Fuel injection, basic function
|
|
Fuel injection, basic function
|
|
1.
|
Basic calculation of fuel mass/combustion

The current air mass/combustion is divided by 14.7 and sent to box 2. The unit is now mg fuel/combustion.
|
|
2.
|
Compensation
In the case of a cold engine, shortly after starting, rapid load changes, knocking or a high load, the current value is multiplied by a compensation factor.
|
|
3.
|
Closed loop
The closed loop value is also used as a multiplier. The value is sent to box 4.
|
|
4.
|
Correction for purging
Multiply by the value for purging adaptation. The value is sent to box 5.
|
|
5.
|
Multiplicative adaptation
The multiplicative adaptation value is also used as a multiplier and the new value sent to box 6.
|
|
6.
|
Additive adaptation
The additive adaptation value is added and the new value sent to box 7.
|
|
7.
|
Fuel mass, secondary air injection
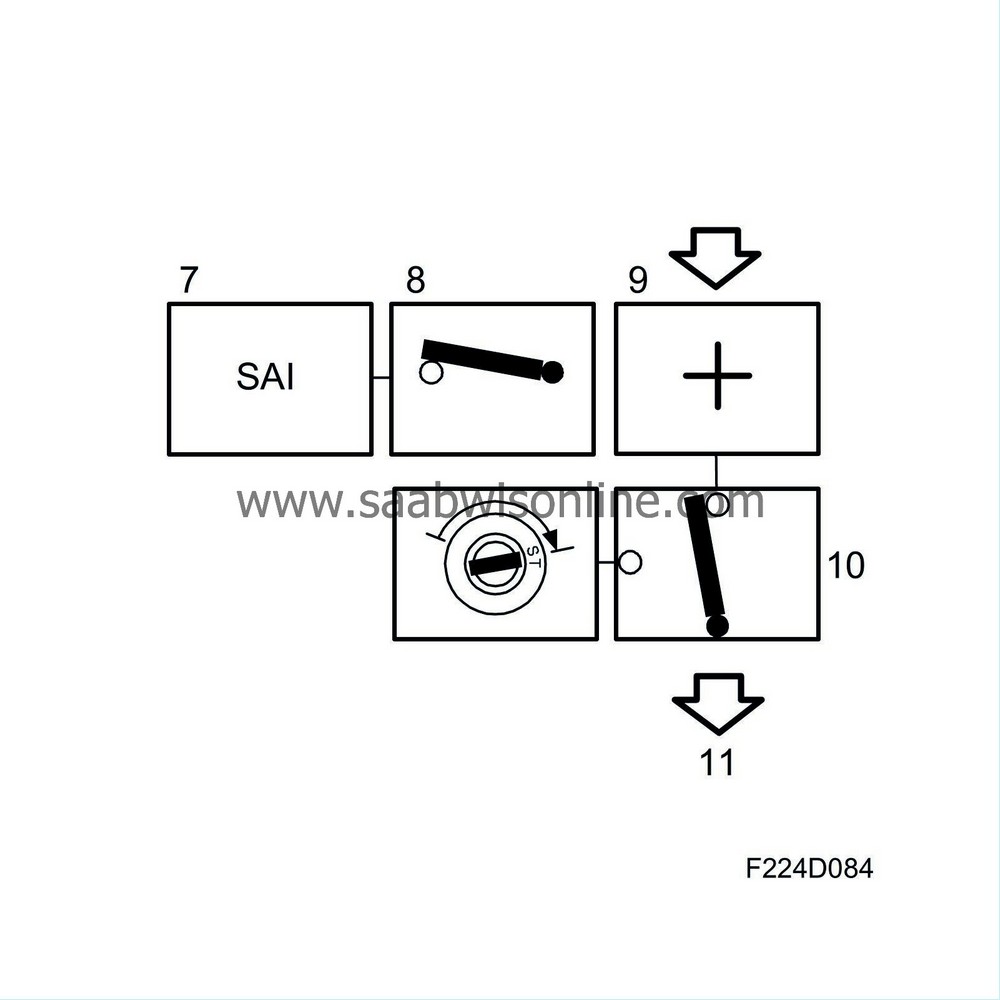
More fuel is added if SAI is active.
|
|
8.
|
Engagement of SAI fuel
|
|
10.
|
Starting fuel mass
Starting fuel mass is selected if the engine has not been started.
