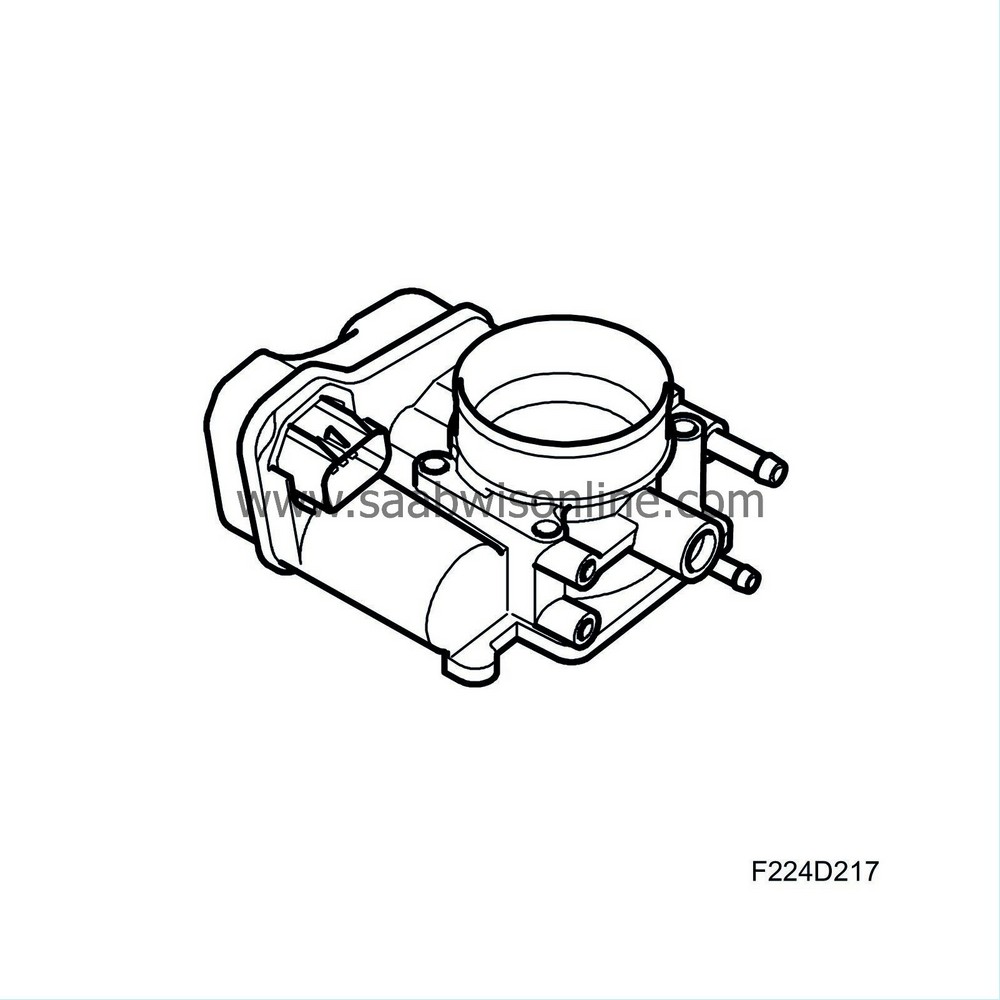
Throttle body actuator (604), Simtec
| Throttle body actuator (604), Simtec |
| Location |
Throttle body actuator (604)
| Principal use |
Air mass control requests a specific air mass/combustion. Throttle control converts this value to a requested value for throttle position sensor 1 and compares this with the actual value for the sensor. The difference generates a throttle motor PWM with a polarity that turns the throttle until the actual value matches the requested one. The control module then checks that actual air mass/combustion matches that requested. If necessary, throttle position is fine-tuned.
