Short description
| Short description |
| Description |
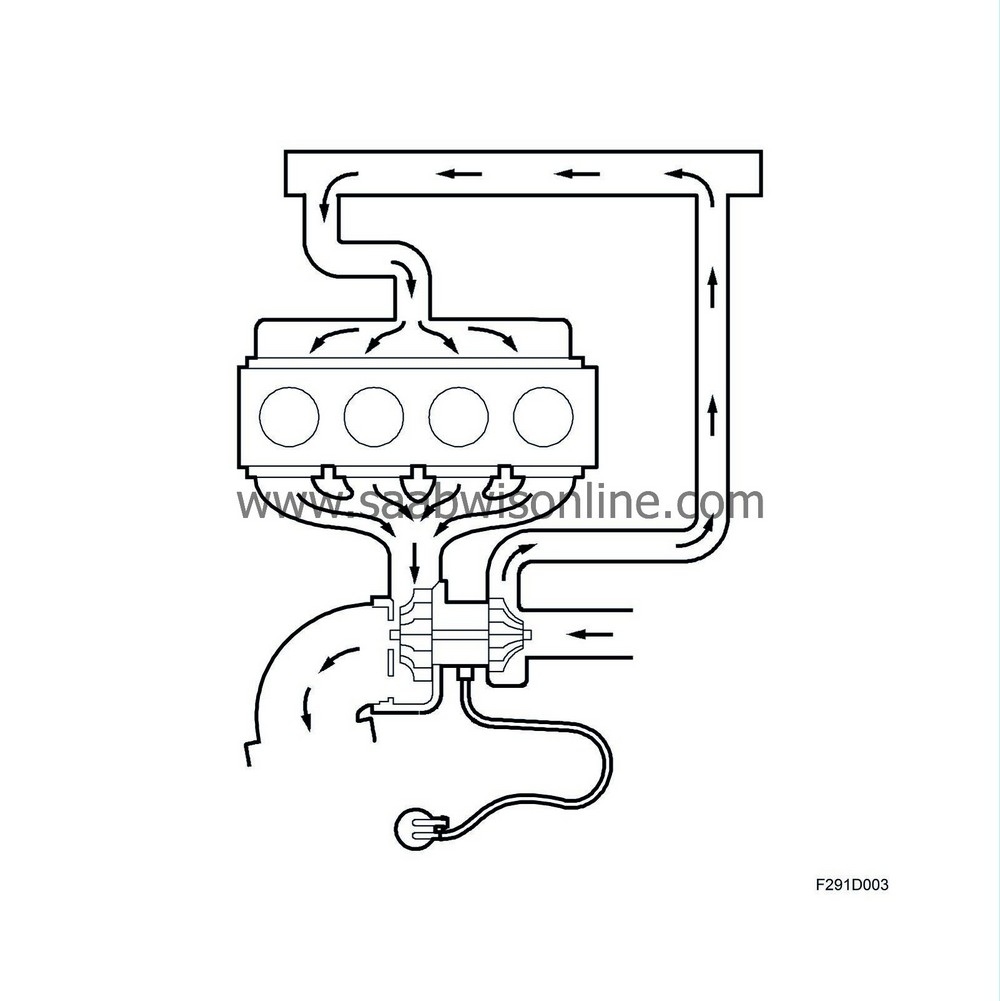
In contrast to a normally aspirated engine, the supercharged engine induces a greater mass of air on the induction stroke, which increases the efficiency of combustion and enables the engine to develop greater power and torque at a lower fuel consumption. Supercharged engines can achieve a level of performance comparable to that developed by larger engines, yet still retain the advantages of better fuel economy, smaller size, lighter weight, etc.
Supercharging is achieved using a turbocharger, which means that the engine's exhaust gases are employed to drive a turbine. The turbine wheel and the compressor impeller are mounted on a common shaft and rotate at the same speed. The compressor impeller is located in the induction system in which it increases the air pressure and thus improves the charging of the combustion chamber.
The turbo compressor is dimensioned so that it begins to operate at relatively low engine speeds and therefore provides high torque in rpm ranges that are used during normal driving conditions.