Detailed description
| Detailed description |
| ACM (Airbag Control Module) |
The control module has the capacity to activate 20 detonation circuits and contains two integrated accelerometers. The primary (1) accelerometer measures acceleration and deceleration forces longitudinally and laterally. The secondary (2) accelerometer measures longitudinal acceleration forces only.
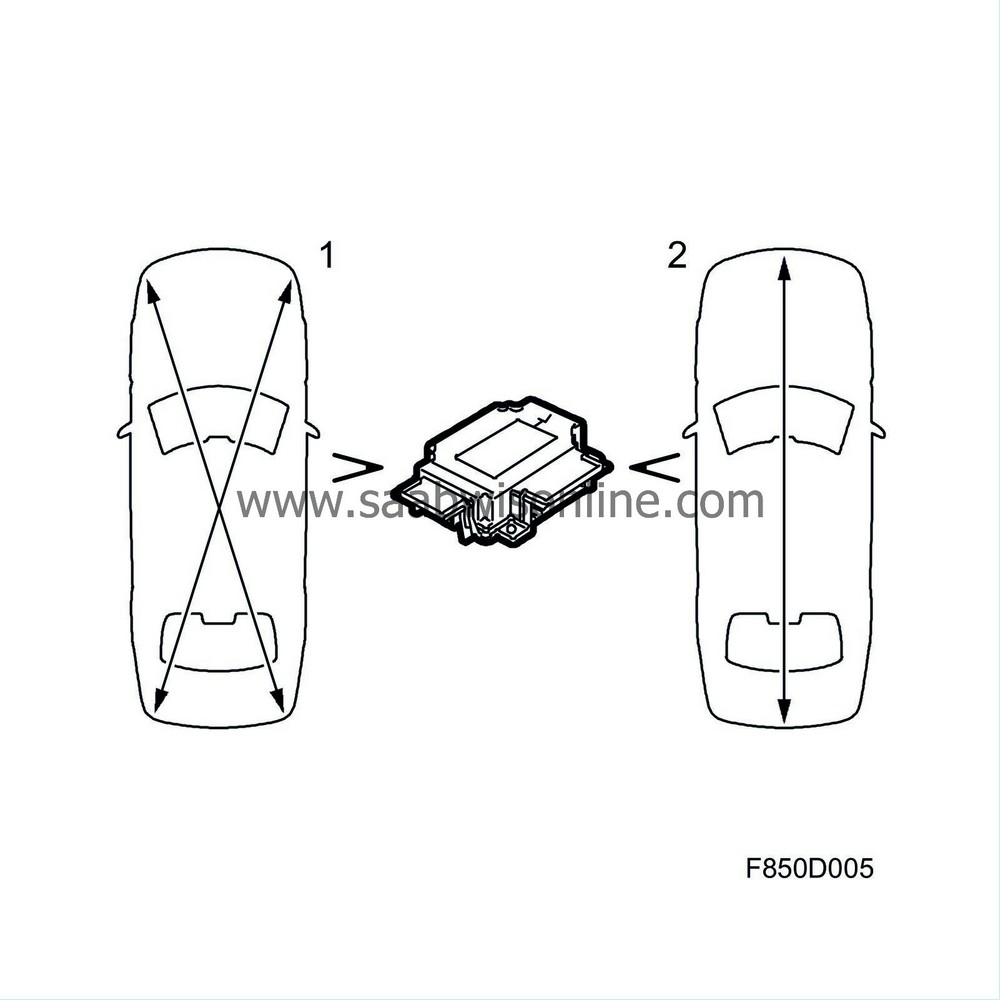
Two side impact sensors send information to the control module regarding side impact intensity and diagnostics. The side impact sensors deploy a side airbag and an inflatable curtain on the side registering an impact.
| Conditions |
The system can be activated at several levels based on the impact force, seat position and use of belts. It is activated individually for the driver and passengers, which means that different decisions can be made for action depending on the seat position and whether or not the belt is in use. The front airbags are activated in step 1 or step 2 under different impact forces depending on whether or not the belt is used. Step 1 means a low force impact and step 2 a high force impact. The front airbag is activated earlier if the seatbelt is not fastened.
Front collision:
At low force impact, the belt tensioners are used. One condition for activation of the driver and front-seat passenger belt tensioners is that the belt is in use.
If the impact force is greater, the front airbags are also activated in step 1 or step 2.
Step 1:
At this level, the battery disconnect switch is also activated and the first of the two stages of the front airbags, which means that around 80% of the maximum pressure is achieved.
Step 2:
At high impact force, the inflatable curtains and the second stage of the front airbag are activated. Activation of stage two takes place with 5 to 20 ms delay after step one, to achieve maximum protection. This means that step 1 (80% of max. pressure) and the trigger charge for step 2 are activated, which means that a further 20% of the maximum pressure is used. To activate step two, the seat must be more than 30% from its forward position. The side inflatable curtains are also activated in step 2.
In the situation where the front airbags are only activated in step 1, a safety activation of step 2 takes place after 80 ms irrespective of seat position. This disarms the airbag so there is no charge left after the impact.
Side impact:
On side impact, the side airbag and inflatable curtain are activated only on the side where the impact occurs, but all belt tensioners are activated. One condition for activation of the driver and front-seat passenger belt tensioners is that the belt is in use.
| Backup power |
The control module is equipped with a built-in backup power source which provides voltage for 150 ms after the normal power supply has been disconnected. The function has three capacitors which maintain system current and allow for front airbag deployment during the 150 ms interval. The side impact sensors are then disabled in order to save energy. During the time interval, bus communication occurs continuously.
| Driver airbag |
There is a gas generator and a nylon fabric bag on the driver side. The gas generator is bolted in a thermosetting plastic housing. The airbag is protected by a plastic casing with scores that is fitted to the plastic housing. The airbag has a volume of about 55 litres.

The airbag is of a two stage type. This means that it can be activated in two stages with different pressures depending on the force of impact and the position of the seat. The airbag consists of a thermosetting plastic housing, two electric detonators with different codings and two pyrotechnical charges with different amounts of powder for stages 1 and 2 as well as a filter.
| Driver airbag gas generator |
| 1. |
Initiator

|
|
| 2. |
Gas generator, 80%
|
|
| 3. |
Gas generator, 20%
|
|
The gas generator is split into two stages. These stages are divided into a primary stage of 80 % and a secondary stage of 20 %. Depending on the which information the control module receives from the different sensors the two stages are activated at different time delays. See control module information.
The gas generator consists of an alloy housing, an initiator (1), two electric detonators, two explosive charges and a filter.
