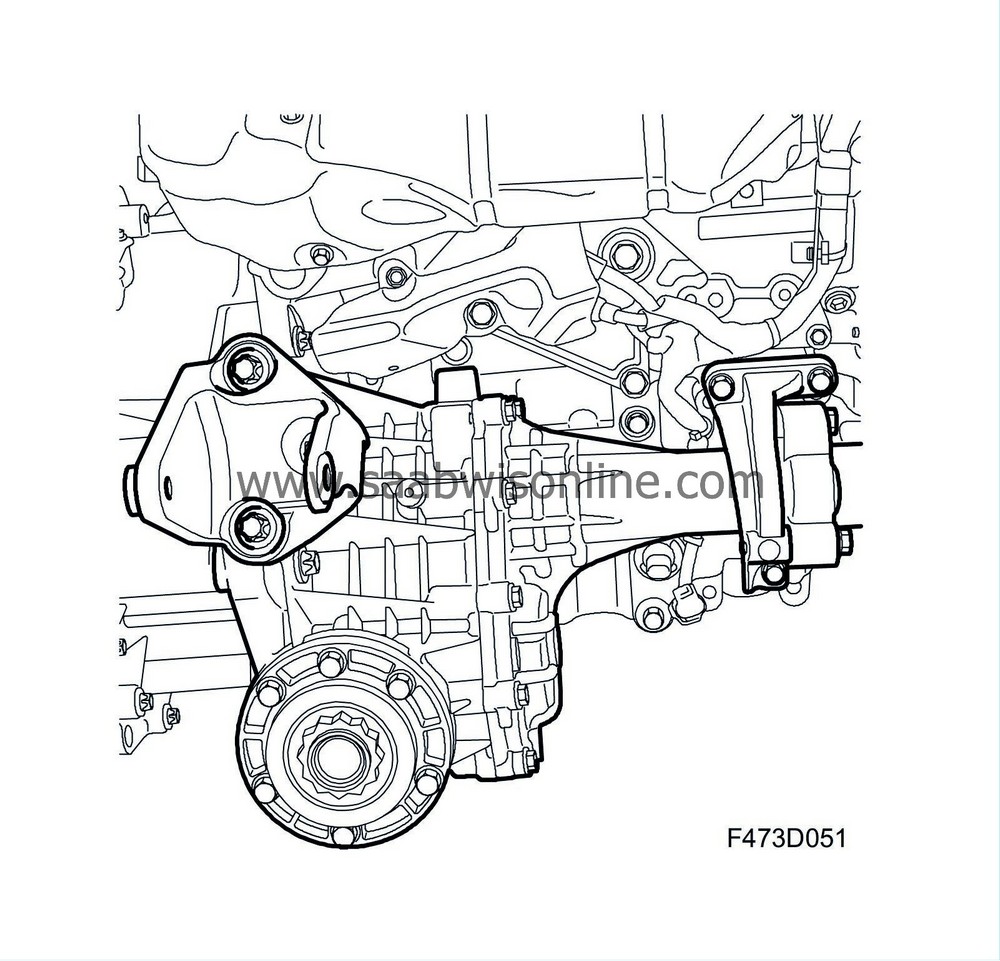
Transfer case
| Transfer case |
Its primary function is to take power from the gearbox and transfer it via a hypoid gear to the differential clutch via the propeller shaft. The intermediate shaft runs to the right-hand front wheel through the transfer case.
The transfer case is fully mechanical.