|
|
11.
|
Fuel mass/combustion
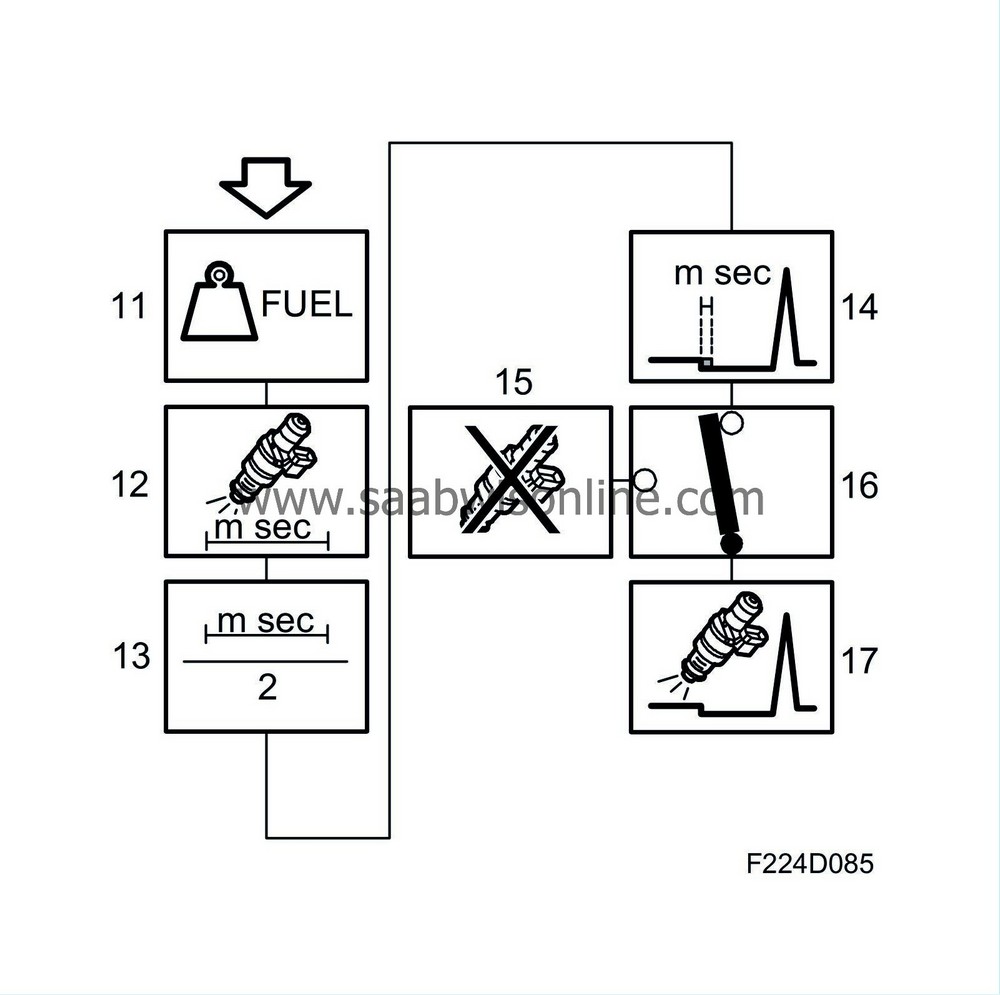
Fuel mass/combustion is the fuel mass to be supplied to the engine for each combustion.
|
|
12.
|
Injector opening duration
Converts fuel mass to nozzle opening duration in ms.
|
|
13.
|
Injection twice/combustion
Before the engine has been synchronised, i.e. the camshaft position has been detected by the ignition system, fuel will be injected twice per combustion. The injection duration calculated in block 12 is divided by two.
|
|
14.
|
Needle lift compensation
Voltage dependent needle lift duration is added to the injection duration. This compensates for the delay between the current in the injector coil being activated and the fuel arriving.
|
|
15.
|
Fuel shut-off
Fuel shut-off can come into question under certain conditions, e.g. when engine braking, car immobilized. Injection duration is then zero.
|
|
16.
|
Selection of fuel shut-off function
|
|
17.
|
Activation of injector
ECM controls the injector that is about to deliver fuel, the sequence depends on the firing order. The crankshaft angle during which injection takes place depends on the prevailing operating conditions.
|





