Brief description
| Brief description |
| • |
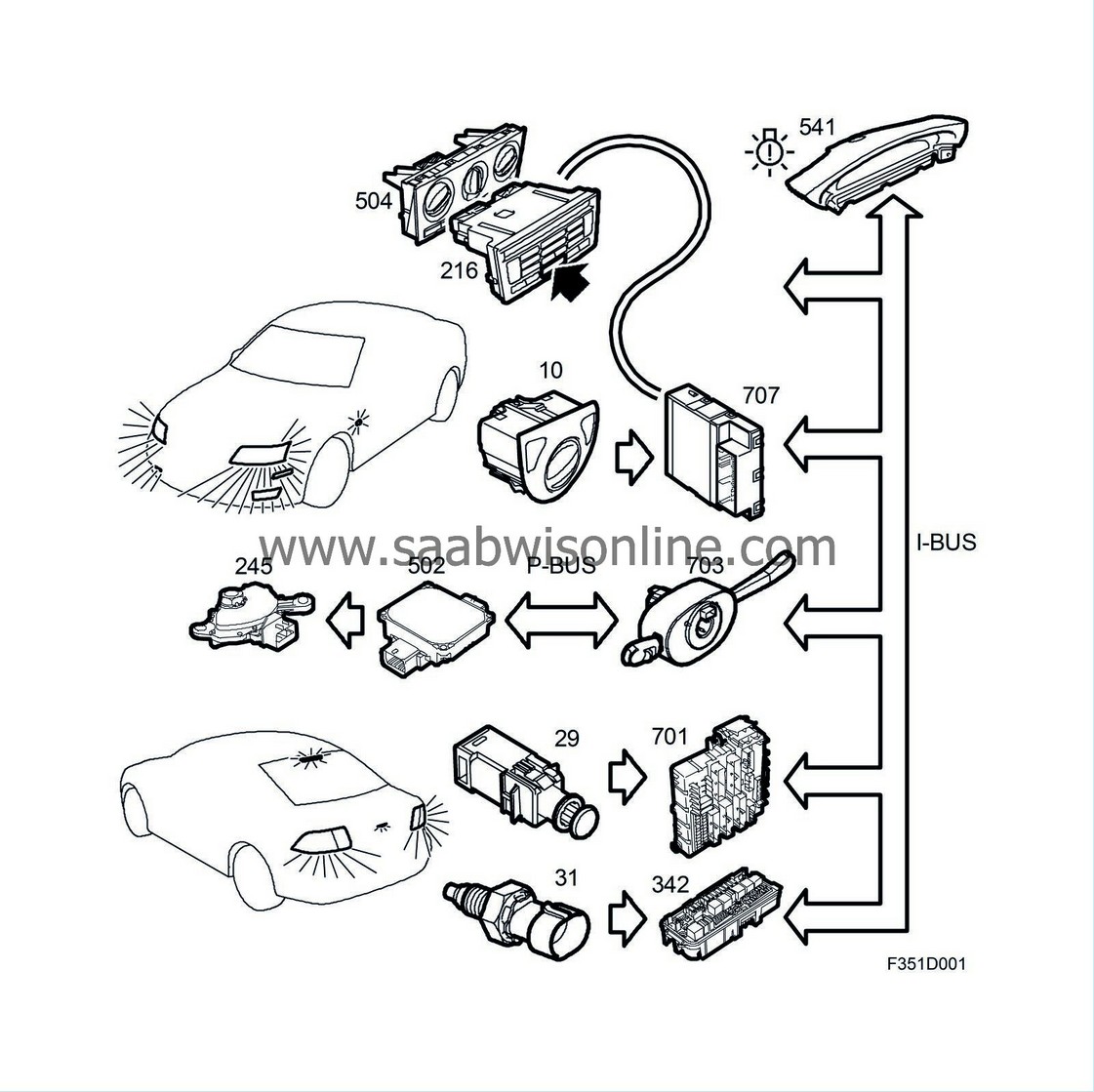
Switch, lights (10)
|
|
| • |
Switch, hazard flashers (25)
|
|
| • |
Switch, reversing lights (31)
|
|
| • |
Transmission range switch, automatic transmission (245)
|
|
| • |
Brake light switch (29)
|
|
| • |
Underhood Electrical Centre, UEC (342)
|
|
| • |
Rear Electrical Centre, REC (701)
|
|
| • |
Control module, BCM (707)
|
|
| • |
Main instrument unit, MIU (540)
|
|
| • |
SID (541)
|
|
| • |
Control module, TCM (502)
|
|
| • |
Column Integration Module, CIM (703a)
|
|
The vehicle's exterior lighting system is controlled by the light switch (in the dashboard) and lighting stalk (on steering wheel).