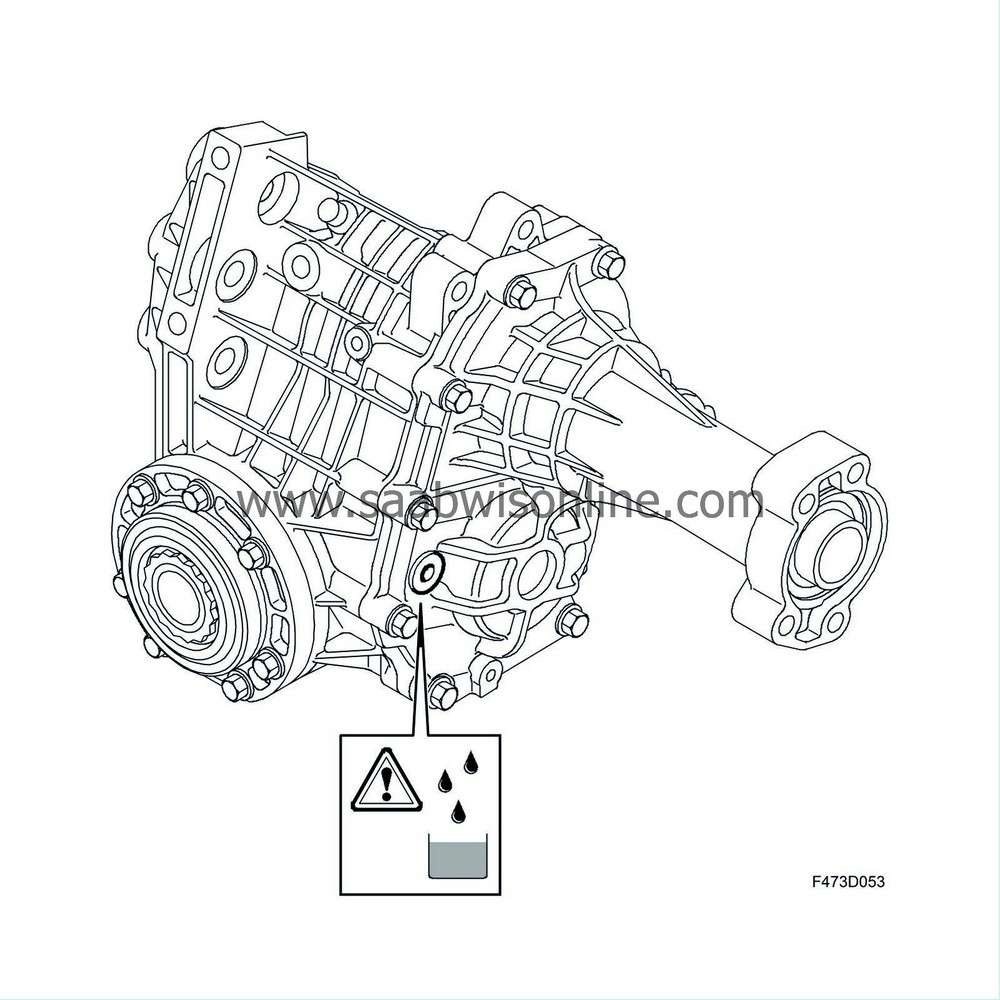
During manufacture the transfer case is filled with oil, which then does not require changing. The correct type of oil must be used without exception when filling. The incorrect type of oil may destroy the transfer case.
| Housing and cover |
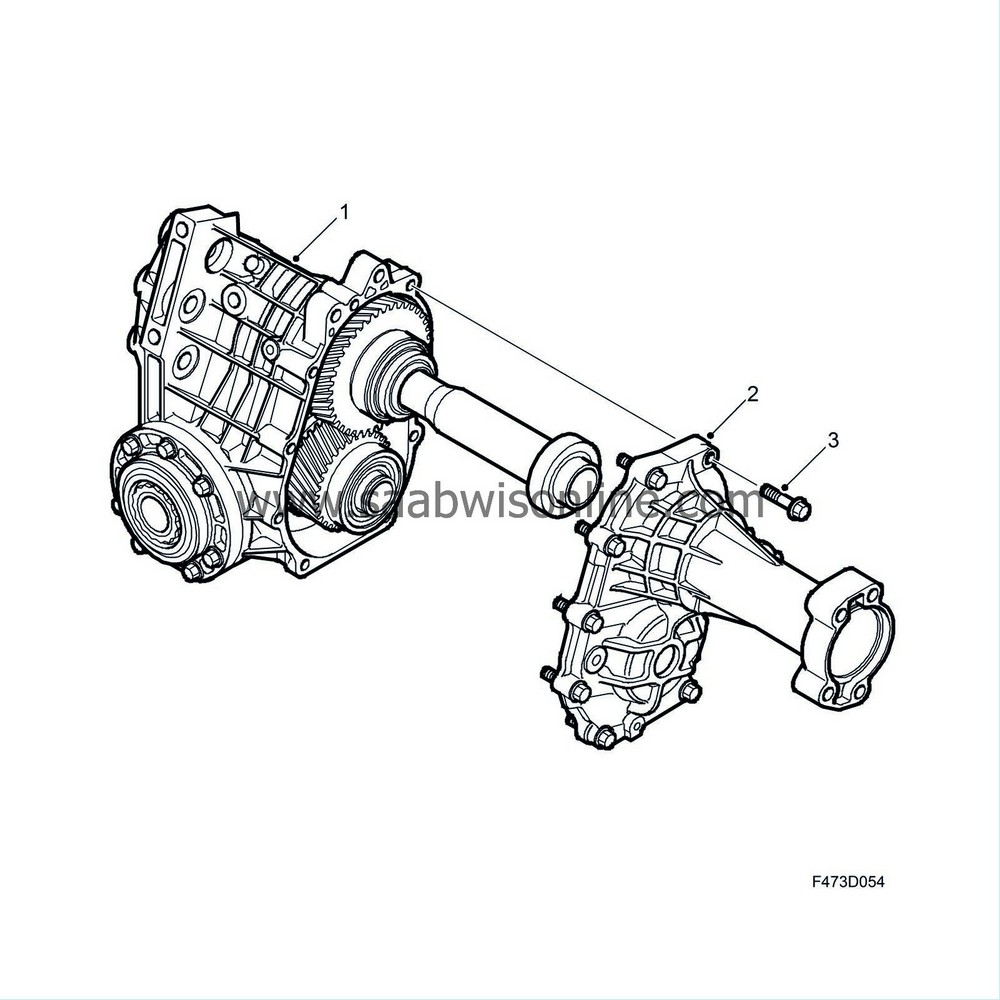
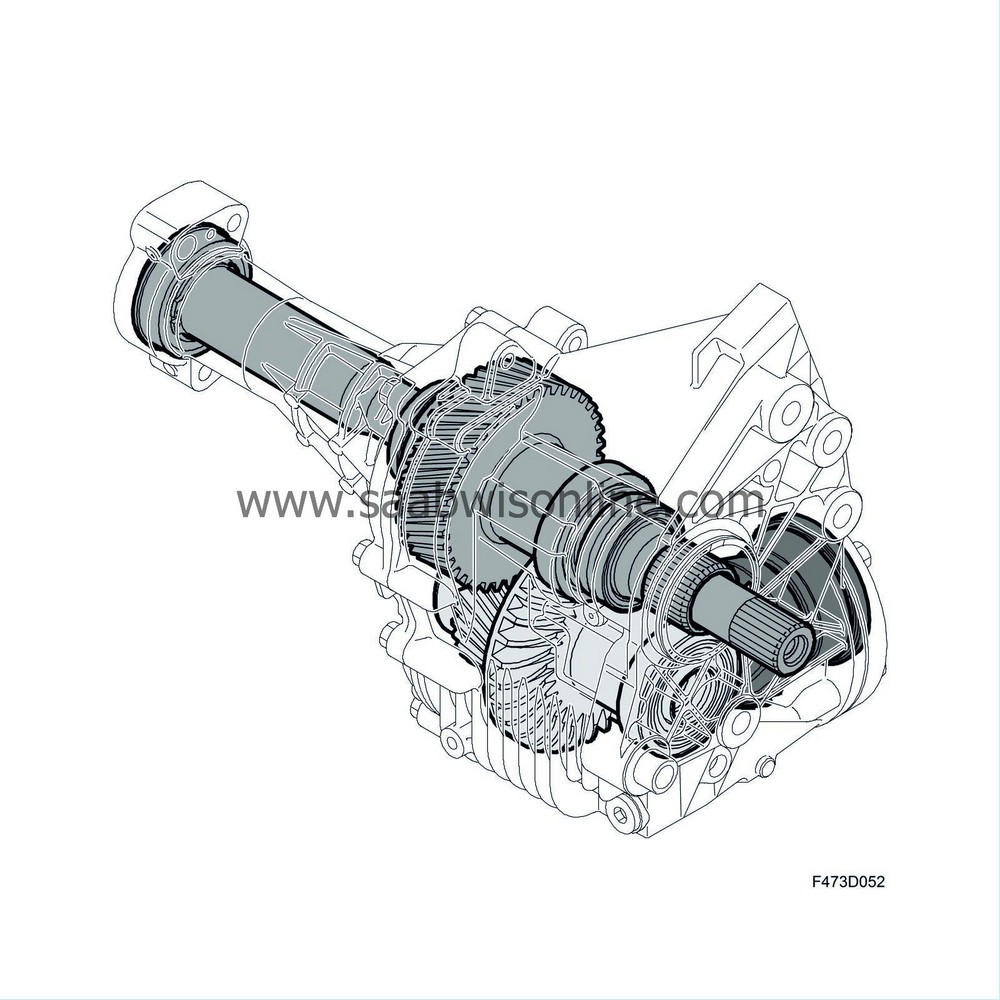
Housing (1) and cover (2) are produced from a high-pressure cast aluminium alloy. A number of reinforcement ribs are fitted in suitable locations to strengthen the housing and cover, and these constitute a vital part of the cooling for the transfer case. The cover is bolted to the housing with nine bolts (3), two guide pins govern their relative position. The mating face between housing and cover is sealed using sealant.
