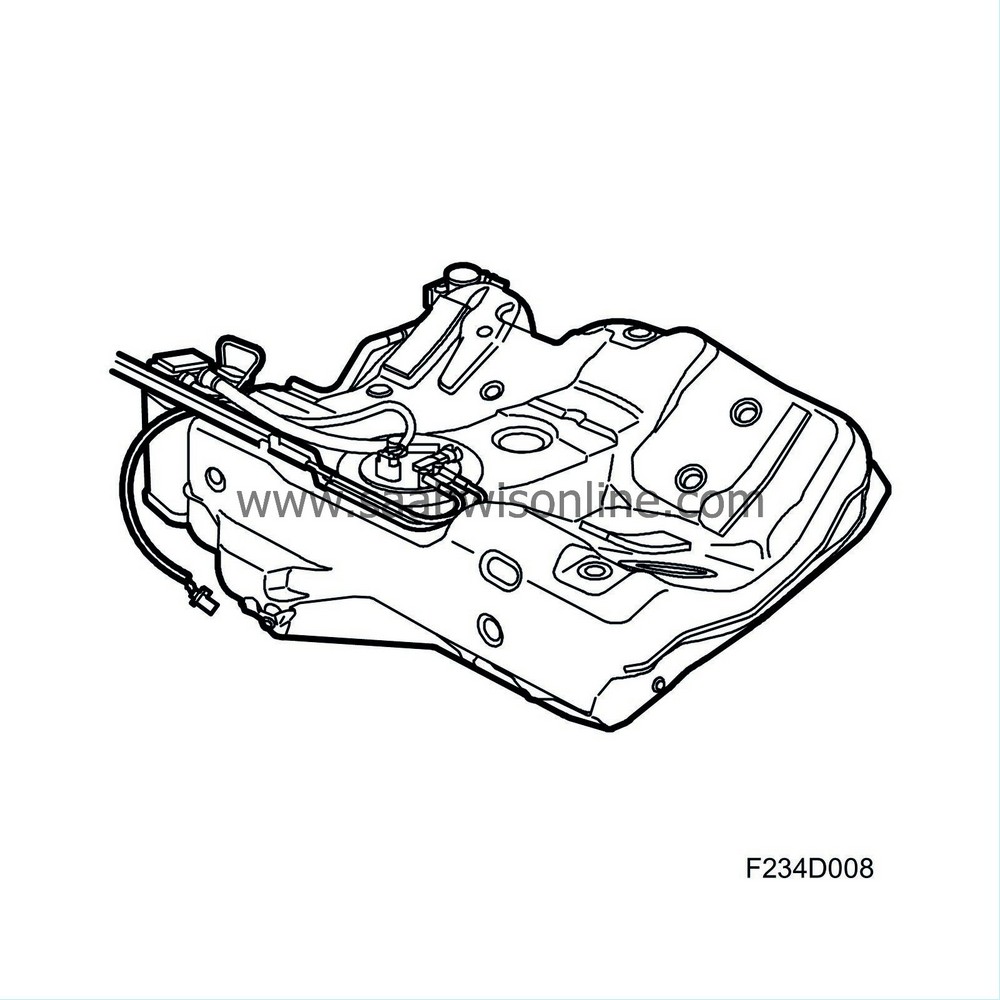
Detailed description
| Detailed description |
| Roll-over shut-off valve |

The roll-over shut-off valve closes only if the car rolls over, preventing fuel leaks.
There is a line connecting the valve with the emission canister. Expanding vapour in the tank is ventilated through the valve and the evaporative emission canister.
| Float valve |

There is a line connecting the float valve with the emission canister. The float valve prevents fuel in a liquid state from reaching the evaporative emission canister. When refuelling, the vapour in the tank is forced through the float valve and into the evaporative emission canister.
