Starter motor
| Starter motor |
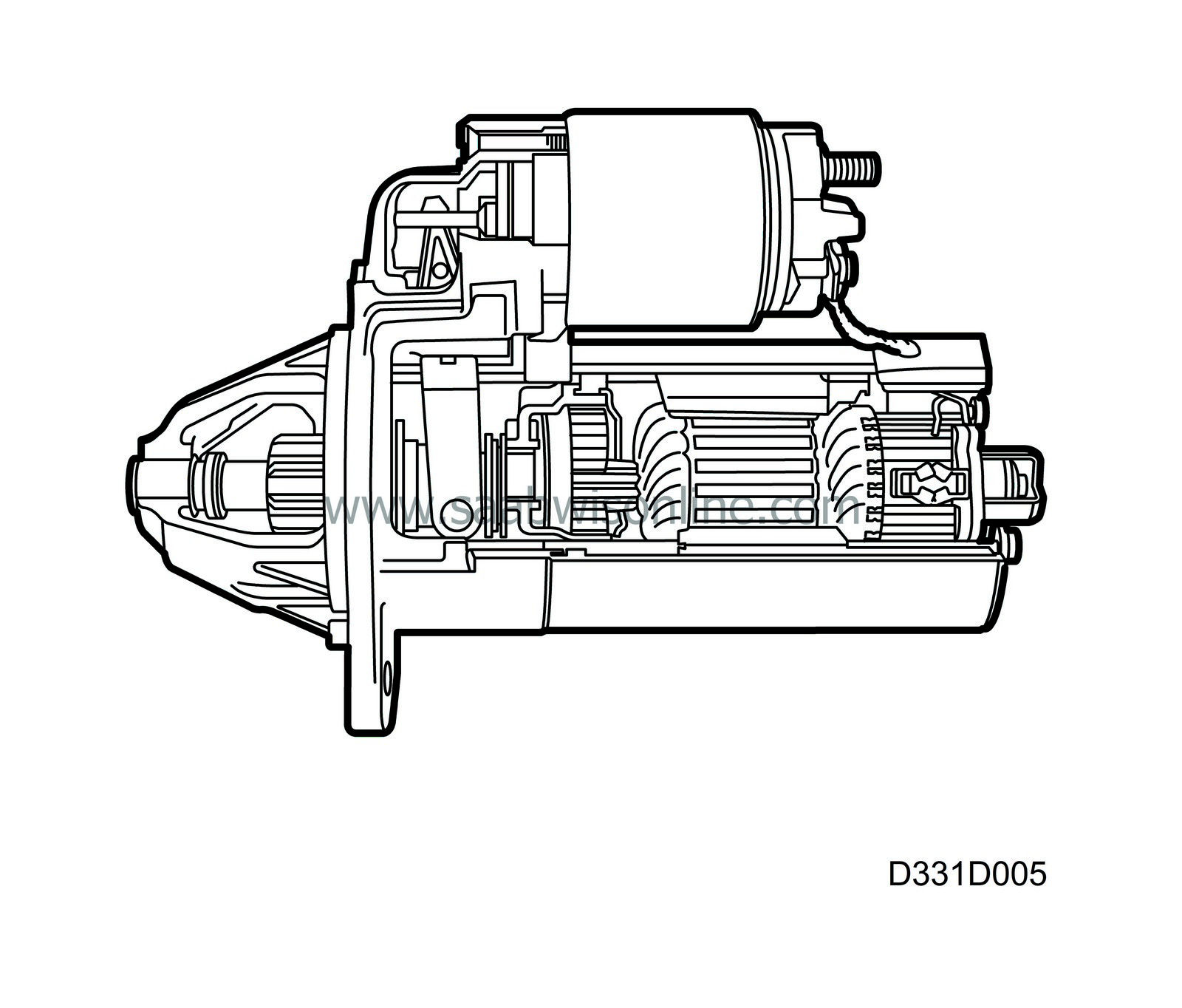
A planetary gear increases the starting torque.
