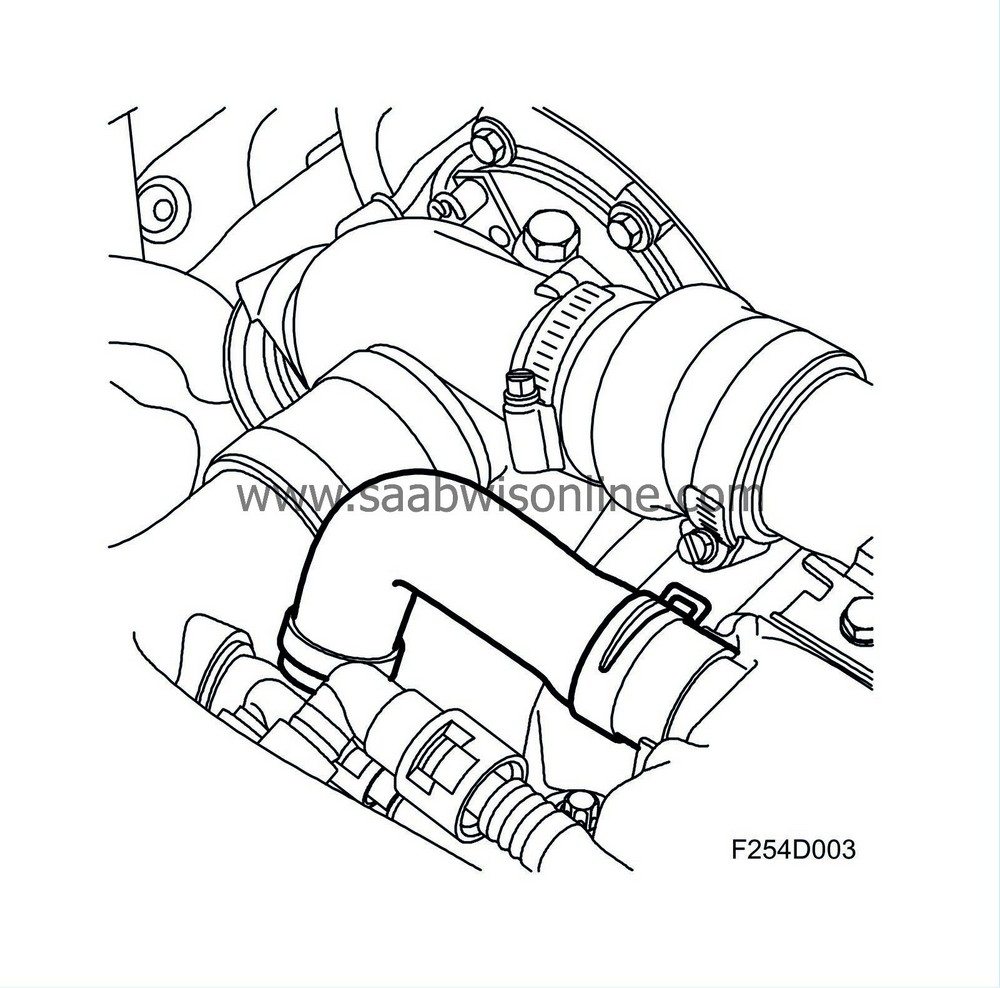
Detailed description
| Detailed description |
The hoses and their connections are dimensioned to provide adequate escape of the crankcase gases under all operating conditions. The crankcase gases are led via a valve in the camshaft cover to the hose between the mass air flow sensor and the turbocharger, where they are mixed with the induction air and then combusted in the engine.
| Catalytic converter |
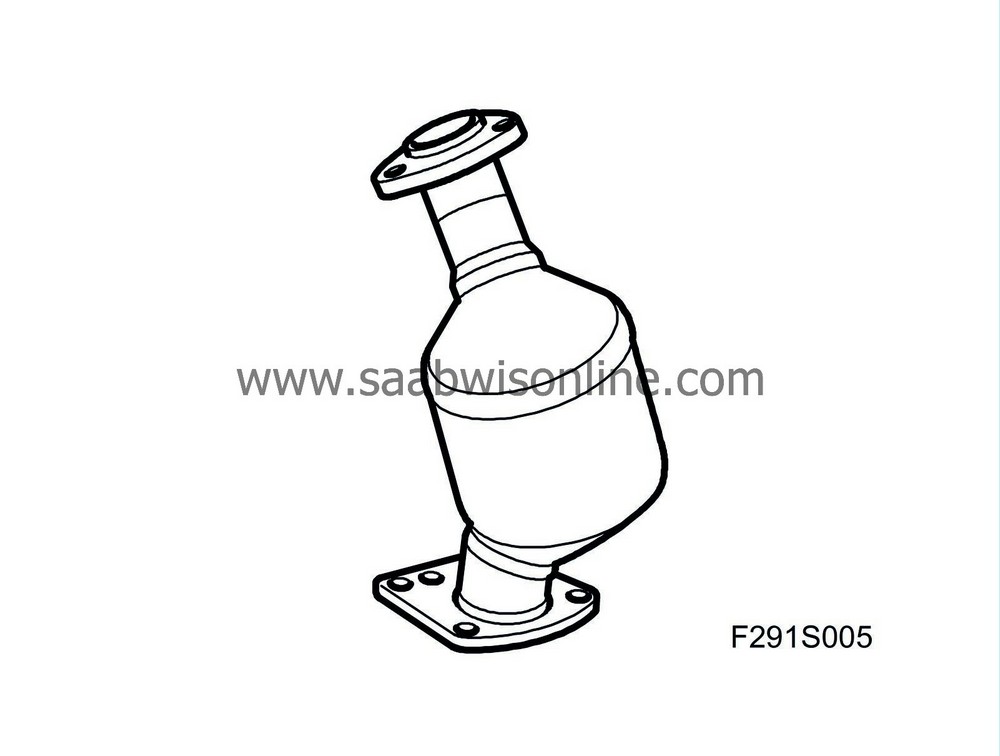
To purify the exhaust emissions, a catalytic converter is used that can oxidise (C n H m ) and carbon monoxide (CO) to carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O). The catalytic converter can also contribute to the partial oxidation of particles formed in the exhaust gases from diesel engines. Diesel fuel with a high sulphur content will lead to the contamination of the catalytic converter and increase the risk of the formation of sulphates.
