(TA410-1003) Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF) noise diagnosis
| TECHNICAL ADVICE - Quick information for your help | |
| Bulletin Nbr: | TA410-1003 |
| Date: ........... | April 2010 |
| Market: | All |
| Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF) noise diagnosis |
| VEHICLES CONCERNED |
Saab 9-3 and 9-5 with Dual Mass Fly Wheel.
| BACKGROUND |
Customer complaint of noise from clutch/ flywheel area. Unnecessary replacements of the clutch kits have been noted.
| ACTION |
A. Check for thermal overload:
During normal driving the friction surface of the dual-mass flywheel, temperatures up to 200 °C can arise and through operating errors much higher temperatures eg due to clutch slippage can arise.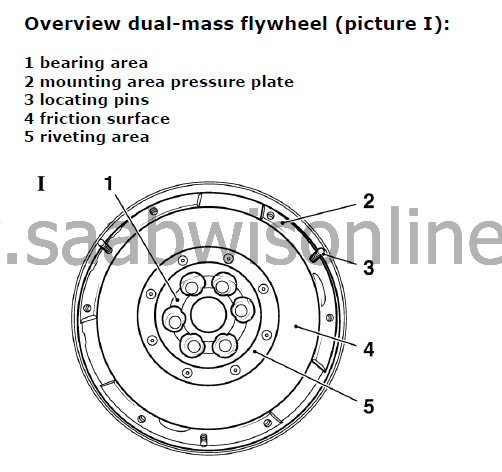
| • |
tarnish (bluish) as well as local hotspots on friction surface
|
|
| • |
tarnish (bluish) near of mounting area and riveting area of clutch
|
|
If all other checkable features are in order, the dual-mass flywheel is still servicable.
Possible indications for a too high thermal load are:
| • |
cracks
|
|
| • |
fusion zones on friction surface (material smear)
|
|
| • |
scores in friction surface (for example through clutch lining
riveting at destroyed or worn clutch plate)
|
|
| • |
tarnish (bluish) which reaches up to bearing area of dual-mass
flywheel
|
|
| • |
bluish discoloration of locating pins (3 locating pins in outer
zone of dual-mass flywheel)
|
|
In these cases the dual-mass flywheel has to be replaced.
B. Check for damaged components:
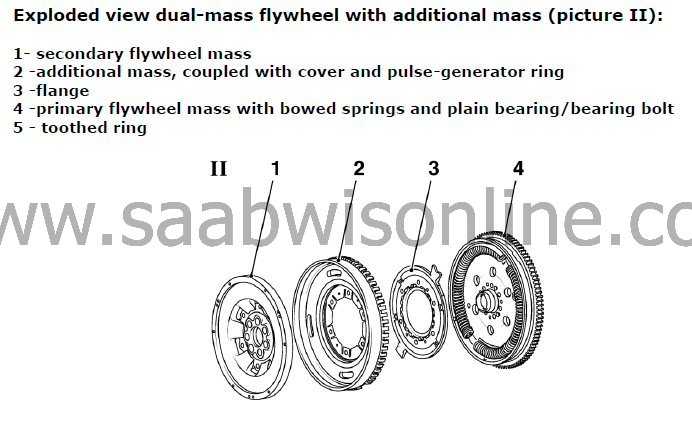
The following checking procedures should be carried out on the dual-mass flywheel. For visual checking a very bright light and additional bright small torch should be used. Damage like grease on primary flywheel and loose or missing balance weights cannot be checked in situ.For comparison, additional failure concerns are shown below.
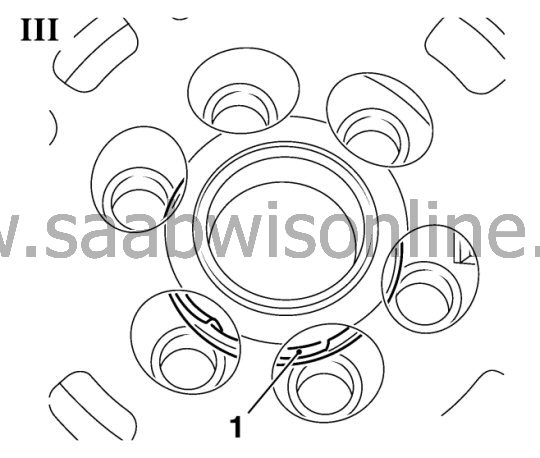
1. Inspect plain bearing for damages (picture III)
Dependent of the manufacturer damages can be detected through ventilation openings of secondary flywheel and parts of the bearing (1) may be detached or lie loose around the bearing bolt.Note: In case of mechanical damages at plain bearing the dual-mass flywheel has to be replaced.