The exterior lighting system of the car includes the following light functions:
| Headlamps, halogen |
Main and dipped beam, tail lights, number plate lighting and parking lights are part of the main lighting. The light switch should be in position 2 and the ignition ON for the main lighting to be active. Main and dipped beam and parking lights are controlled by the fuse box in the engine bay. The dipped beam lamps are supplied with a PWM voltage.
On certain markets, the dipped beam is used as daytime running lights. The light switch must then be in position 0.
| Xenon headlamps |
Main and dipped beam, tail lights, number plate lighting and parking lights are part of the main lighting. For the headlamps to be active, the light switch must be in position 2 and the ignition must be switched ON. Main/dipped beam and parking lights are controlled by the underhood electrical centre. With dipped beam, the Xenon lamps and parking lights shine. With main beam, the H7 halogen lamp also shines. Once switched on, the Xenon lamp always shines at the same power. For main beam, the shutter is completely down. For dipped beam, the Xenon lamp is partially screened. The halogen lamp and Xenon lamp shine together for main beam.
On certain markets, the dipped beam is used as daytime running lights. The light switch must then be in position 0.
| Xenon headlamps (US/CA) |
Main and dipped beam, tail lights, number plate lighting and parking lights are part of the main lighting. For the headlamps to be active, the light switch must be in position 2 and the ignition must be switched ON. Main/dipped beam and parking lights are controlled by the underhood electrical centre. With dipped beam, the Xenon lamps and parking lights shine. For main beam, an H7 halogen bulb also shines.
On certain markets, the dipped beam is used as daytime running lights. The light switch must then be in position 0.
| Parking lights |
The vehicle parking lights consist of front and rear parking lights.
The parking lights can be on together with the headlamps or on their own. The parking lights come on when the light switch is turned to position 1 if the ignition is off. The parking lights are on in other light switch positions depending on the programming alternative selected. On certain markets, dipped beam is used for daytime running lights. Side marker lights are also turned on together with the parking lights.
The lamps of the rear parking lights are supplied PWM voltage.
| Brake lights |
Come on when the brake pedal is pressed. The rear electrical centre monitors the circuits to the brake lights and sends error messages to the bus.
The vehicle has a brake light in the right and left lighting clusters and a high-level brake light in the top of the rear screen. The high-level brake light is of the LED type. The brake light bulbs in the light clusters are of the filament type and combined with the parking lights. The brake light bulbs in the light clusters are supplied with a PWM voltage.
If a filament breaks in the lamp which normally serves as a brake light, the function is replaced by the parking light bulb next to it.
| Reversing lights |
The reversing light is placed in the light cluster. The electrical unit in the boot receives a bus message on the current gear and lights the reversing light when reverse gear is selected.
| Front fog lights |
Two lamps are placed in the spoiler. They are activated by a switch when the light switch is in position 1 or 2 (depending on market). The function is programmable.
The fog light switch is connected to BCM. BCM detects the position of the switch and sends a bus message "Front fog lights, button active ON/OFF", which is used by the main fuse box in the engine bay to control the fog lamps. The lamps are supplied with a PWM voltage.
| Rear fog light |
There is a lamp on the left-hand side on cars intended for right-hand traffic and on the right-hand side on cars intended for left-hand traffic. The lamp is located in the light cluster housed in the boot lid.
The fog light switch is connected to BCM. BCM detects the position of the switch and sends a bus message "Rear fog light, button active ON/OFF". This bus message is used by the main fuse box in the luggage compartment to control the rear fog light.
| Direction indicators |
The direction indicator bulbs are placed in the front headlamps, front wings and rear light clusters.
On activation, CIM sends a message to the engine bay and boot electrical unit which control the front and rear direction indicators respectively.
The flash frequency is 90 flashes per minute. If a filament breaks, the flash frequency is increased to 180 flashes per minute.
| Hazard flashers |
The warning function when all direction indicators flash is activated by the hazard flasher switch. The switch is placed in the ACC unit panel (cars with ACC) or the control panel for heating and ventilation (cars without ACC).
| Side marker light (US) |
The side marker lights are placed in the left and right corners of the front bumper. The lamps come on at the same time as the parking light.