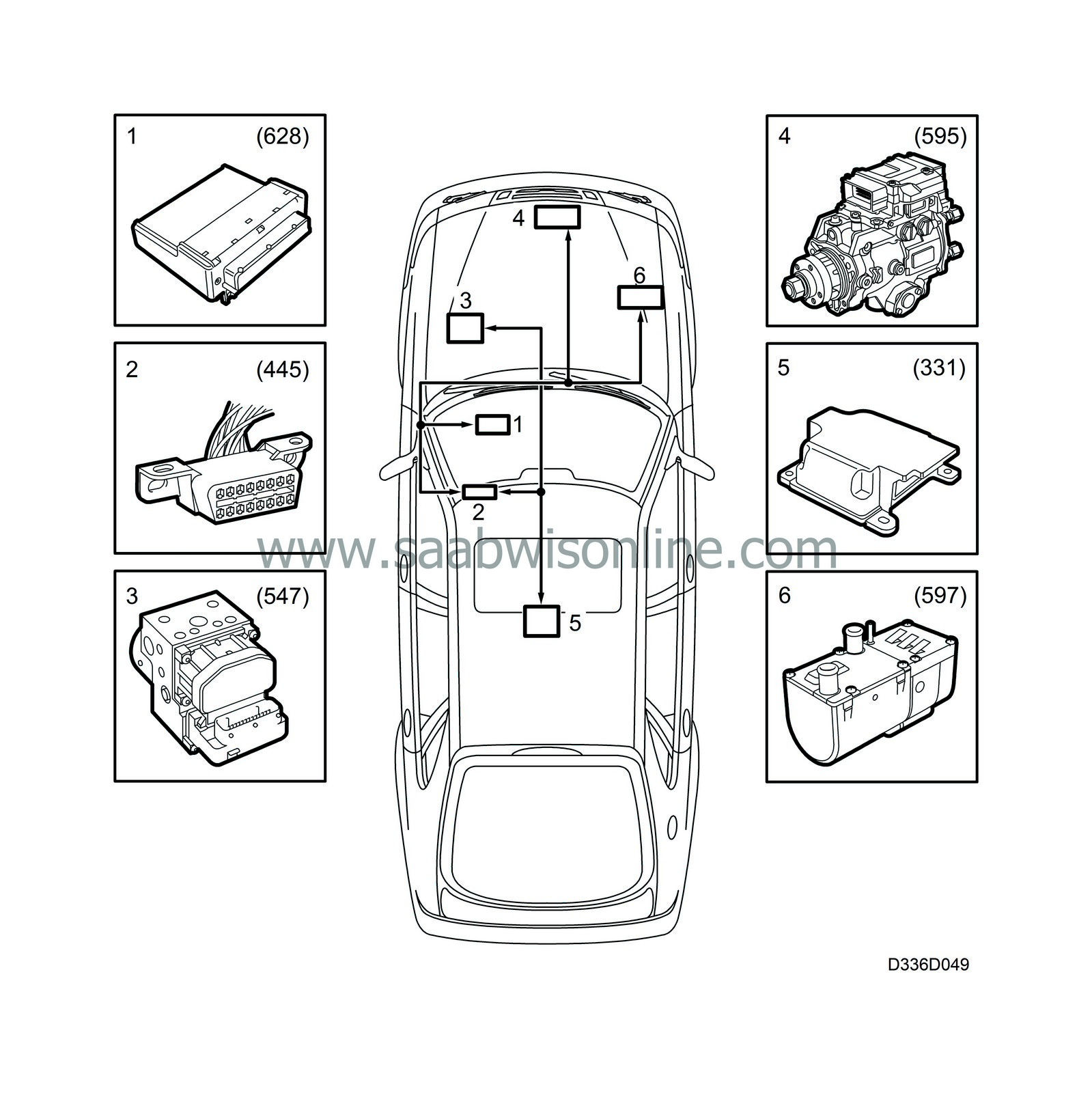
|
1.
|
DICE (Dashboard Integrated Central Electronics) (628)
|
|
2.
|
Data link connector (H16-5/445)
|
|
3.
|
ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) (547)
|
|
4.
|
PSG 16, engine management system diesel (595)
|
|
6.