The primary stage (2) contains a 45g charge and the secondary stage (3) contains a 9g charge. When an activation command is received, the control module sends a current pulse to the detonators which ignites the charges and produces a gas. The filter cools and purifies the gas before it is released into the bag.
| Passenger airbag |
A passenger airbag is standard equipment for all models. It is mounted in the dashboard and steering wheel member above the glove box on the passenger side and is connected to the control module. See control module information for conditions.

| Passenger airbag gas generator |
| 1. |
Projectile
|
|
| 2. |
Diaphragm
|
|
| 3. |
Gas cartridge
|
|
| 4. |
Gas generator, 80%
|
|
| 5. |
Gas generator, 20%
|
|
| 6. |
Filter
|
|
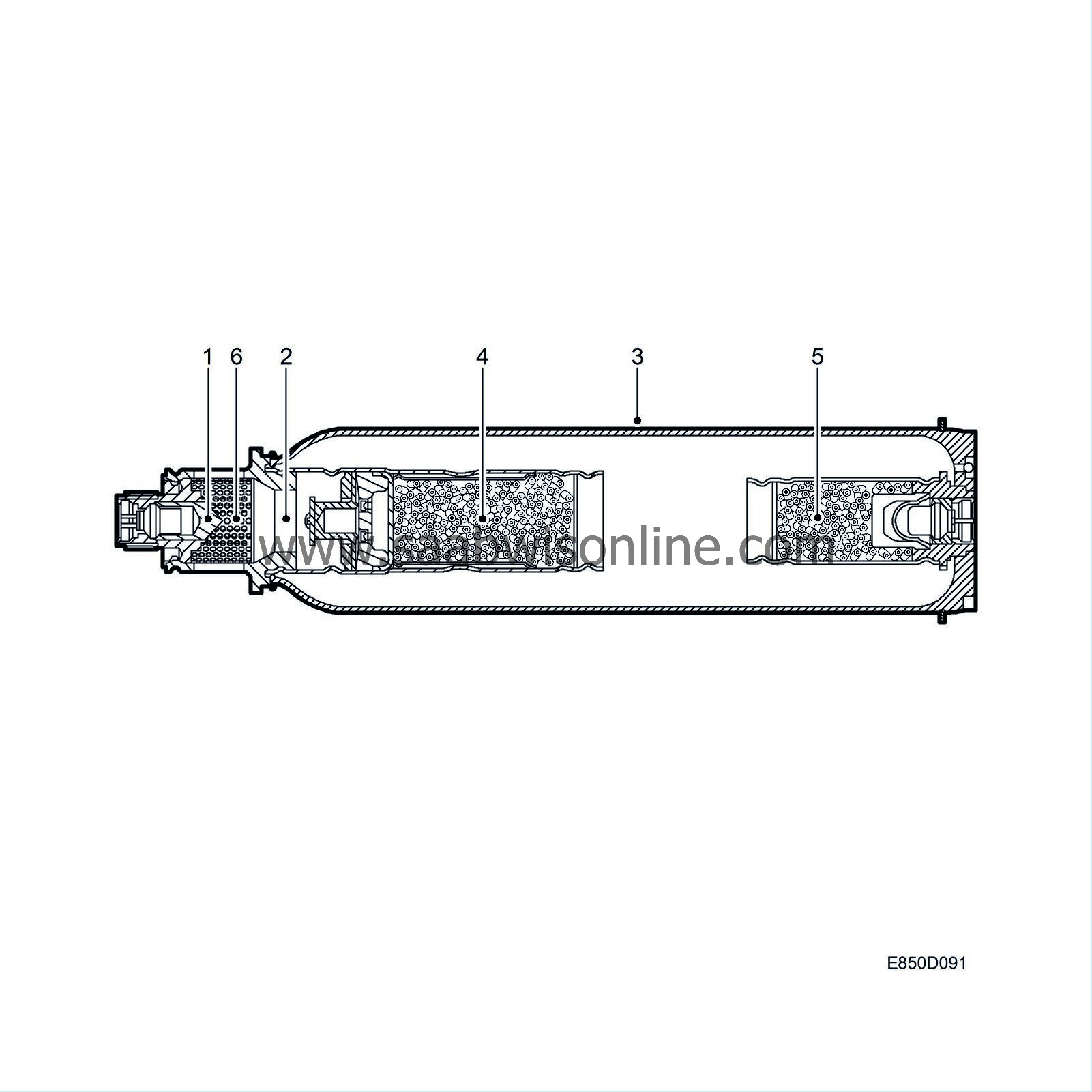
The passenger airbag contains a gas generator and airbag with a volume of 111 litres. The gas generator is attached to the airbag housing which is attached to the dashboard. A scored sheet holds the airbag in place. The dashboard contains corresponding scores.
The gas generator consists of a steel housing with two electric detonators, two explosive charges with different amounts of propellant for stages one and two, pressurised gas and a gas distribution unit.
The dual-stage gas generator includes a 80% primary stage and a 20% secondary stage. Depending on the information received by the control module from the various sensors, the two stages are ignited after different intervals. See control module information for conditions.
When a deployment command is received, the control module applies voltage to the detonators which ignites the charges. During stage 1, a projectile (1) is forced through a diaphragm (2) which opens a pressure vessel (3) containing the gas mixture. The projectile continues in a pre-determined path and ignites the stage 1 (28g) charge (4). The compressed gas expands due to the heat build-up and passes into a gas distribution unit (6) before it is released into the bag.
The gas mixture consists of
| • |
70% Argon
|
|
| • |
20% Nitrogen
|
|
| • |
10% Helium
|
|
| Front impact sensor |
The purpose of the front impact sensors includes early impact detection and providing information to the control module. The sensors send digital information containing diagnostic status messages and five levels of acceleration values to the control module via wiring. Calculations and decisions regarding detonation occur in the control module. If the front impact sensors are no longer functional, airbags are deployed after a slight delay. See control module information.
