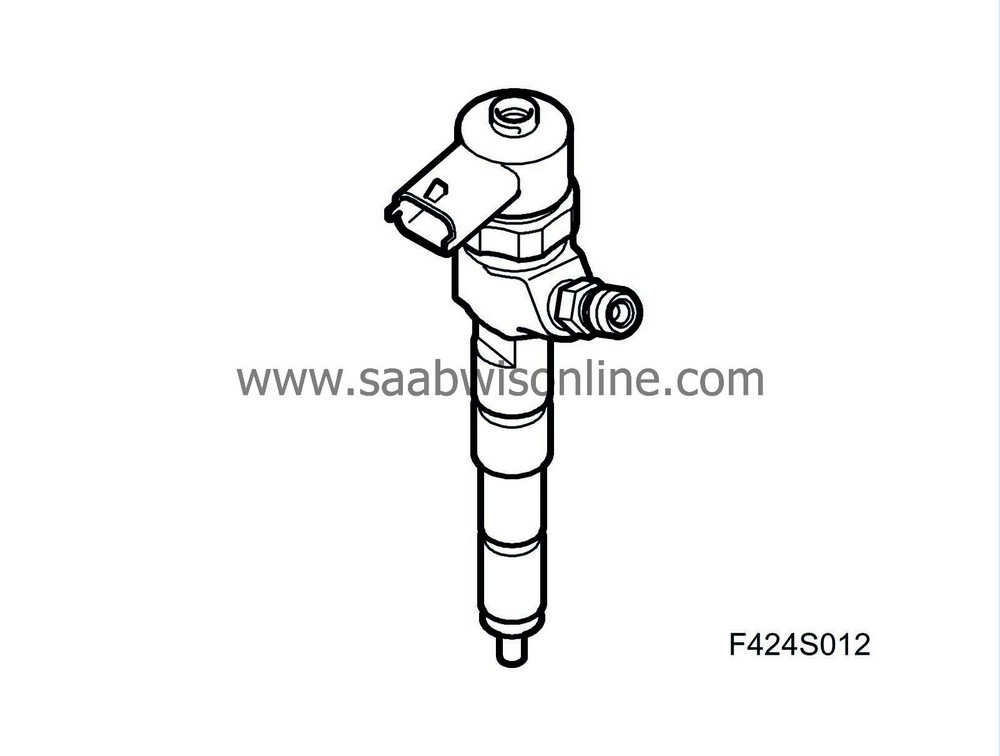
Injector (206) EDC16
| Injector (206) EDC16 |
| Location |
Injector, cyl 1 (206a)
Injector, cyl. 2 (206b)
Injector, cyl. 3 (206c)
Injector, cyl. 4 (206d)
| Main task |
Adds fuel to the air that flows into the cylinders. Distributes the fuel in the combustion chamber.