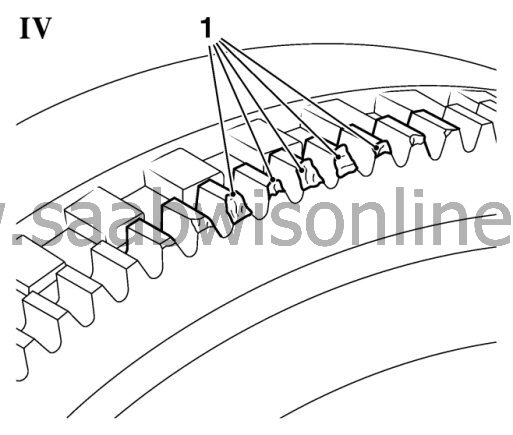
2. Inspect toothed ring for damage (picture IV)
The toothed ring can be damaged through a lot of engine starts and/or incorrect engaging of the starter. signs of abrasion can occur on teeth of the toothed ring. The profile of damages can reach from only low signs of abrasion up to heavy material removal. The installation of a crank sensor ring depends on the flywheel manufacturer.Image IV shows signs of abrasion and mechanical damages at toothed ring (1), they occur through abrasion due to a lot of starting procedures. In this case the dual-mass flywheel has to be replaced.
Note: Light abrasion on frontal areas of teeth is allowed. If problems occur during starting the engine the dual-mass flywheel has to be replaced.
3. Inspect tilt clearance
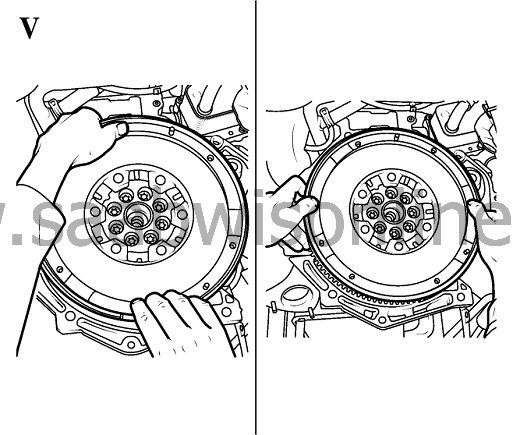
At dual-mass flywheel the additional-mass ring looms over the gap between primary and secondary flywheel. It is not possible to carry out just a visual check.- Hold dual-mass flywheel and apply thumbs onto the outer radius of secondary flywheel
- Apply pressure onto the secondary flywheel alternating on upper, lower, left and right side (picture V).
During the tilt clearance check a functional metal rattling noise may occur.
Note: The check must be carried out only by hand without any tools.
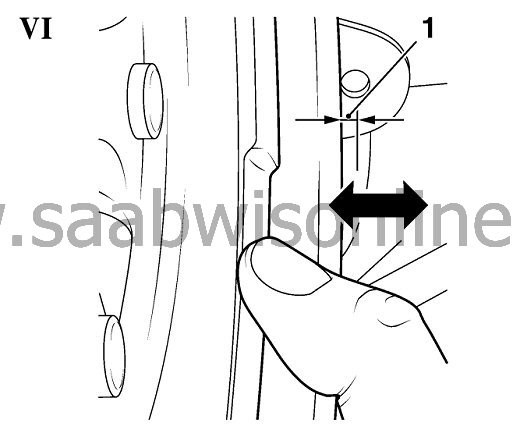
If tilt clearance is higher than 3 mm (should be measured, do not make an estimation) (1, picture VI) the dual-mass flywheel should be replaced.
Note: An absolute clear measurement is not possible with this check due to the different applied forces of different workshop staff during the check.
4. Inspect clearance angle
Before the inspection of the clearance angle the dual-mass flywheel should be rotated several times clockwise and anticlockwise to receive a feeling for the resistance of the springs. In addition unusual loud clicking noise or possible rattle, crunch, grinding noise can be sounded out during rotating the dual-mass flywheel.If the rotation of the flywheel is impossible the flywheel is defective and has to be replaced.