The starter motor circuit consists of tow sub-circuits:
| • |
working circuit
|
|
| • |
operating circuit
|
|
| Working circuit |
The working circuit goes from the battery's positive terminal to terminal 30 on the starter motor.
| Operating current circuit, automatic transmission |
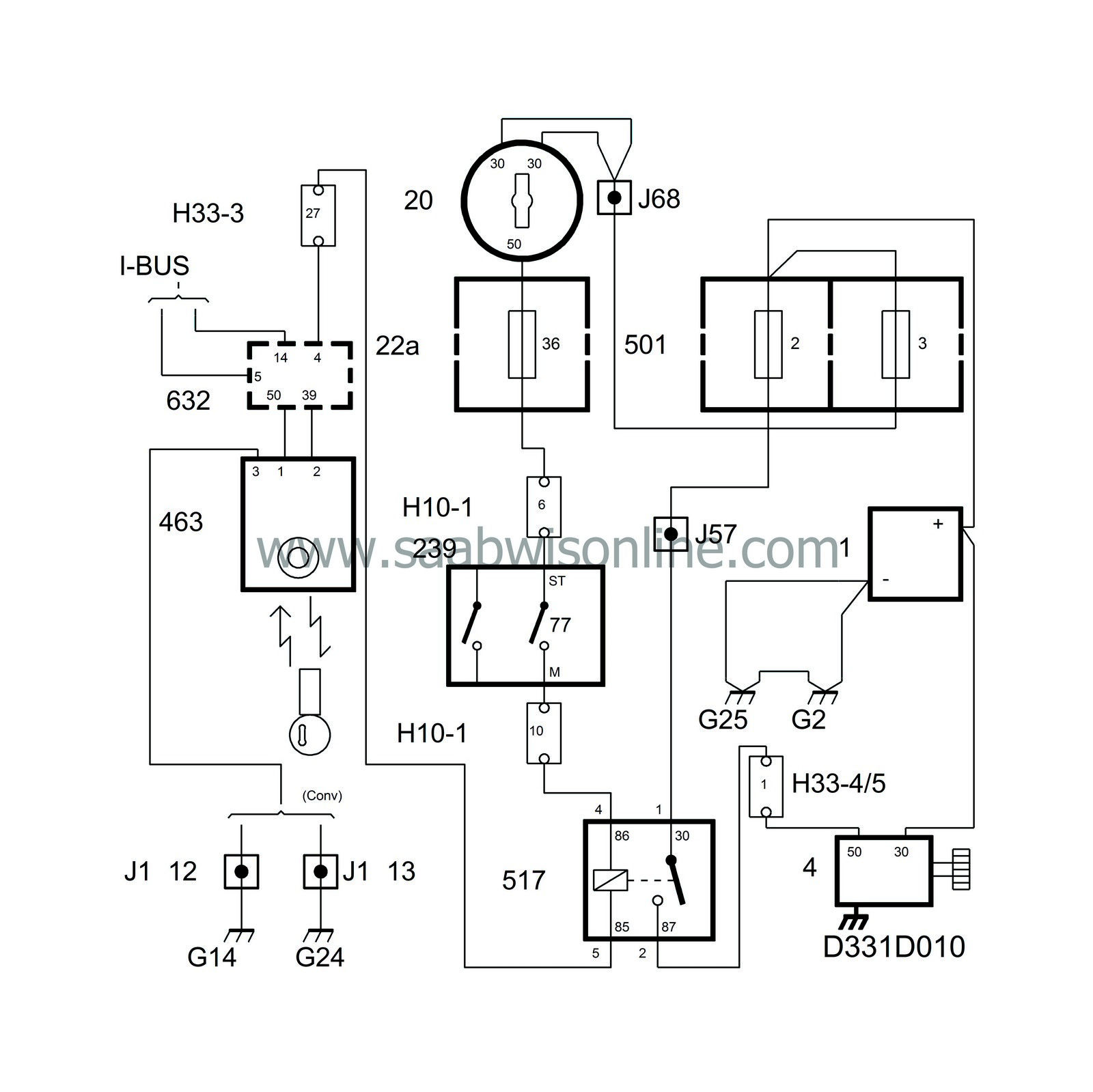
The operating circuit goes from the battery's positive terminal to the ignition switch and on to the starting relay, and via the starting relay to terminal 50 on the starter motor, which is the operating current connection on the solenoid.