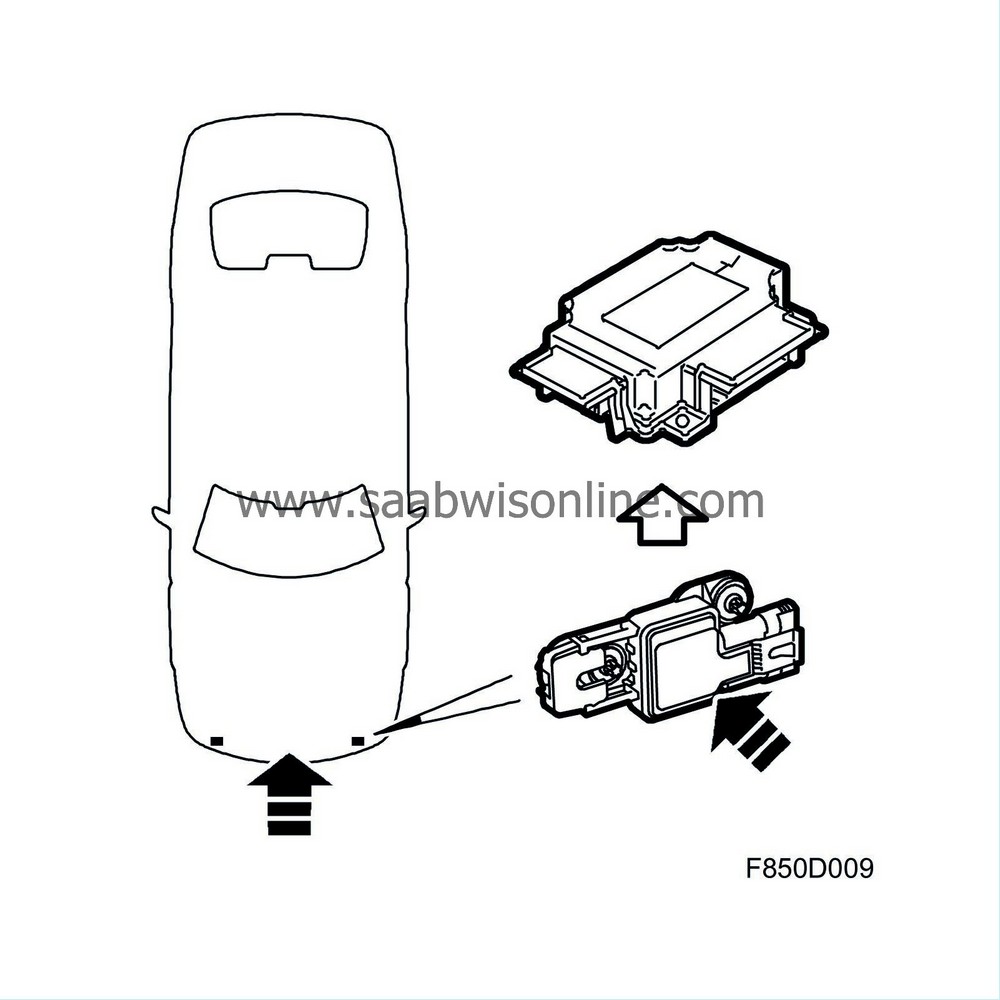
The front impact sensors communicate by modulating the continuous voltage feed from the airbag control module which means that the sensors use more or less current. Changes are registered by a microprocessor in the control module.
| 1. |
Identification message - during start-up
|
|
| 2. |
Status message for diagnostics every second
|
|
| 3. |
Acceleration values in 5 levels
|
|
| Inflatable curtain |
The inflatable curtain consists of a nylon bag with an approximate volume of 17 litres and a gas generator. During a side impact, the gas generator fills the curtain with gas. By forcing away the headlining, the curtain is positioned within approximately 20 milliseconds and provides passengers in the front and rear seats with effective safeguard against head injury and glass fragments.

The inflatable curtain is a part of the entire protection system available in the event of a side collision. The protection is supplemented by a side airbag for the driver and front seat passenger. During a side impact, the inflatable curtain is activated to provide head protection for front and rear seat passengers and a side airbag is activated for the driver and front seat passenger on the side of the impact.
The inflatable curtain is also activated in the event of a head-on collision when stage 2 is activated.
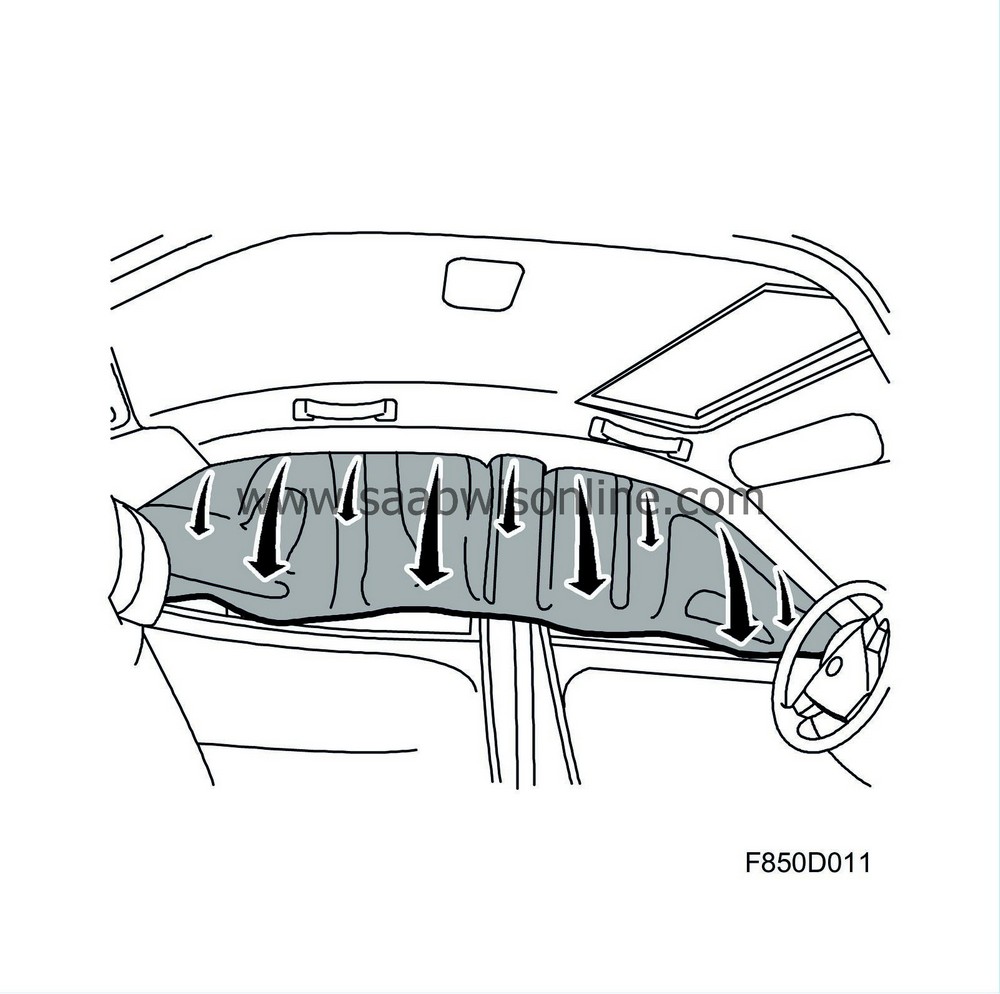
The inflatable curtain is located under the headlining along the roof member from the A-pillar to the C-pillar and is mounted in the body with four screws and three clips. Fixation clips A and B as well as the third clip are removable and should be replaced if damaged.