The clearance angle is the angle (1, picture VII) about the secondary and the primary flywheel can be turned light against each other. Thereby the flange wings (3) are moved in the duct of the bowed springs without adjoining the bowed springs (4). Dictated by functional factors the clearance angle is up to 8 teeth.
If the secondary flywheel is rotated beyond this point the bowed springs in the duct are moved to spring arrestor (2) in the primary flywheel/cover. The spring force of the bowed springs is now active.
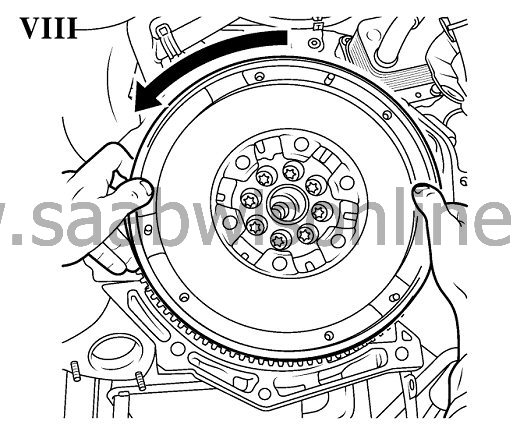
| • |
Rotate secondary flywheel anticlockwise (arrow, picture VIII)
until the elastic counterforce (spring force) is clear noticeable
|
|
| • |
Release secondary flywheel slowly until the bowed springs are
relaxed, so no counterforce acts onto the springs
|
|
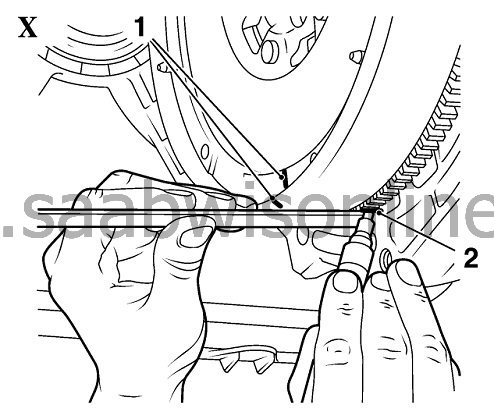
| • |
Mark position with a vertical line by a white pencil on secondary
flywheel (1, picture IX and X) and on toothed ring for starter (2, picture
X)
|
|
| • |
Rotate secondary flywheel clockwise until the elastic counterforce
is clear noticeable
|
|
| • |
Release secondary flywheel slowly until the bowed springs are
relaxed.
|
|
| • |
Apply new marking on secondary flywheel (1, picture XI) on the
height of the marking on the toothed ring for starter (3)
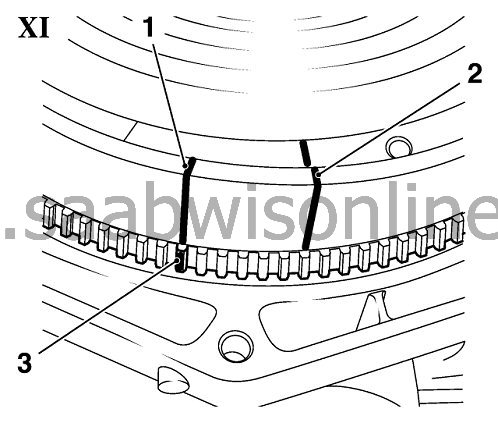
|
|
| • |
Count amount of teeth on toothed ring for starter from marked
tooth up to the first marking on secondary flywheel(2).
|
|
Dictated by functional factors up to 8 teeth are allowed.
The dual-mass flywheel has to be replaced if…
| • |
the difference exceeds the amount of 8 teeth.
|
|
| • |
the flywheel cannot be rotated.
|
|
| • |
during rotating the flywheel a hard metallic arrestor is audible
or noticeable.
|
|
C. Starter motor not turning the engine at sufficient speed at cranking speed
Check the battery voltage and electrical connections to the starter motor and if necessary substitute the motor for a known good unit before replacing the DMF.| New Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF) parts number |
New improved DMF p/n 55570197.
This applies both 9-3 and 9-5 DTH up to and incl eng num 17361103 (Previous p/n 93185496).
For cars with eng num 17361104 onwards use p/n 93196710.