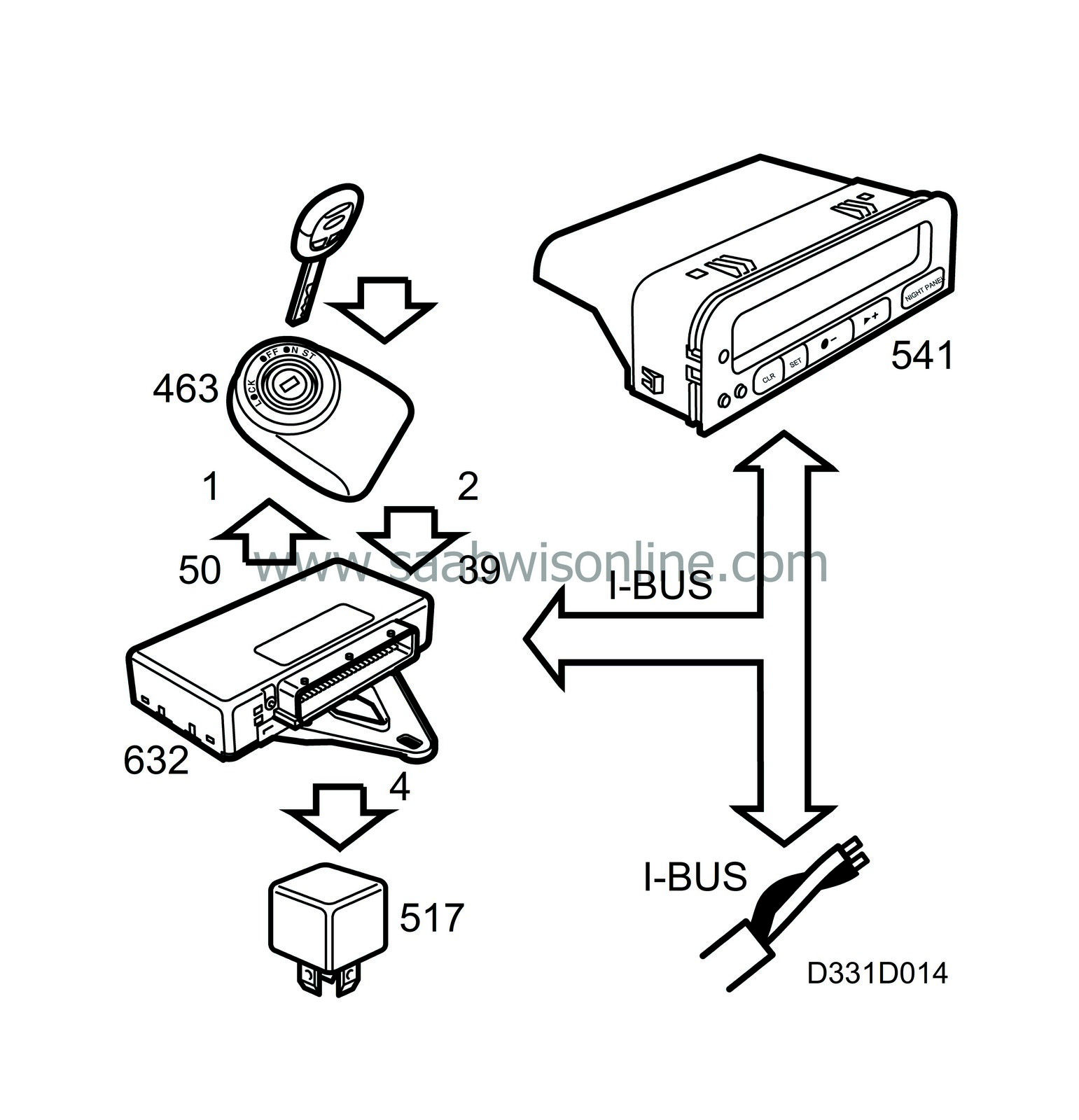
On cars with automatic transmission, the gear selector lever must be in position P or N if the start relay coil is to receive a current.
The starting relay actuating coil is grounded via the TWICE control module when it has received the ready signal from the immobilizer unit.