| Inflatable curtain gas generator |
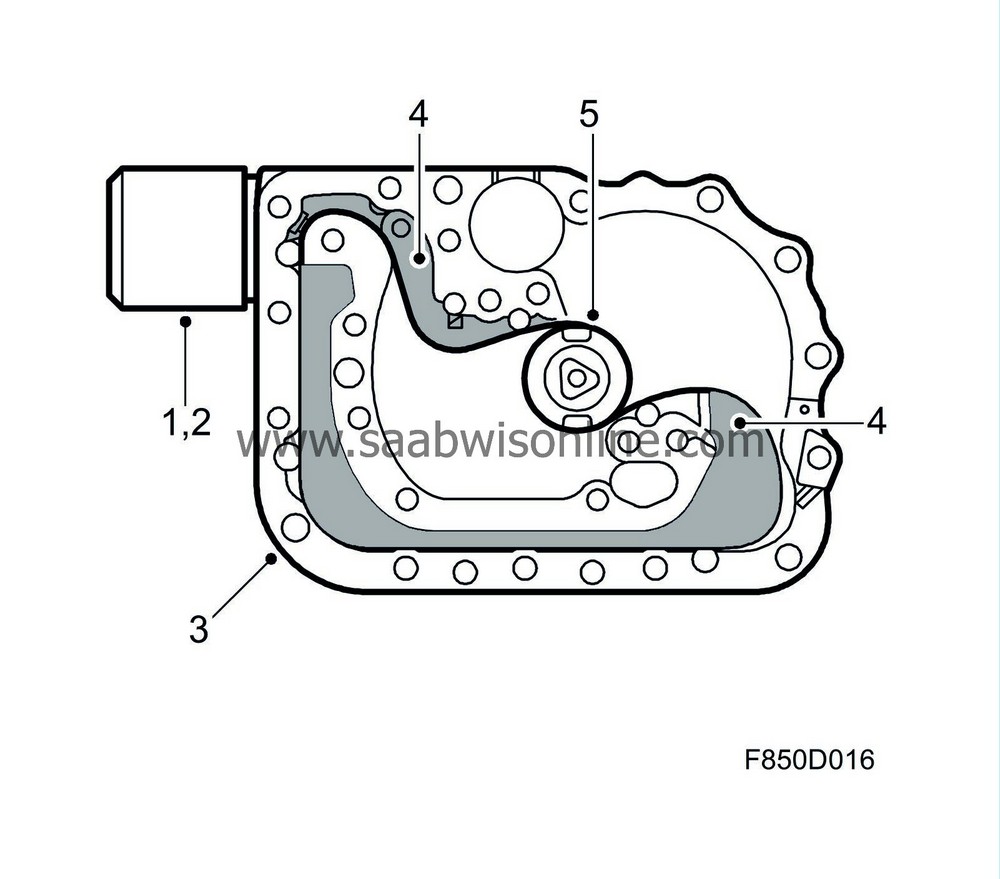
The gas generator is mounted on a metal bracket which rests on the rear courtesy handle bracket. Gas is forced into the inflatable curtain through a steel pipe during deployment.
The gas mixture in the gas generator consists of 70% argon, 20% nitrogen oxide and 10% helium. The charge contains 0.5 grams of propellant.
When the gas generator is activated, the initiator (1) receives voltage and ignites the charge. The charge causes the inner diaphragm (3) to burst and the energy starts a chemical reaction inside the chamber (2).

When the gas begins to react, the pressure inside the chamber increases, causing the outer diaphragm (4) to burst so that the gas can flow out via a gas distributor and fill the inflatable curtain.
| Side airbag |
The purpose of the side airbag is to reduce the effects of a side impact with an airbag which inflates between the passenger's upper body and the door.

This protection is supplemented with an inflatable curtain, which provides head protection for the driver, front and rear seat passengers. In the event of side impact an inflatable curtain for head protection for the driver, front and rear seat passengers as well as a side airbags for the driver or front seat passenger are activated on the side where the crash has occurred. In the side airbag there is a gas generator and a bag. The bag has a volume of approx. 9 litres. The bag and gas generator are protected by a plastic case with clips, which opens on activation.
Side airbags are available in different variants depending on market (US/CA or EU) and location of the steering wheel.
| Side airbag gas generator |
The gas generator consists of a steel housing, electric detonator, explosive charges with different amounts of propellant for stages one and two, pressurised gas and a gas distribution unit for gas cooling and pressure distribution.
When a deployment command is received, the control module sends a current pulse to the electric detonator which starts fuel combustion. When the electric detonator (1) is activated, the explosive charge is ignited (2). The charge expands and forces a projectile (3) through the diaphragm (4) to the pressure vessel (5) due to the pressure and heat build-up. The gas is mixed with the charge, which expands due to the increase in heat. The pressure forces a diaphragm (6) to burst in another part of the gas generator and the gas flows into the bag via a gas distributor.

The gas mixture is 95% argon and 5% helium.
Gas pressure: approximately 300 bar.
| 1. |
Detonator
|
|
| 2. |
Charge
|
|
| 3. |
Projectile
|
|
| 4. |
Diaphragm, inner
|
|
| 5. |
Pressure chamber
|
|
| 6. |
Outer diaphragm and gas distributor
|
|
| Side impact sensor |
The purpose of the side impact sensor includes early impact detection and providing information to the control module. The sensor contains an acceleration sensor and a communication circuit (able to store DTC) and sends digital information containing status messages for diagnostics and acceleration values in five levels to the control module via wiring. Calculations and decisions regarding detonation occur in the control module. The control module increases the level of sensitivity and measures more precisely.