A spring-loaded float closes the valve when the tank is full or if the car rolls over.
| Evaporative emission canister |

The evaporative emission canister is located on the right-hand side of the tank and comprises a container filled with a special type of carbon pellets. Carbon pellets are used so that as little resistance as possible is obtained from the evaporative emission canister. The hydrocarbons that evaporate in the tank are passed to the evaporative emission canister. When refuelling, hydrocarbons and air from the tank are evacuated to the evaporative emission canister, which absorbs the hydrocarbons.
Separate lines connect the evaporative emission canister with the fuel tank, EVAP purge valve and shut-off valve. When the engine starts, air is drawn in through the shut-off valve to the evaporative emission canister and then via the purge valve into the intake manifold. The hydrocarbons are taken with it and are burned in the engine.
The evaporative emission canister absorbs approx. 70 g hydrocarbon for each full tank. The emission canister is purged while the car is being driven, the time it takes depends on the driving. The evaporative emission canister can absorb a maximum of approx. 125 g hydrocarbon.
| Check valve, fuel tank |
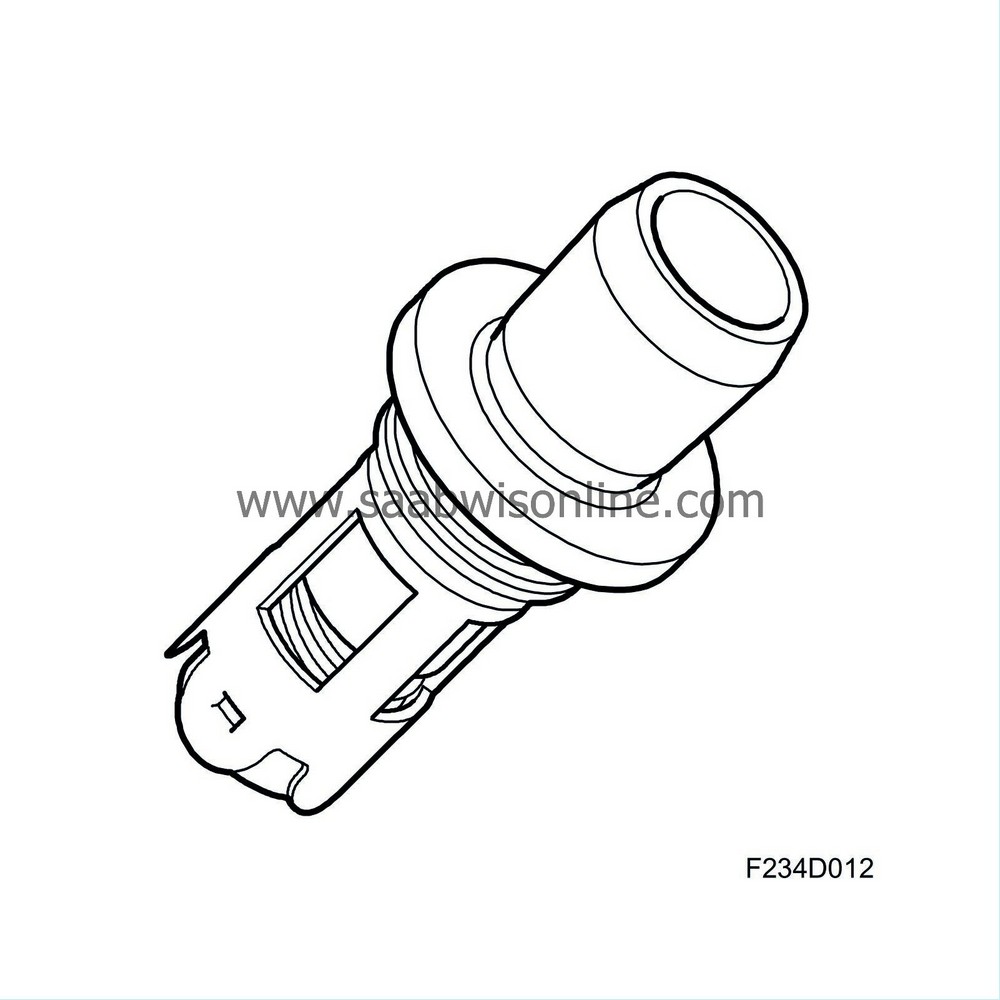
The check valve is normally in the closed position and allows flow only in the direction towards the tank.