|
DAH (Diesel Additional Heater) (597)
|
|
System overview, brief description, cars with engine management system Trionic T7
|
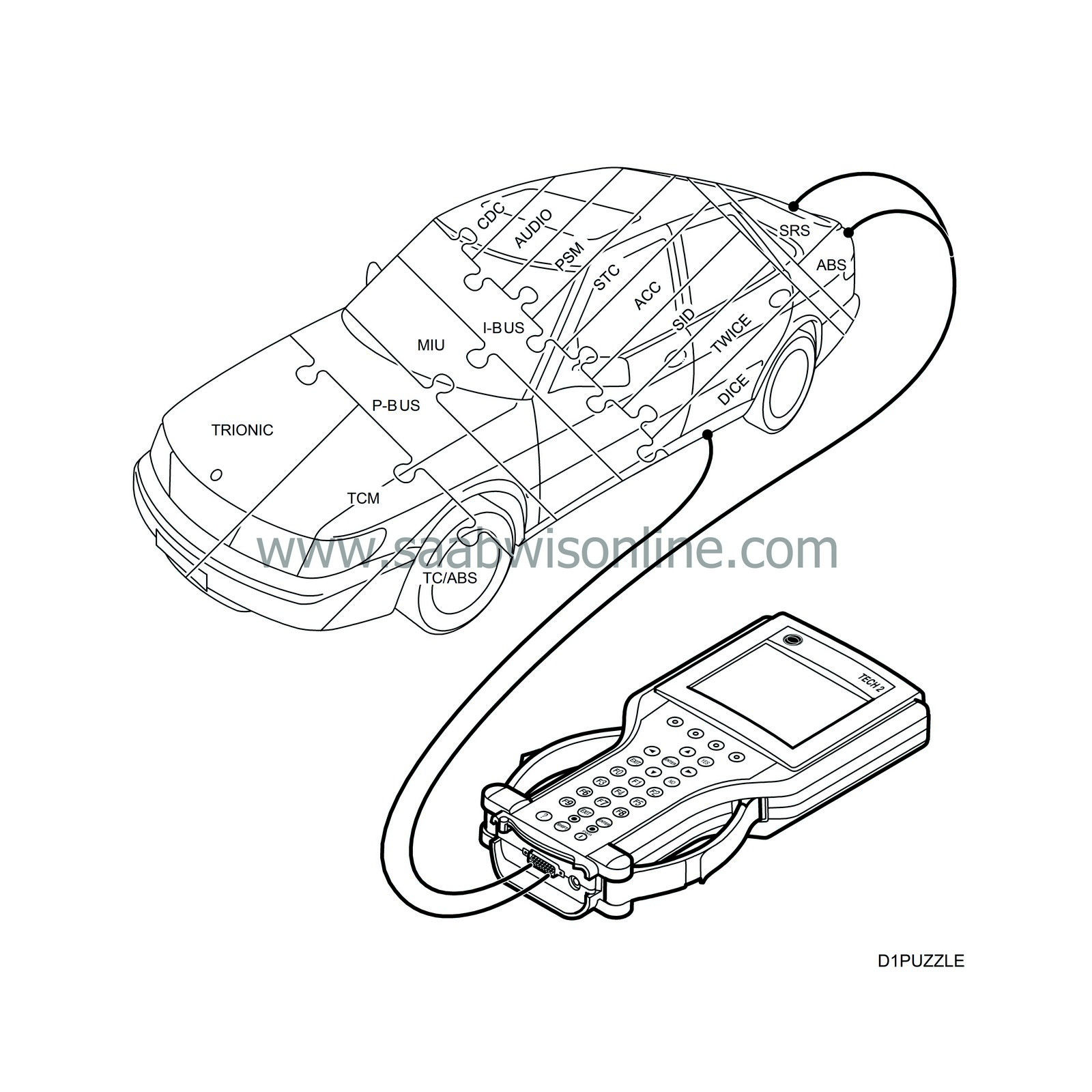
P-bus and I-bus in the Saab 9-3
In Saab 9-3, all control modules are connected to the bus except for ABS and SRS. On cars with Traction Control, the TC/ABS control module is connected to the bus.
The bus facilitates the transfer of a great deal of information between the control modules on only two leads. The bus is divided into a Powertrain bus (P-bus) and an Instrument bus (I-bus).
The powertrain systems Trionic, TCM and TC/ABS require fast communication so that there are no noticeable delays during torque limitation when shifting and the like.
Trionic, TCM and TC/ABS are connected to the P-bus, which whose speed of data transfer is ten times greater than that of the I-bus.
The P-bus and the I-bus are connected to MIU. MIU is responsible for ensuring that information available on one bus is also available on the other.
The diagnostic instrument is not directly connected to the bus. It communicates via DICE, one of the control modules connected to the I-bus. This provides it access to all bus-connected control modules.