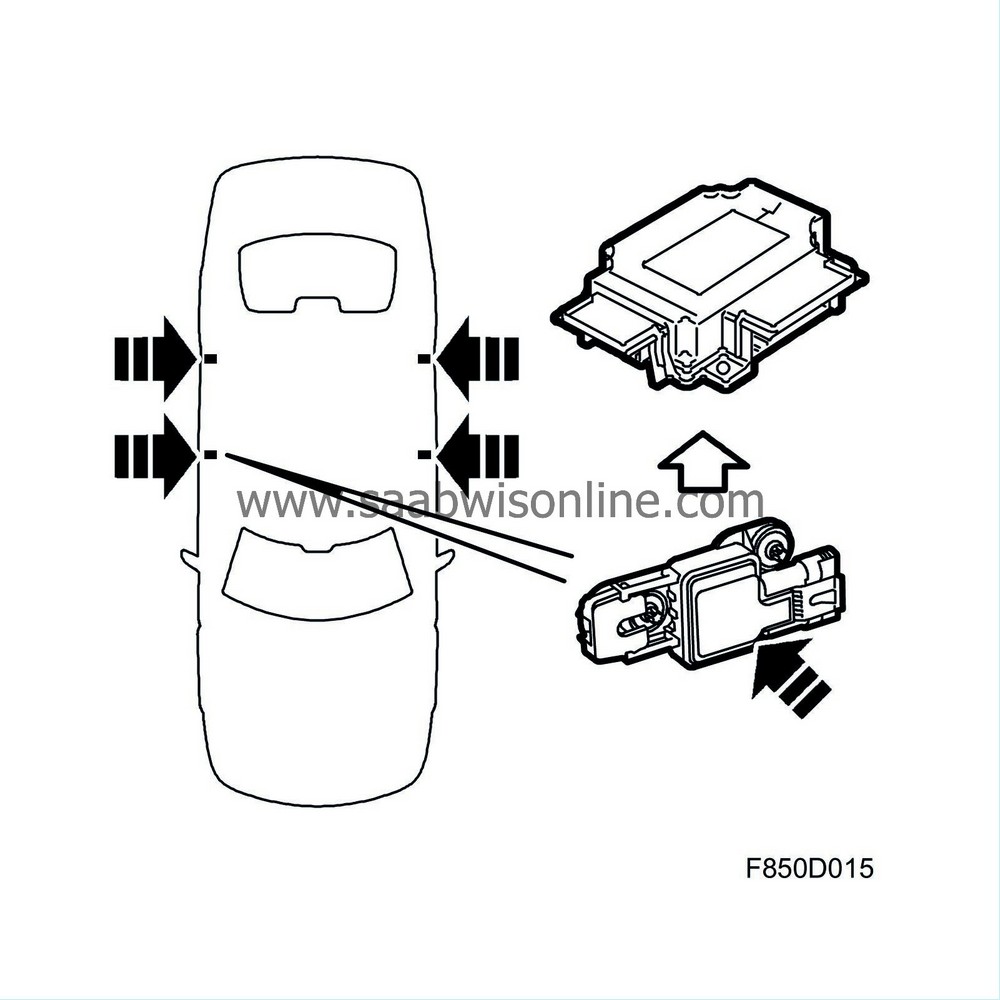
Side impact sensors are unique and have an individual colour
| • |
Light grey
|
|
| • |
Dark grey
|
|
| • |
Yellow
|
|
| • |
Brown
|
|
They possess a unique electronic identity and have specific mechanically coded connectors.
| Belt tensioners |
The car is equipped with belt tensioners for the driver and front seat passenger as well as rear seat passengers (certain markets only). The front belt tensioners are mounted in the lower section of the B-pillar and the two front door sills. The rear belt tensioners are mounted on the wheel housing with brackets under the parcel shelf for the outer passenger seats.
The belt tensioner pulls the belt taut during the event of a collision, reducing forward movement of the driver or passenger. Additionally, force limiters release the belt according to a controlled sequence.
The seat belt tensioner consists of a pyrotechnic charge that is activated by the airbag control module together with the airbags. The seat belt tensioners can also be activated separately with a minor head-on collision.
When the compact belt tensioners are activated, the airbag control module applies a B+ voltage feed. An electric detonator (1) ignites an explosive charge (2) which heats and expands in the belt tensioner housing (3).
The gas flow is distributed into two chambers (4) which push a steel band (5) which tightens the seat-belt. The belt is pulled taut and takes up the slack in the belt while restraining the passenger. The belt is taken up aided by a force-limiting torsion unit in the belt roller which restrains bodily movement as gently as possible.

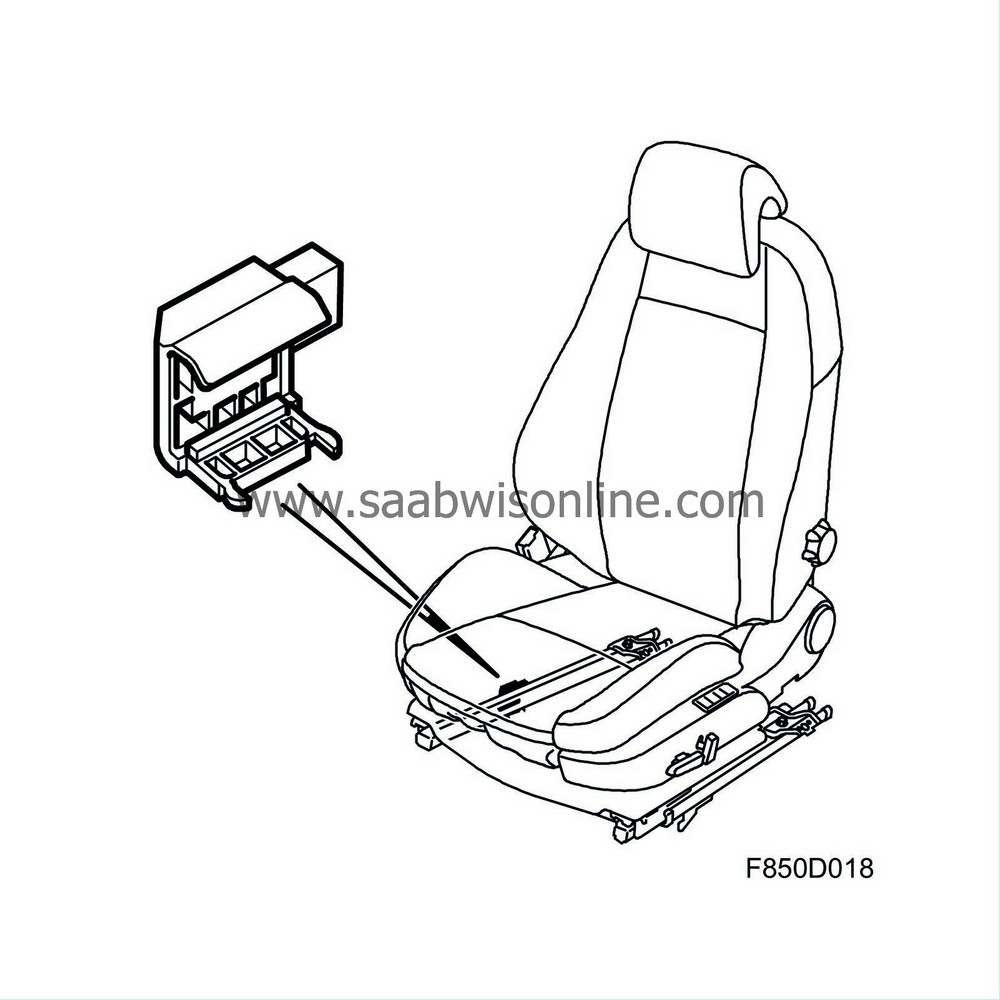
| Seat position sensor |
The seat position sensor provides information regarding a forward seat position (less than 30% from the its forward position). Furthermore, the sensor provides information regarding a rear position (more than 30% from the seat's forward position).