The catalytic converter consists of a ceramic monolith with a porous layer that increases the active area. In this layer, there are small particles of the catalytic material platinum (Pt).
| Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) |
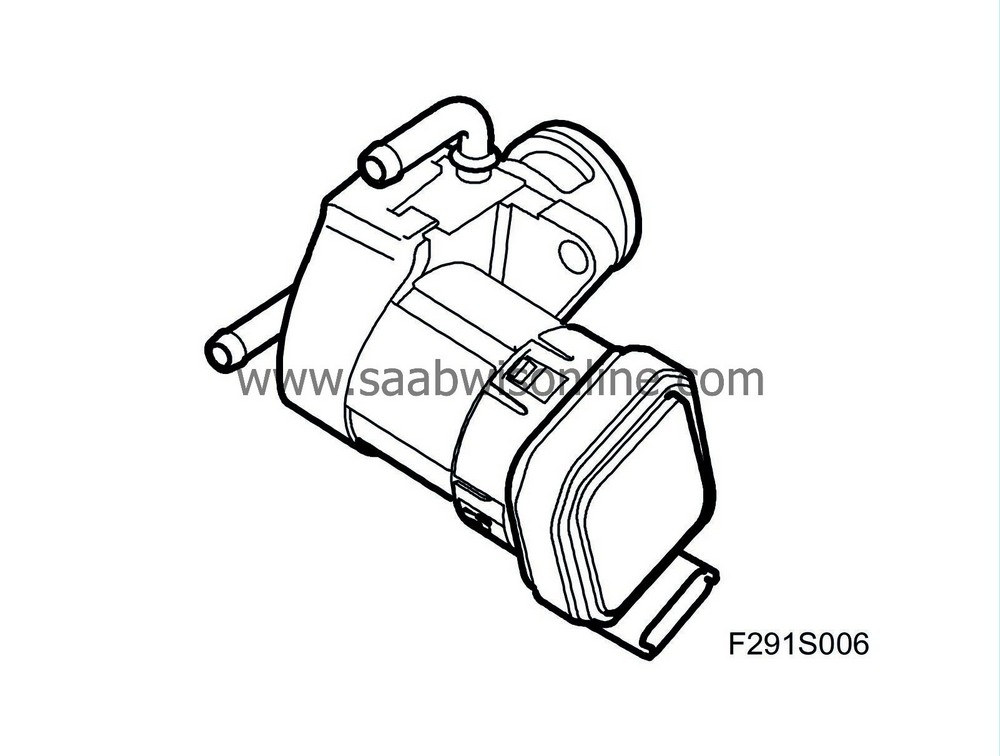
For a diesel engine, operating with excess air in combustion, there is today no effective catalytic converter technology available for reducing the NO x emissions. This means that the formation of NOx has to be restricted.
With an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, a controlled amount of exhaust gas is led to the induction side and mixed with the induction air. The result is slower combustion at a lower temperature and maximum pressure, which in turn reduces the formation of NO x .
The EGR valve is electronically controlled and has its own microprocessor. The EGR valve is controlled by a 140 Hz PWM signal from the PSG 16 control module.
The processor in the EGR valve keeps track of how far open the valve is. This means that when the PSG 16 signals how much to open or close the valve, the reaction time is very short. The combustion temperature can therefore be kept low, which effectively reduces NO x emissions. The EGR function is deactivated after one minute of idling to reduce the build-up of carbon deposits.
The processor in the EGR valve also allows self-diagnosis. If, for example, the valve sticks, the engine control module is informed by a 100 Hz PWM signal, and a DTC is generated. If a DTC for the EGR valve has been generated, engine torque will be reduced and the EGR and swirl functions deactivated. In addition, the CHECK ENGINE lamp will light.