|
|||||||
| Operating current circuit, manual gearbox |
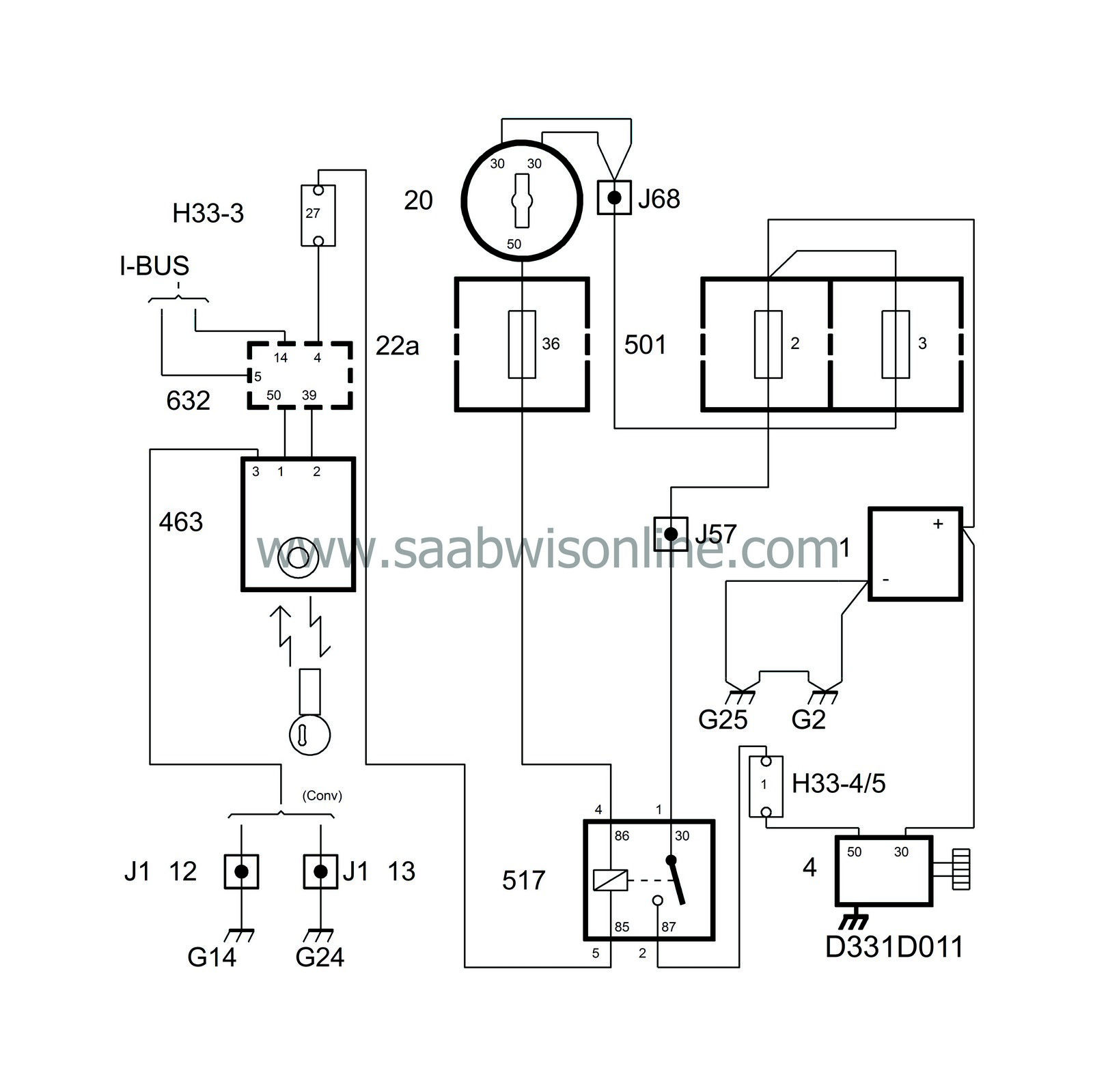
The operating circuit goes from the battery's positive terminal to the ignition switch and on to the starting relay, and via the starting relay to terminal 50 on the starter motor, which is the operating current connection on the solenoid.
The starting relay actuating coil is grounded via the TWICE control module when it has received the ready signal from the immobilizer unit.
|
|||||||
| Operation |
When the correct ignition key is put in the ignition, the transponder sends a code to TWICE, which grounds the starting relay actuating coil.
As the ignition is turned to start position, the starting relay operates and the operating circuit to the solenoid terminal 50 closes. The solenoid engages the pinion with the ring gear on the engine's flywheel and closes a switch so that the starter motor commutator is supplied with power via the slip brushes from terminal 30.
Once the engine is started and the engine speed exceeds the starter motor rpm, the pinion is disengaged from its shaft via a free wheel, preventing the starter motor from overrevving. Releasing the ignition key breaks the starting circuit and also the operating circuit to the solenoid, whereby a spring returns the pinion to its rest position.

 Warning
Warning