When the control module receives information from the seat position sensor, the control module determines how the detonation circuits should be activated. See control module information. Seat position sensors are mounted on both manual and electric seats.
Cables are used for power supply and communication between the seat position sensor and the control module. The sensor provides the control module with a constant current. The level of amperage is dependent on whether or not the sensor is affected.
| • |
Forward position, < 30% 2-5 mA
|
|
| • |
Rear position, > 30% 12-15 mA
|
|
The seat position sensor consists of a magnetic strip (2) which is mounted on the section of the seat rail fixed to the floor. A Hall sensor (1) is mounted on the moveable upper seat rail. When the seat is between the forward position and 30% towards the rear, the Hall sensor is not affected by the magnetic strip. The control module provides the Hall sensor with constant voltage and measures once every 100 ms while simultaneously measuring which current is passing through the sensor. The current through the Hall sensor is dependent on the magnetic field which affects the sensor.
| Seat-belt buckle |
The sensor detects if the seat-belt buckle is fastened or unfastened. Using information from the seat-belt buckle sensors and seat position sensors, the airbag control module determines if the belt tensioner detonation circuits should be activated. The front belt tensioners can be activated individually while the tensioners for the outer rear seat passengers are always activated simultaneously with at least one of the front belt tensioners.
The seat-belt buckle sensors consist of a Hall sensor (1) containing a circuit board and a magnet (2) which is mounted in front of the Hall sensor on the belt mechanism. The sensor detects the magnetic field generated by the fixed magnet.
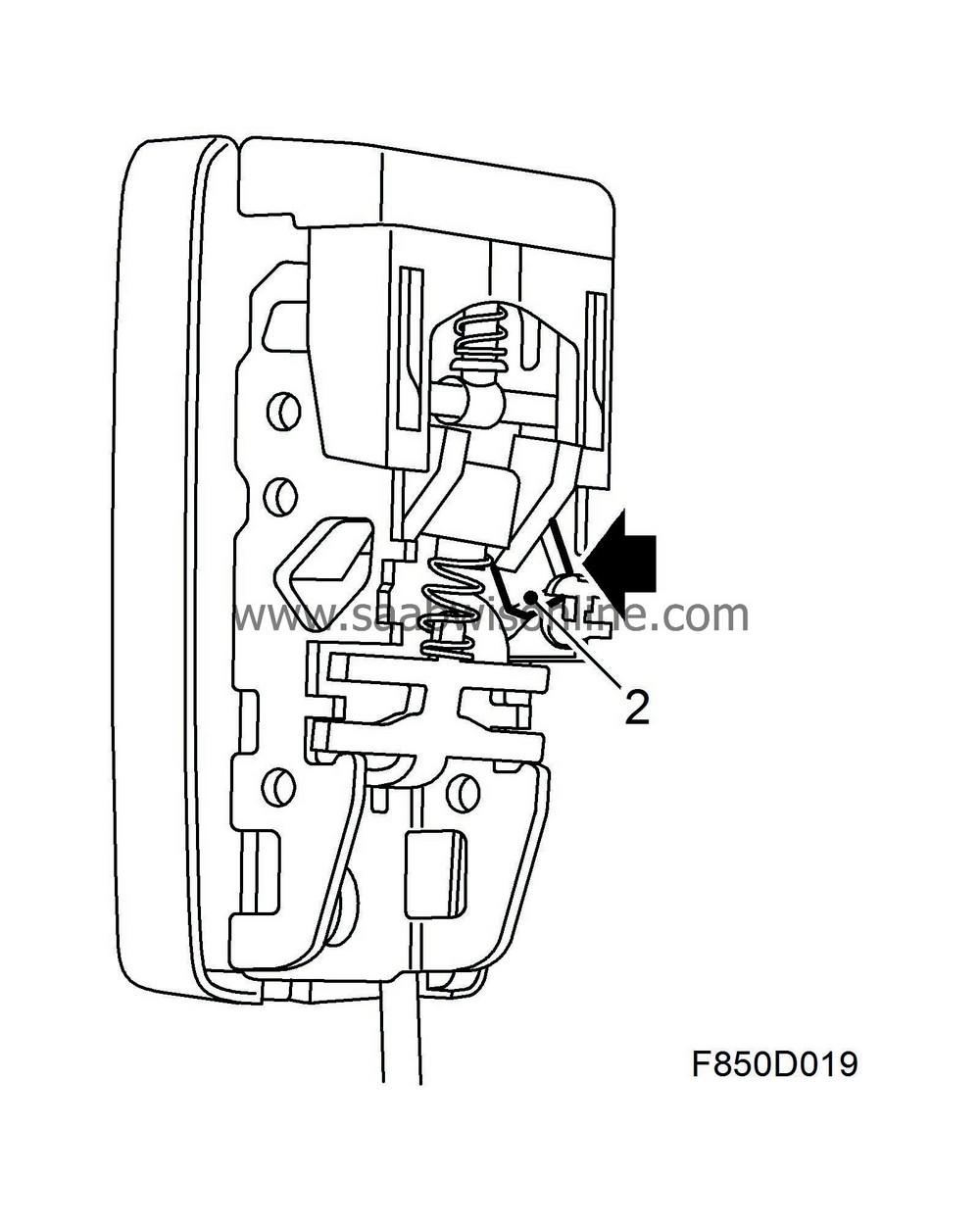
When the belt tongue (3) is not inside the buckle, the magnet (2) lies near the sensor. When the tongue is fastened, the magnet (2) is moved from the Hall sensor and the magnetic field is altered.
