Short description
| Short description |
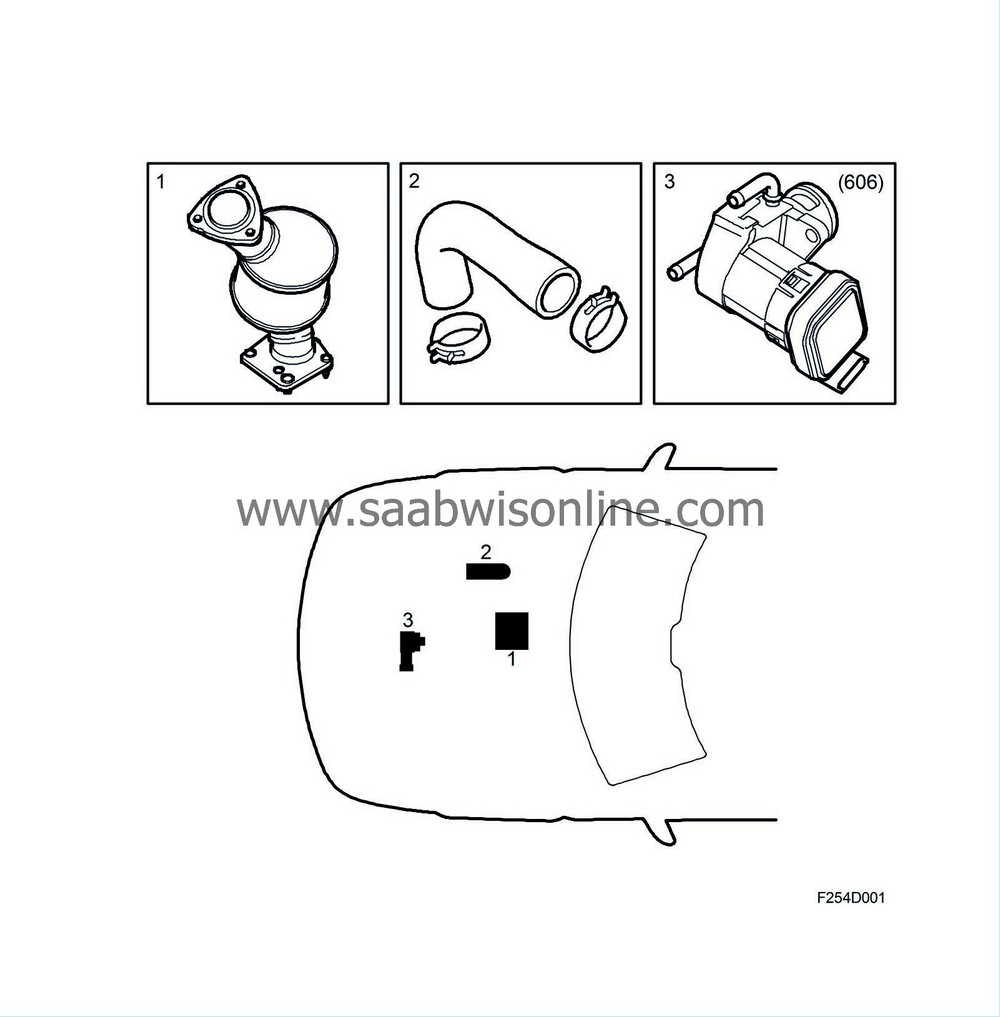
| 1. |
Catalytic converter
|
|
| 2. |
Crankcase ventilation
|
|
| 3. |
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve (606)
|
|
| Description |
The engine has a closed crankcase ventilation system. The crankcase vapours are led via a nipple in the camshaft cover to the hose between the mass air flow sensor and the turbocharger, where the gases are mixed with the induction air and then combusted in the engine.
To purify the exhaust emissions, a catalytic converter is used that can oxidise carbon hydroxide (C n H m ) and carbon monoxide (CO) to carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O). The catalytic converter can also contribute to partial oxidation of particles that are formed in exhausts from diesel engines.
With an Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system, a controlled amount of exhaust gas is led to the induction side and mixed with the induction air. The result is slower combustion at a lower temperature and maximum pressure, which reduces the formation of NOx. The EGR valve is electronically controlled and has its own microprocessor. The EGR valve is controlled by a 140 Hz PWM signal from the PSG 16 control module. This controls the degree of opening and induction air/exhaust emission mixture.