| Type |
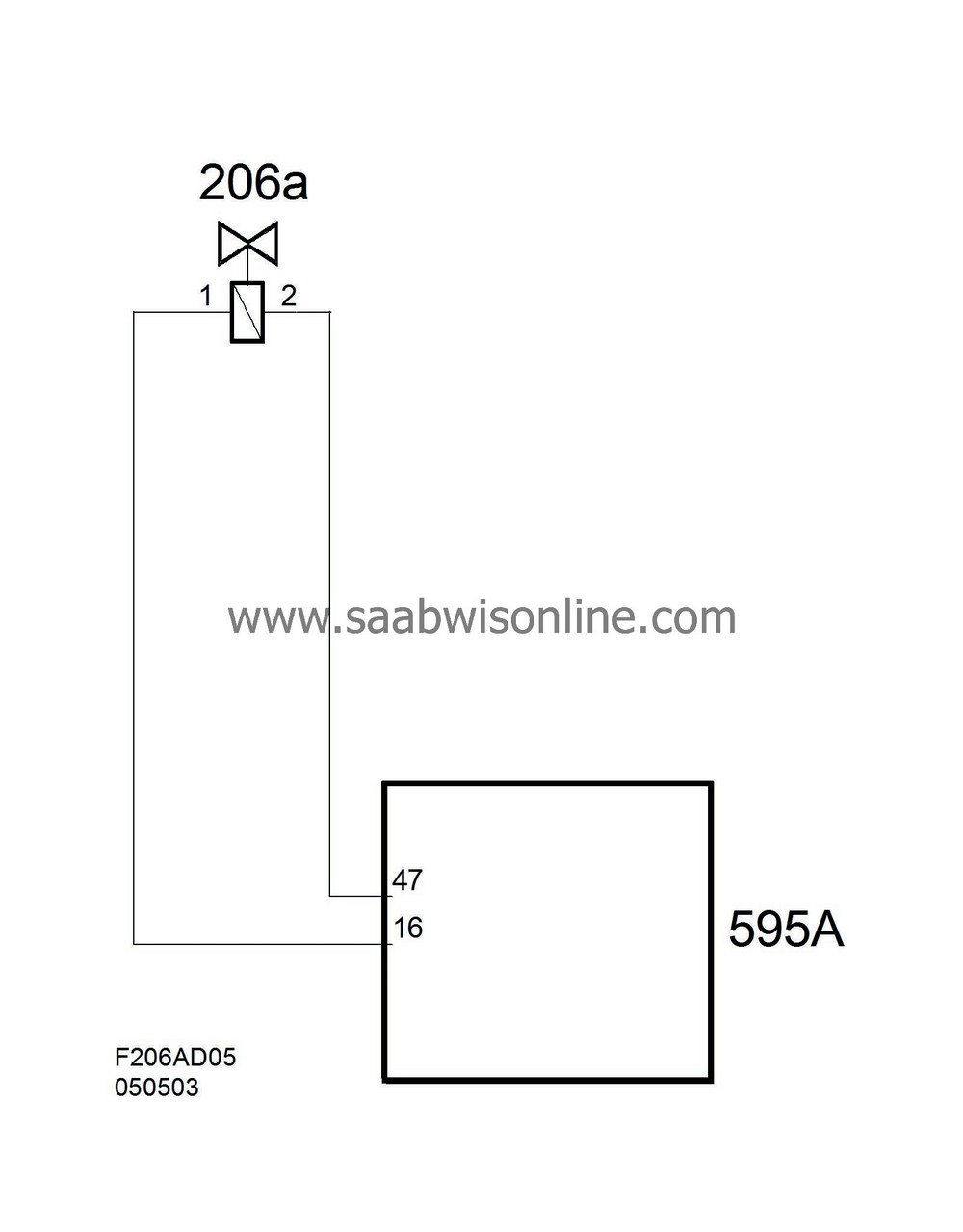
| Connection, cylinder 1 |
| Pin No. | Signal type | Description |
| 1 | Connected to ECM pin 16(A). | |
| 2 | Connected to ECM pin 47(A). |
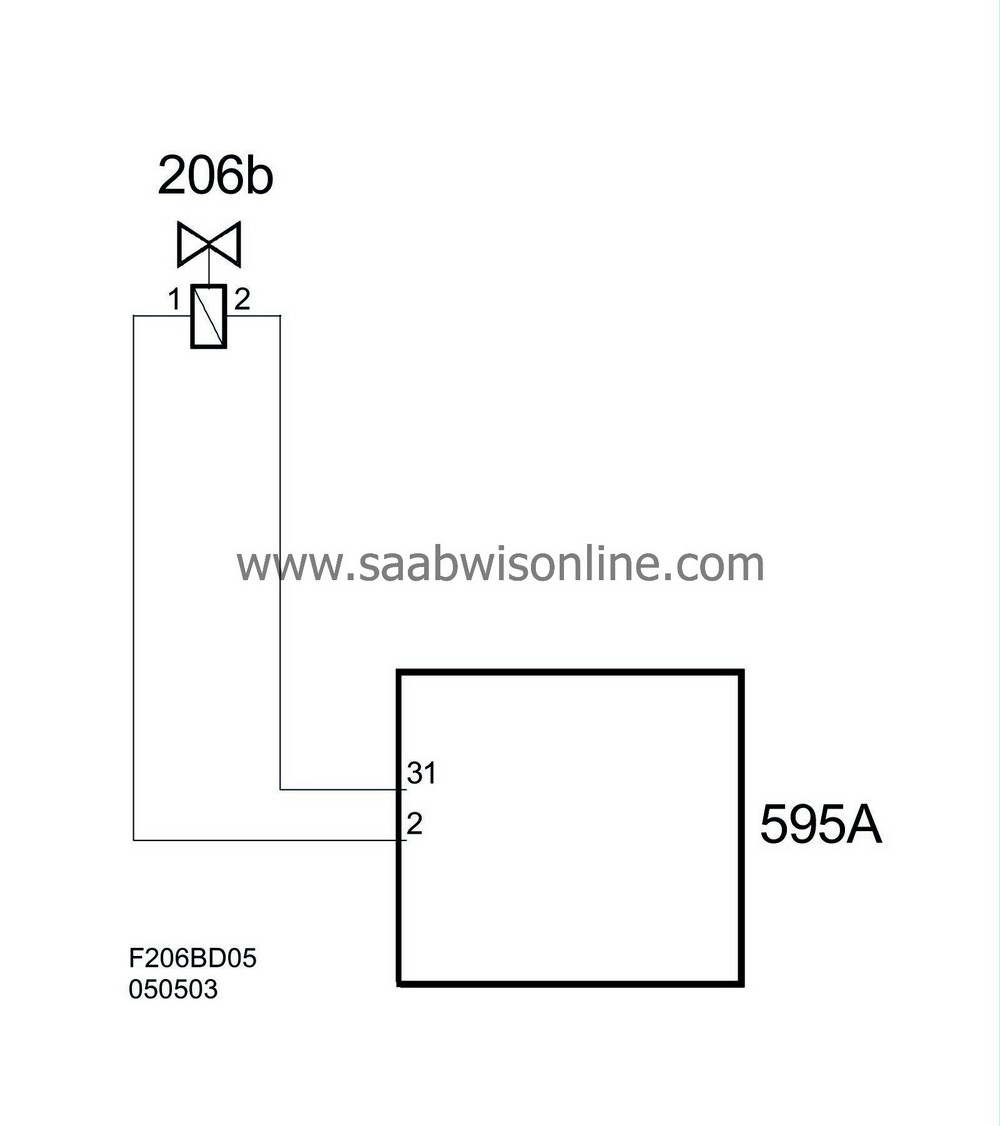
| Connection, cylinder 2 |
| Pin No. | Signal type | Description |
| 1 | Connected to ECM pin 2(A). | |
| 2 | Connected to ECM pin 31(A). |