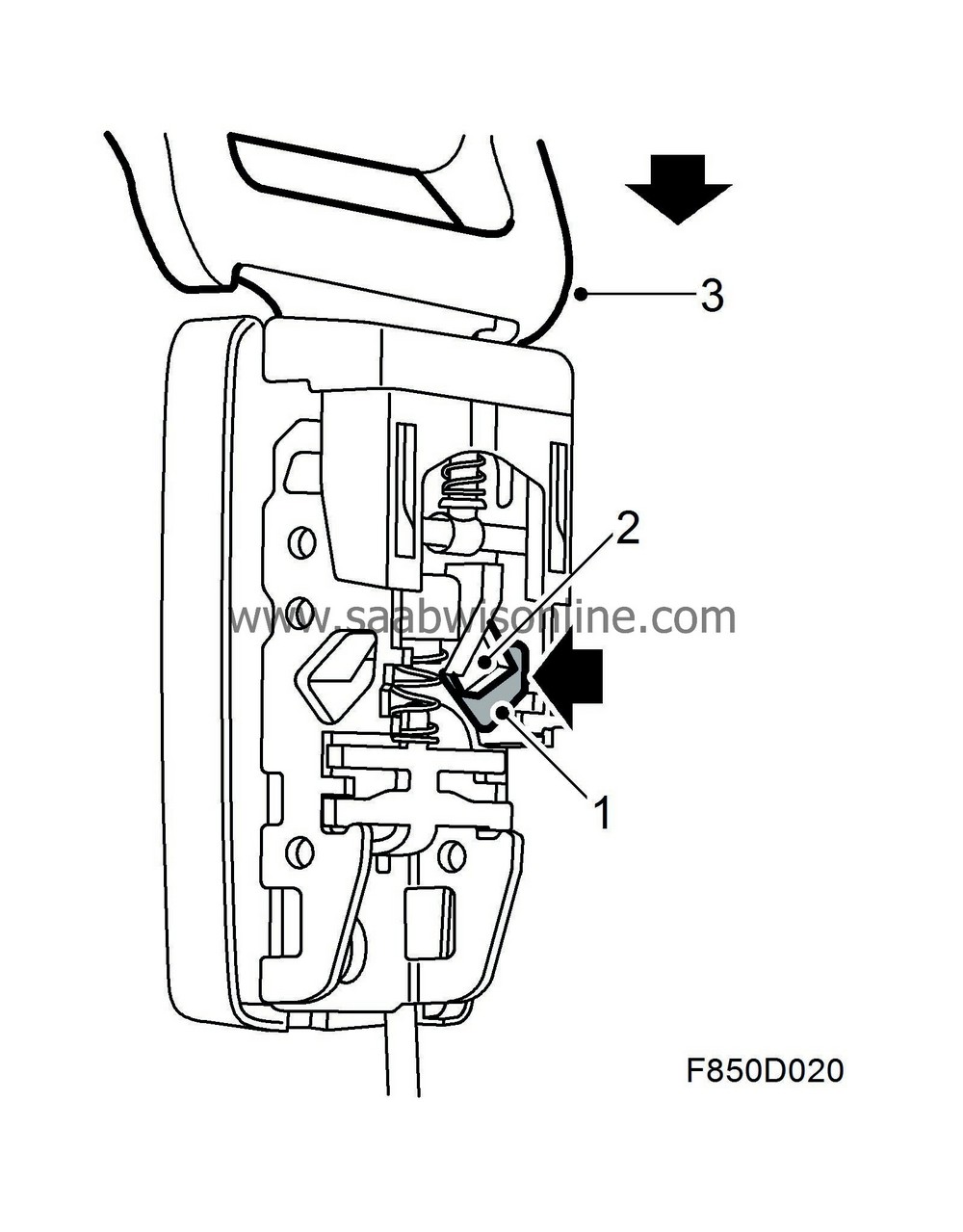
| • |
Unfastened: 4.0-7.0 mA
|
|
| • |
Fastened: 12.0-15.0 mA
|
|
The airbag control module provides voltage to the Hall sensor every 100 ms while simultaneously measuring the amount of current passing through the sensor. The current passing through the Hall sensor is dependent on the magnetic field that affects the sensor. The airbag control module sends out a bus message and the BCM uses this information in order to switch on the seat-belt warning.
| Battery disconnect switch |
The electromagnetic battery disconnect switch is mounted on the positive battery terminal. The switch acts as a part of the front collision protection and is electrically connected to the airbag control module, which monitors the battery disconnect switch.
During a head-on collision, the switch is activated through B+ voltage which closes the circuit. The battery disconnect switch cuts the voltage to components connected by the front engine harness such as the alternator, starter motor, front relay board and fuse box.
Other functions which are switched off include the A/C compressor, injectors and the fuel pump.
The battery disconnect switch interrupts the flow of current to high temperature and high current areas. Other sections of the car are still supplied with voltage in order to ensure that driver and passenger safety functions remain operational.
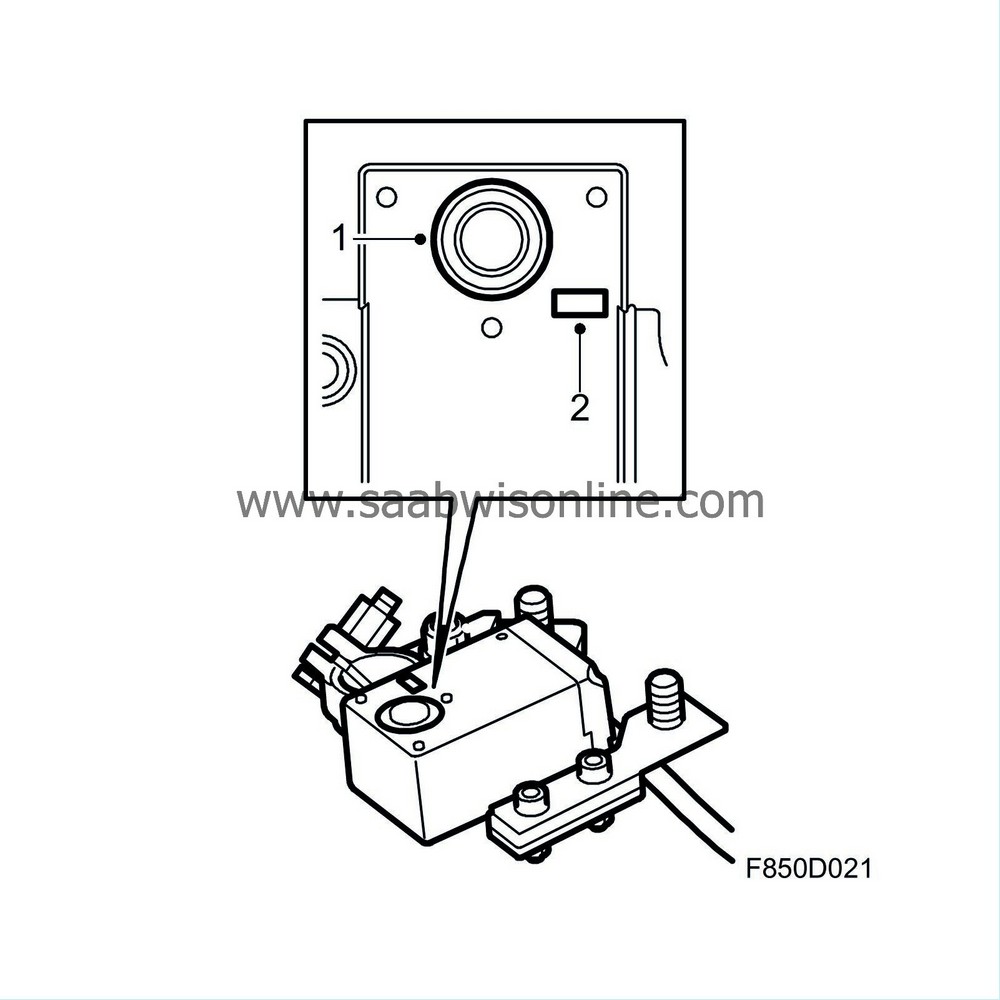
It is possible to reset the battery disconnect switch by pressing the yellow button (1). A red glow in the window (2) indicates battery disconnect switch activation status.
