Brief description of Z19
| Brief description of Z19 |
There are two variants of basic engine:
Z19DT OHC, 88 kW / 280 Nm
Z19DTH DOHC, 110 kW / 315 Nm
The engine is a transversely mounted, water cooled, 4-cylinder in-line engine with 2 valves (Z19DT) or 4 valves (Z19DTH) per cylinder, 1 overhead camshaft (Z19DT) or 2 overhead camshafts (Z19DTH). The engine has direct fuel injection, which means fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber. It is also cross-flow type, i.e. the inlet ports on one side of the combustion chamber and the outlet ports on the other. The total swept volume is 1910 cm3.

Cylinder block, crankshaft pistons
The cylinder block is manufactured in special cast iron. The same block is used on both the Z19DT OHC and Z19DTH DOHC. The cylinder barrels are bored directly in the block. The crankshaft has five bearings, with the thrust bearing being located on the third main bearing. The pistons are manufactured in light alloy and have depressions for combustion chambers and floating gudgeon pins in piston and connecting rod. To reduce piston temperature, the pistons are oil-cooled from a jet of oil directed at the bottom of the piston crown.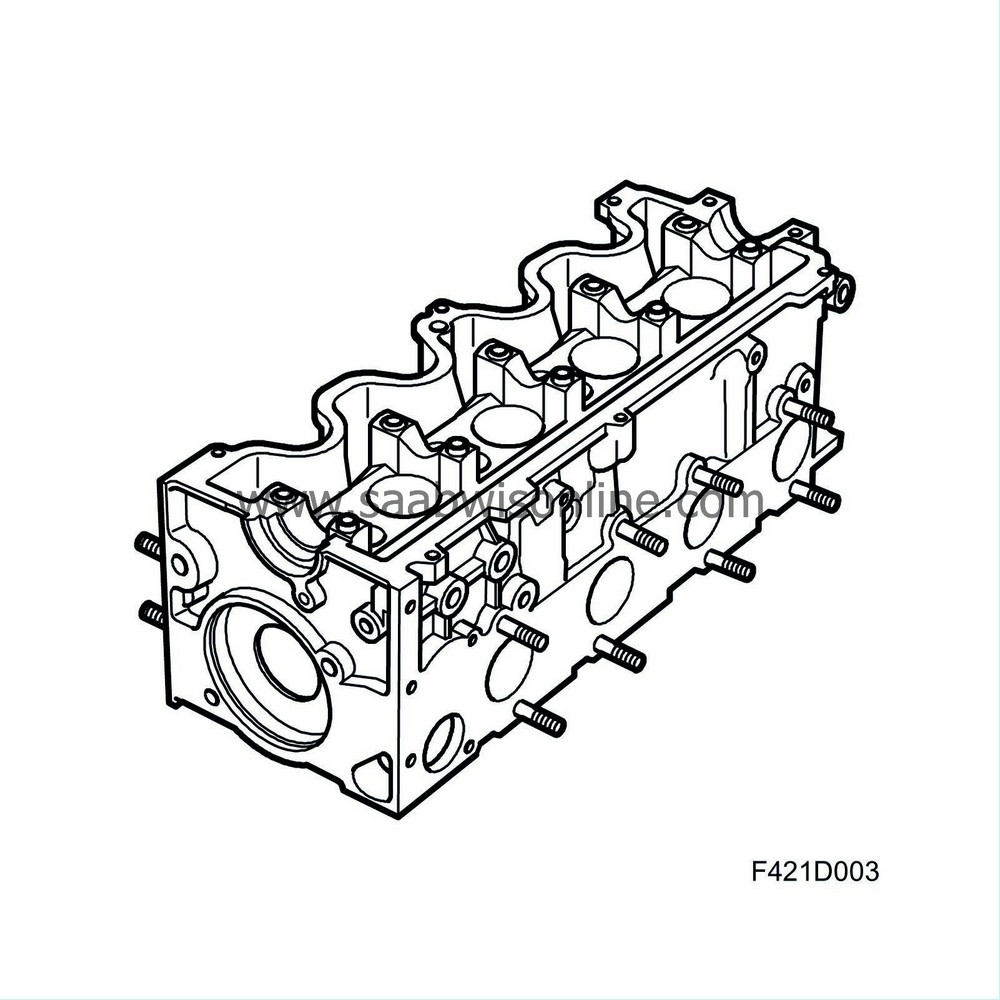
Cylinder head 8 V, OHC (Z19DT)
The cylinder head is made of aluminium and has two valves per cylinder. A camshaft is mounted with separate bearing shells. The camshaft acts on the valves via fixed valve tappets. In order to adjust the valve clearance, the valve tappets are fitted with adjusting washers. The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft via a drive belt. The supply of lubricating oil to the camshaft bearings takes place through a separate steel pipe. The shape of the inlets is designed to give a considerable rotation of the intake air.Mounted in the cylinder head are four injector valves and four glow plugs.