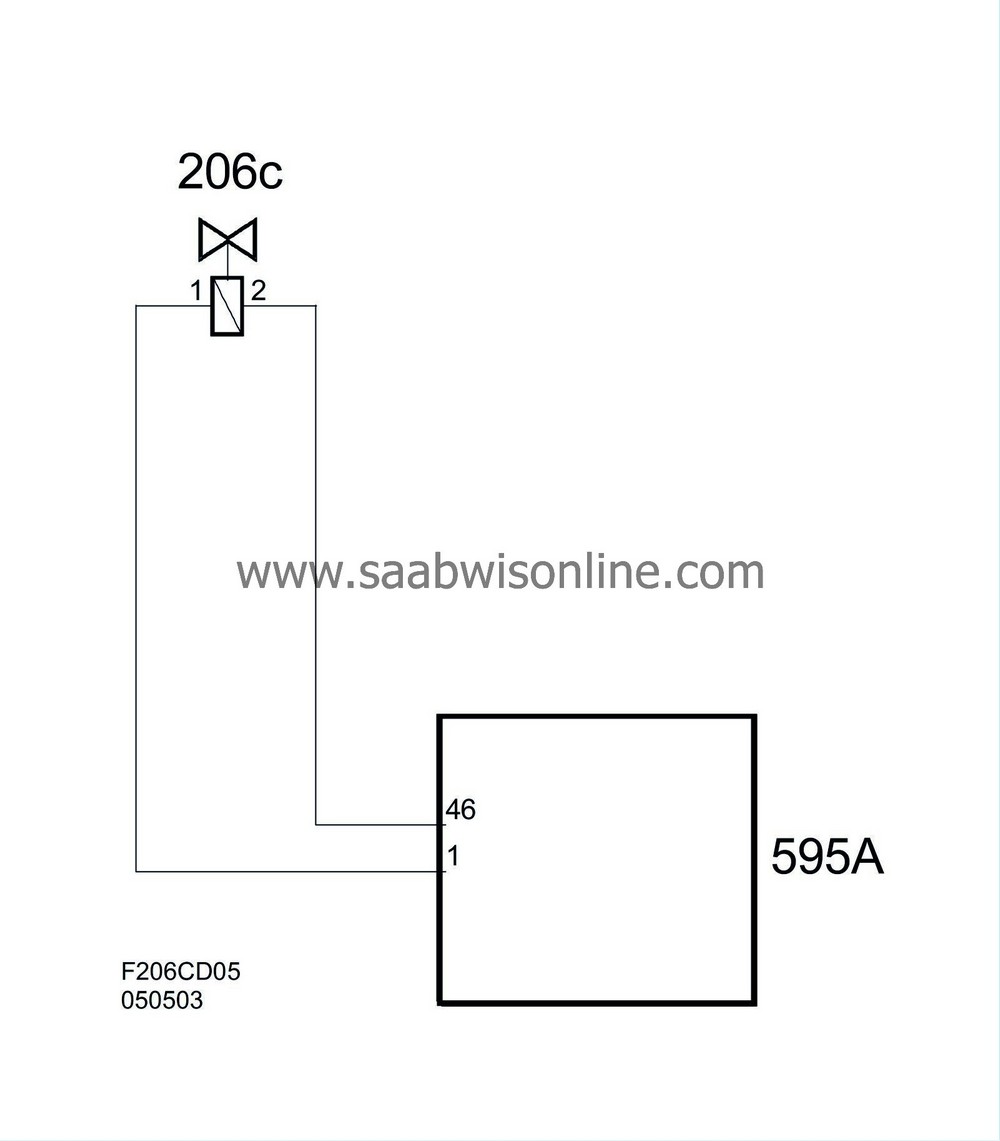
| Connection, cylinder 3 |
| Pin No. | Signal type | Description |
| 1 | Connected to ECM pin 1(A). | |
| 2 | Connected to ECM pin 46(A). |
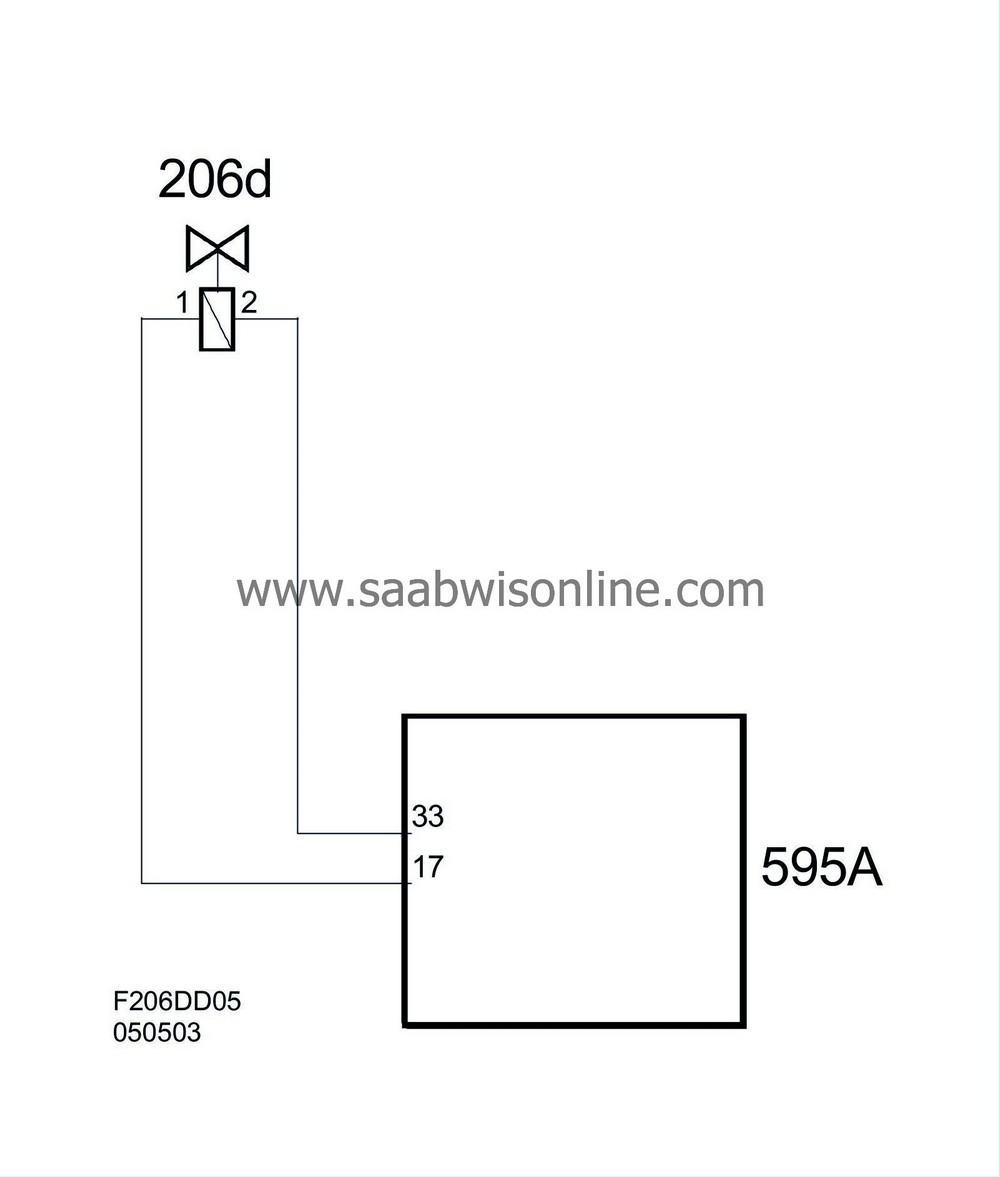
| Connection, cylinder 4 |
| Pin No. | Signal type | Description |
| 1 | Connected to ECM pin 17(A). | |
| 2 | Connected to ECM pin 33(A). |
| Function |
The injectors open when the current flows through the coil and close by means of a strong spring when the current is interrupted.
The injectors have six holes and consequently there are six jets of fuel. The holes through which the fuel is injected have a diameter of 0.14 mm. As a comparison, a human hair is 0.08 mm. The holes have to have a small diameter so that the fuel will be atomized into small droplets. Certain manufacturing tolerances are only a few thousandths of a millimetre.
The injection volume is, for example, about 1 mm 3 for the pilot injection, to be compared with a drop of water for example with a volume of around 30 mm 3 .
The injector must be regarded as a precision instrument. Consequently, it is extremely important that no dirt enters the fuel system.