| Airbag warning lamp |
When the ignition switch is turned to the start or drive position, the airbag warning lamp is turned on in the MIU (Main Instrument) for 3-4 seconds and is then turned off provided that no diagnostic trouble codes are generated. For normal function, the airbag control module sends out a bus message on the I-bus: Airbag indicator - Off.

If any active diagnostic trouble codes are stored, the lamp in the MIU will light for 4 seconds and extinguish for 1/2 second; whereupon it will light again and remain lit until the ignition is switched off or the DTC is erased.
An error in the airbag system is indicated by a continuous glow of the airbag warning lamp in the main instrument panel (MIU) as well as a check message with symbol which is activated in SID (Saab Information Display).
Faults in the airbag system will result in a bus message sent from the airbag control module on the I-bus: Airbag indicator - On. If these messages occur, the MIU will display the airbag warning lamp and the SID will generate a check message.
SID displays the following airbag warning text with a symbol:
If an airbag or seat-belt tensioner has been triggered, the airbag warning lamp will remain lit continuously.
| Message |
An airbag system fault will result in a warning message and symbol displayed in SID.
| Contact roller |
In order to conduct test and detonation current to the driver airbag, a contact roller is located between the steering wheel and the steering column assembly. The contact roller is mounted and integrated in the CIM (Column Integrated Module), which means that it is not available as a separate spare part. The contact roller also conducts current for the horn, audio system, telephone and speak button.
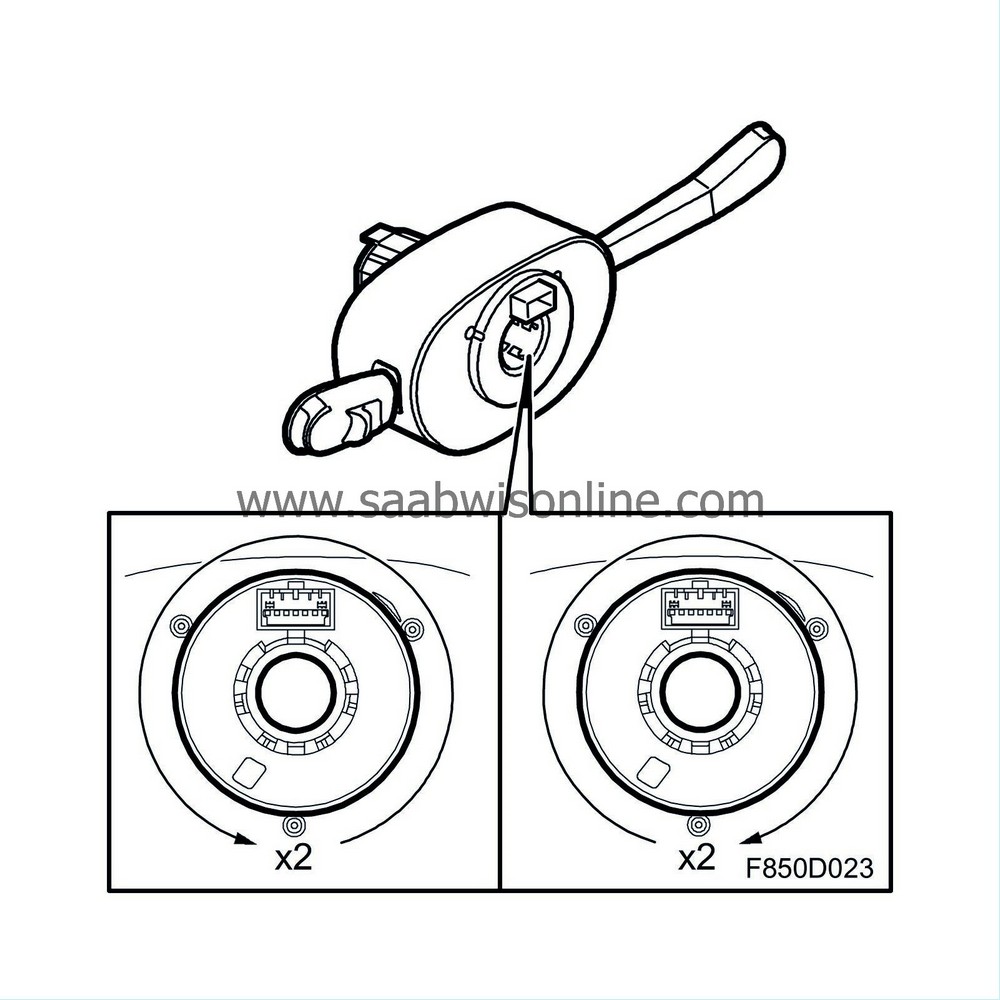
The contact roller consists of one fixed and one moving part. A spiral plastic tape with eight embedded leads is fitted between the fixed and moving part. The contact roller forms a connection between a circuit board in the CIM and the steering wheel. Four of the leads are connected to the driver airbag.
The moving part of the contact roller can be rotated approximately 4 revolutions, in other words, approximately 2 turns in either direction from the centre position. If over-rotation occurs, the spiral tape will break and the SRS system will no longer function. This break is detected by the control module and the airbag warning lamp will switch on.