| Type |
| Connection |
| Pin No. | Signal type | Description |
| A | Signal | Position for P1 |
| B | Power supply +5V | Power supply for P2, +5V from ECM |
| C | Ground | Ground of P2 |
| D | Signal | Position for P2 |
| E | Control, PWM | Control of throttle motor PWM voltage from ECM |
| F | Control, PWM | Control of throttle motor PWM voltage from ECM |
| G | Power supply +5V | Power supply for P1, +5V from ECM |
| H | Ground | Ground of P1 |
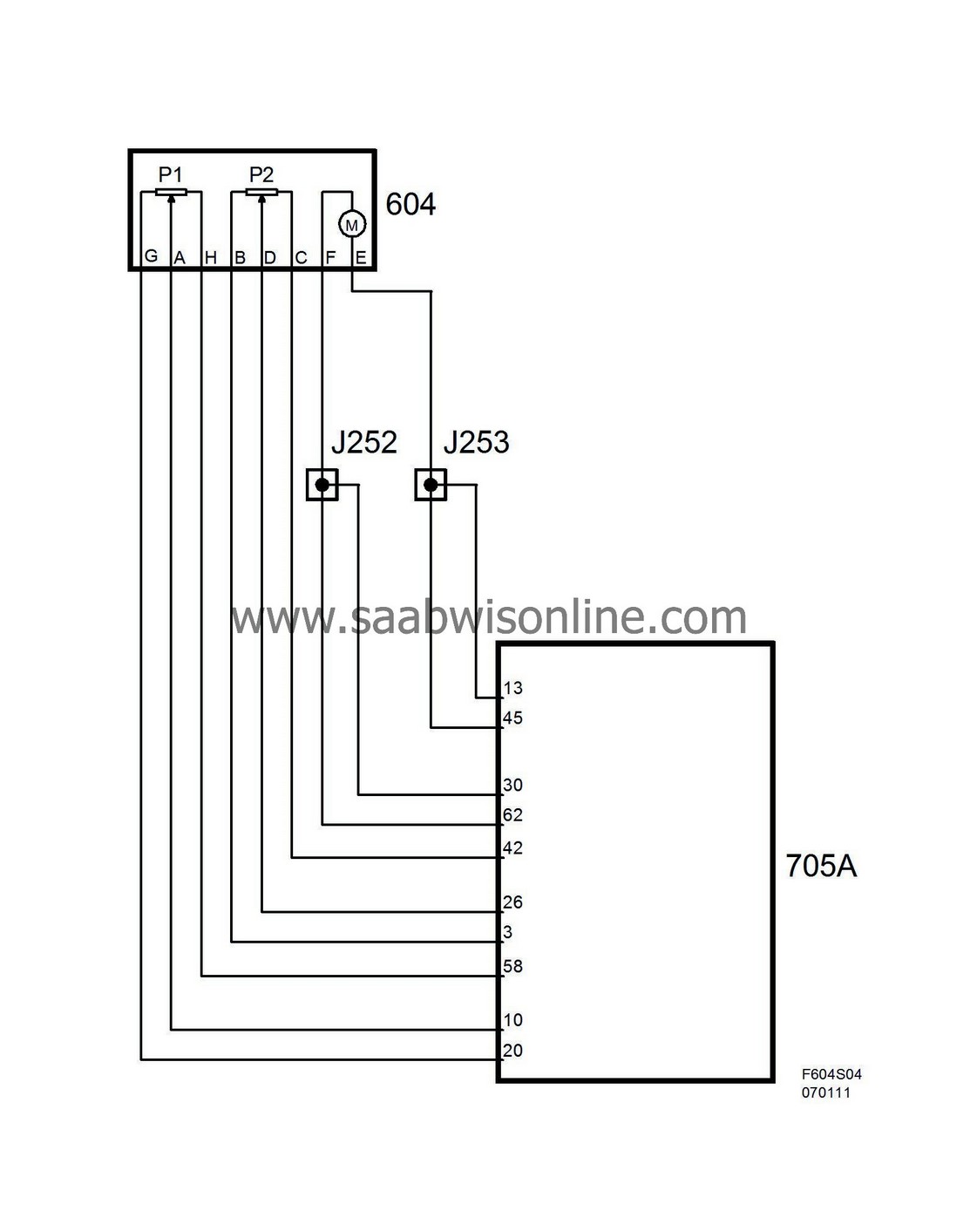
The throttle is rotated by a throttle motor with brushes that is fed PWM voltage from control module pins 13(A), 45(A), 30(A) and 62(A).
The control module can rotate the throttle in either direction by reversing the polarity of the motor. The PWM ratio increases as the throttle moves farther away from the desired value. Two throttle position sensors are connected to the throttle spindle.
The sensors consist of potentiometers that are supplied 5 V from control module pin 20(A) for sensor 1 and 3(A) for sensor 2. They are grounded from control module pins 58(A) and 42(A). Voltage from sensor 1 is connected to control module pin 10(A) and increases with the throttle position.
Voltage from sensor 2 is connected to control module pin 26(A) and decreases with the throttle position. The total of the two sensor voltages is always approx. 5 V. Voltage from sensor 1 is used by the control module as the value of the actual throttle position.
In the event of a serious fault in throttle control, it is switched off and the control module goes into limp-home mode. The throttle assumes its parked position, providing the engine a certain throttle area and thereby a certain air mass.