In this way, the valve prevents ”back-spit” when the nozzle is shut-off.
| Fuel filler pipe |
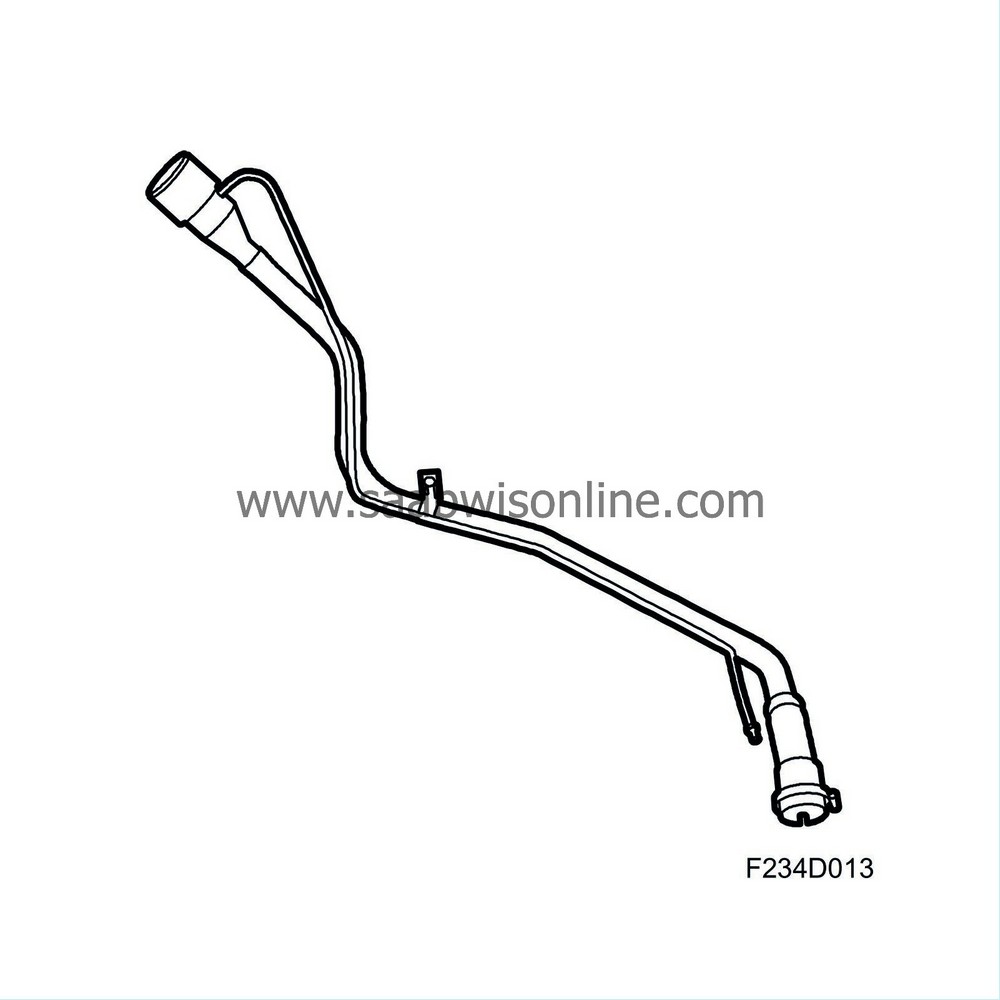
Fuel is filled into the filler pipe and then passes through a check valve and into the tank.