Vehicle speed is important information for many control modules. Because ABS is not connected to the bus, vehicle speed has its own lead from ABS to MIU. MIU then sends information on vehicle speed further on the buses. On cars with Traction Control, MIU receives speed information from TC/ABS via the P-bus.
|
System overview, brief description, cars with engine management system PSG 16
|
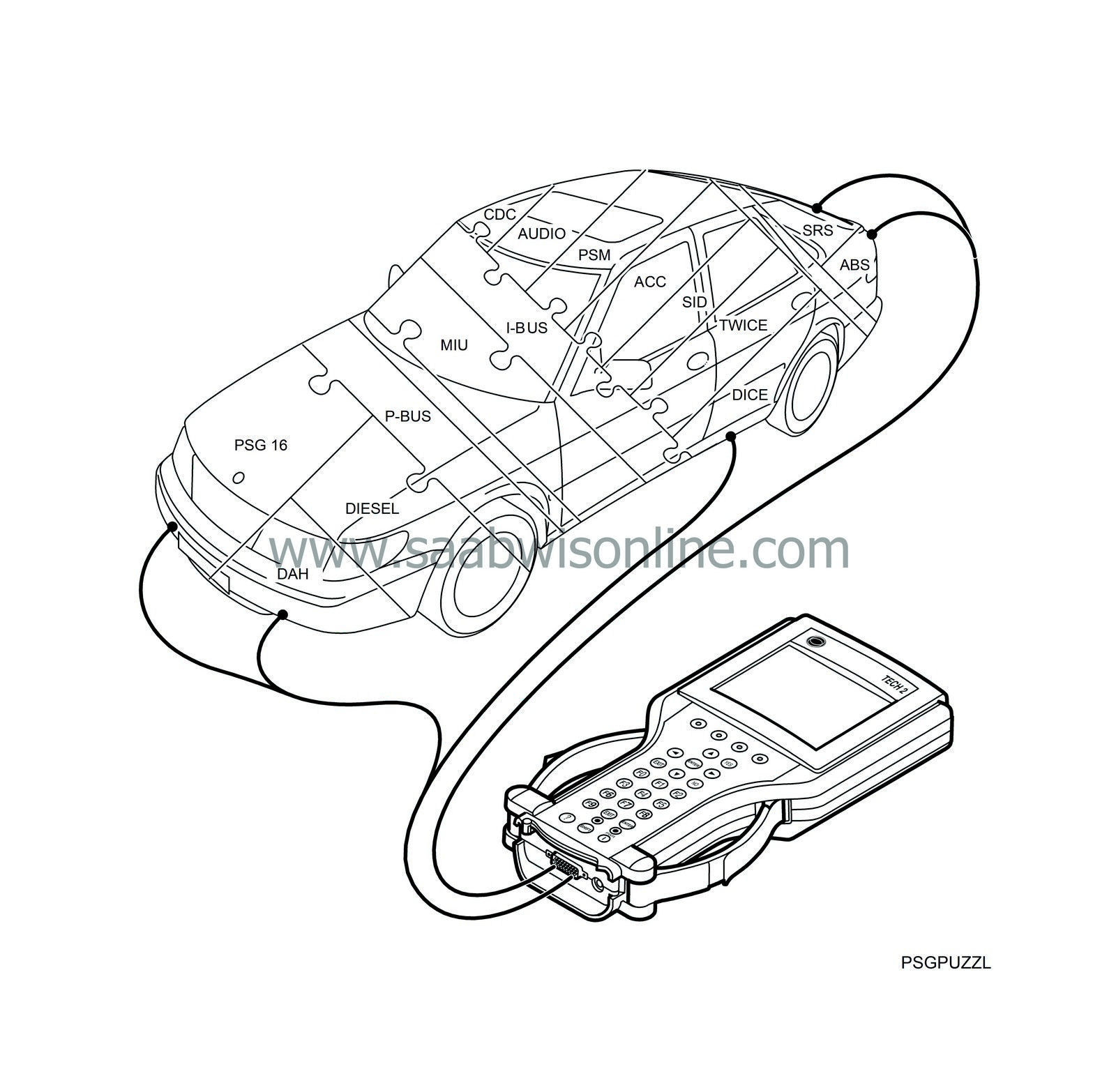
Engine control module PSG 16 is not connected on the I-bus. This system needs
much faster
communication so that there are no noticeable delays when the control module requests a new amount of fuel per injection, a new injection angle or the like.
The engine control module is connected to a separate bus called the P-bus (Powertrain Bus). The communication speed of the P-bus is ten times faster than that of the I-bus.
The P-bus is also connected to MIU. MIU is responsible for ensuring that information available on one bus is also available on the other. Note also that PSG 16 has a separate K-lead to the diagnostic tool.











