Ignition, basic function
| Ignition, basic function |
| 1. |
Idling speed ignition timing
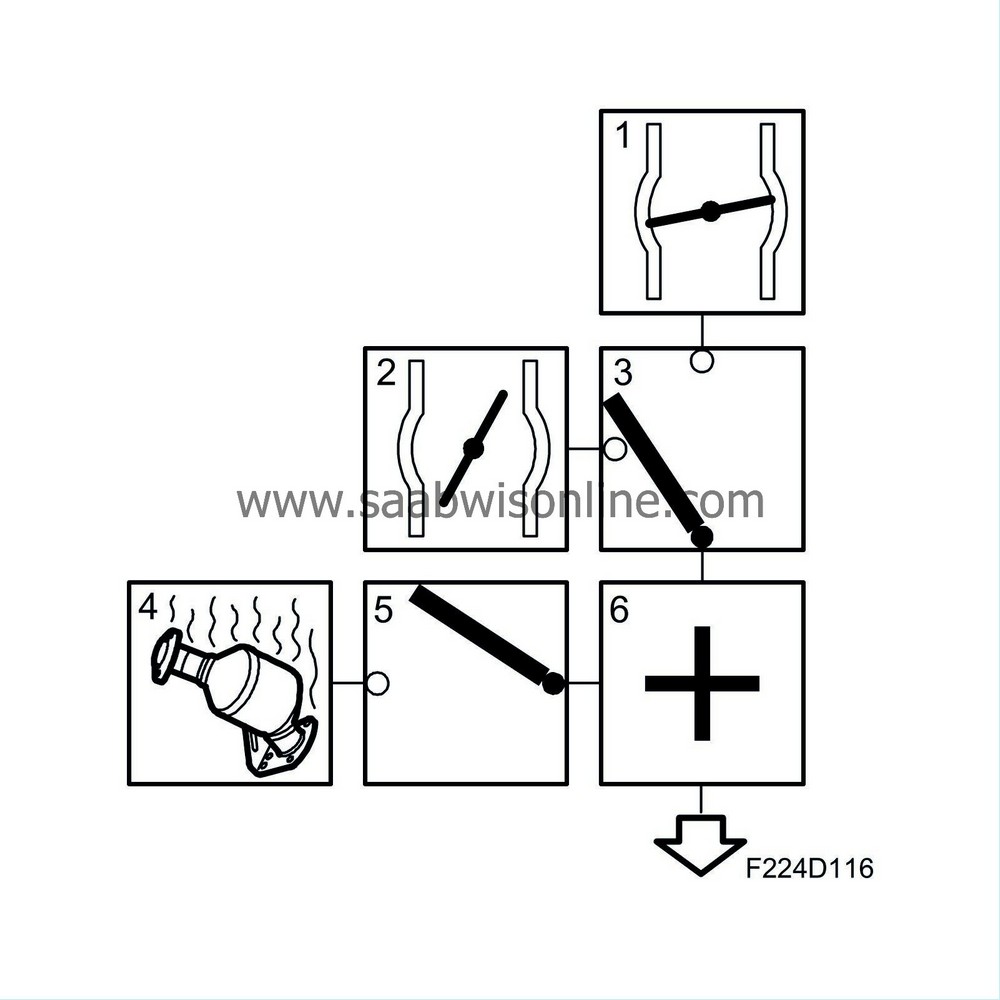
When idle speed control is active, the ignition timing is adjusted to stabilise idling speed. The value is sent to box 3. |
|
| 2. |
Normal ignition timing
When the idle speed control is not active, the ignition timing is obtained from a load and speed-dependent matrix. The matrix value is optimised for the lowest fuel consumption (best torque). The value is sent to box 3. |
|
| 3. |
Selection of ignition timing
One of the ignition timing calculations is selected, depending on which function is active. The value is sent to box 6. |
|
| 4. |
Catalytic converter heating ignition
In order to heat the catalytic converter as fast as possible after starting, the ignition will be retarded. The value is load and engine speed dependent. |
|
| 5. |
Engagement of catalytic converter heating ignition
The function is active when the coolant temperature is above -8°C and below +35°C. |
|
| 6. |
Total
The value from box 5 is added to the value from box 3. |
|
| 7. |
Compensation

The ignition timing is corrected depending on the engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature. The value is sent to box 6. |
|
| 8. |
Knock control
If knocking occurs, the amount by which the ignition should be retarded is calculated. The value is sent to box 6. |
|
| 9. |
Total
The compensation angle and knock retardation are added to the current ignition timing. The value is sent to box 7. |
|
| 10. |
Selection of ignition timing

Starting ignition timing is selected when the engine has not yet started. The value is sent to box 9. |
|
| 11. |
Starting ignition timing
Starting ignition timing is calculated depending on intake air temperature and engine coolant temperature. The value is sent to box 9 via box 7. |
|
| 12. |
Activate relevant trigger
At the calculated crankshaft angle, the microprocessor controls the transistor for the trigger which is next in the firing order. |
|