There is an insert at the top of the filler pipe that ensures that the pump nozzle fits well while refuelling. The insert also includes an ejector.
| Filler cap |

The filler cap constitutes an important component in the tank integrity diagnosis. Trionic will generate a fault code if the tank integrity diagnosis indicates a leak.
| Tank integrity diagnosis |
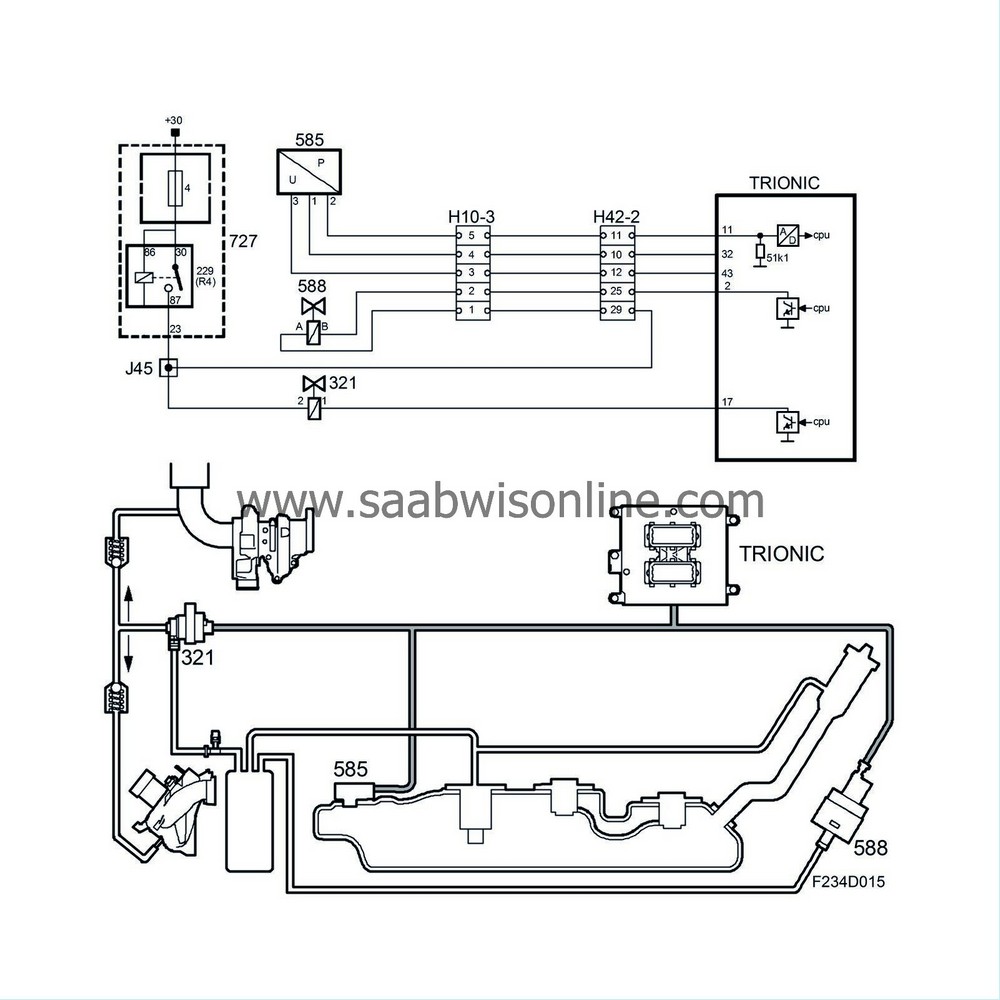
It is possible to check the evaporative emission system for leaks with the tank integrity diagnosis. If there is a leak, it will not be possible to create or retain a vacuum in the system during the diagnosis.
The diagnosis is performed once per trip and its objective is to determine whether a leak corresponding to a hole larger than 0.5 mm (0.020”) in diameter is present in the evaporative emission system.