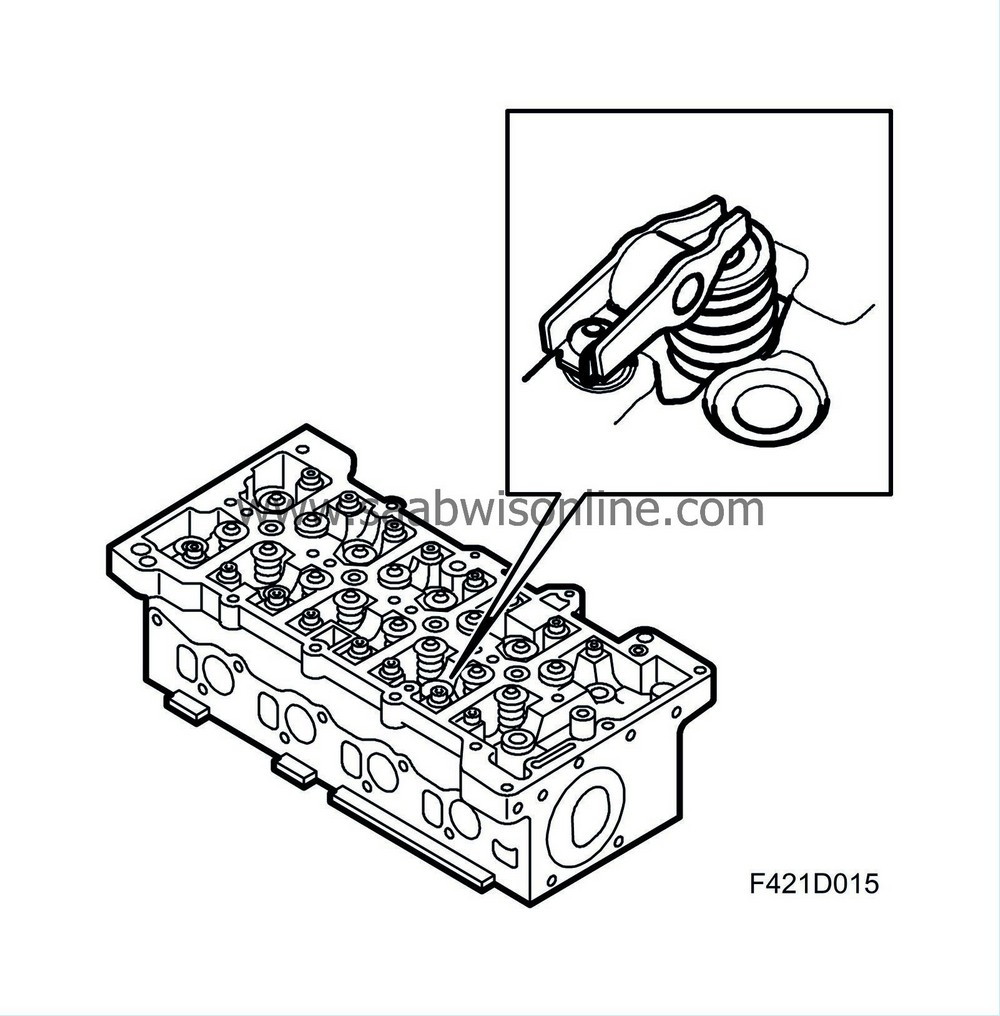
Cylinder head 16V DOHC (Z19DTH)
The cylinder head is manufactured in aluminium and has four valves per cylinder. Two camshafts are mounted in the camshaft housing where the bearings are fitted. The bearings are of different dimensions so that the camshaft can be extracted through one end of the camshaft housing. The camshafts act on roller bearing rocker arms that are pivoted at one end. A ball cup constitutes the upper part of the hydraulic valve clearance balancers and pressed on the valve stem on the other end of the rocker arm. The hydraulic valve clearance balancers keep the play between camshaft and rocker arm/roller bearing close to zero. The exhaust camshaft is driven by the crankshaft via a drive belt and has a gear pinion that transfers power to the intake camshaft gear pinion.Mounted in the cylinder head are four injector valves and four glow plugs.