The housing is bolted to the gearbox with four bolts (3), of which one bolt is accessible via the tube sleeve (6) that runs inside the crown wheel shaft. A guide pin on the housing (2) runs into the gearbox to ensure that the relative position is correct. The connection between the transfer case housing and the gearbox is sealed with an O-ring (1). Two opposite radial seals (5) seal the input shaft, and there is an overflow hole (4) in the housing between the radial seals.
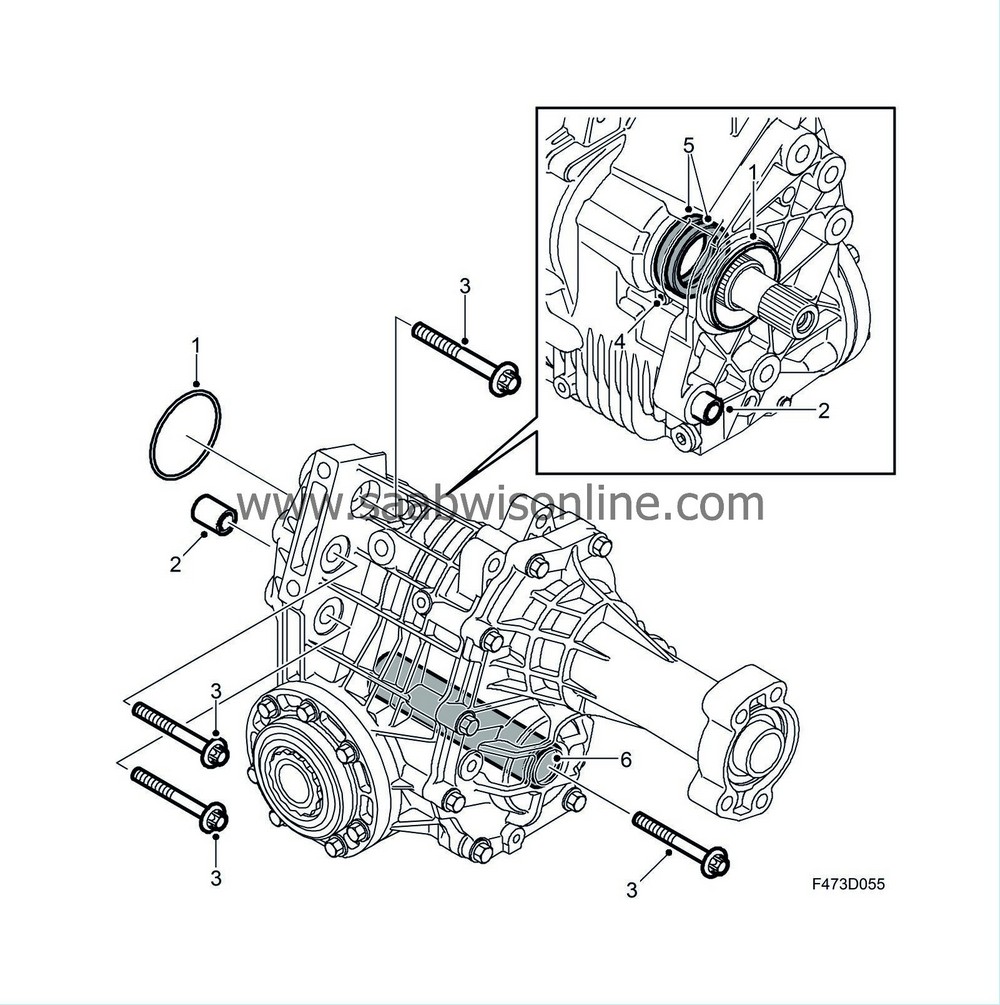
A vent is located above the housing. There is a magnetic drain plug fitted in the bottom. The transfer case housing also constitutes the attachment point for the rear unit's mounting. A bracket for this is bolted to the housing with three bolts. Inside the housing are bearing races for the input shaft and the crown wheel shaft, behind the bearing races are shims to provide the correct bearing preload.
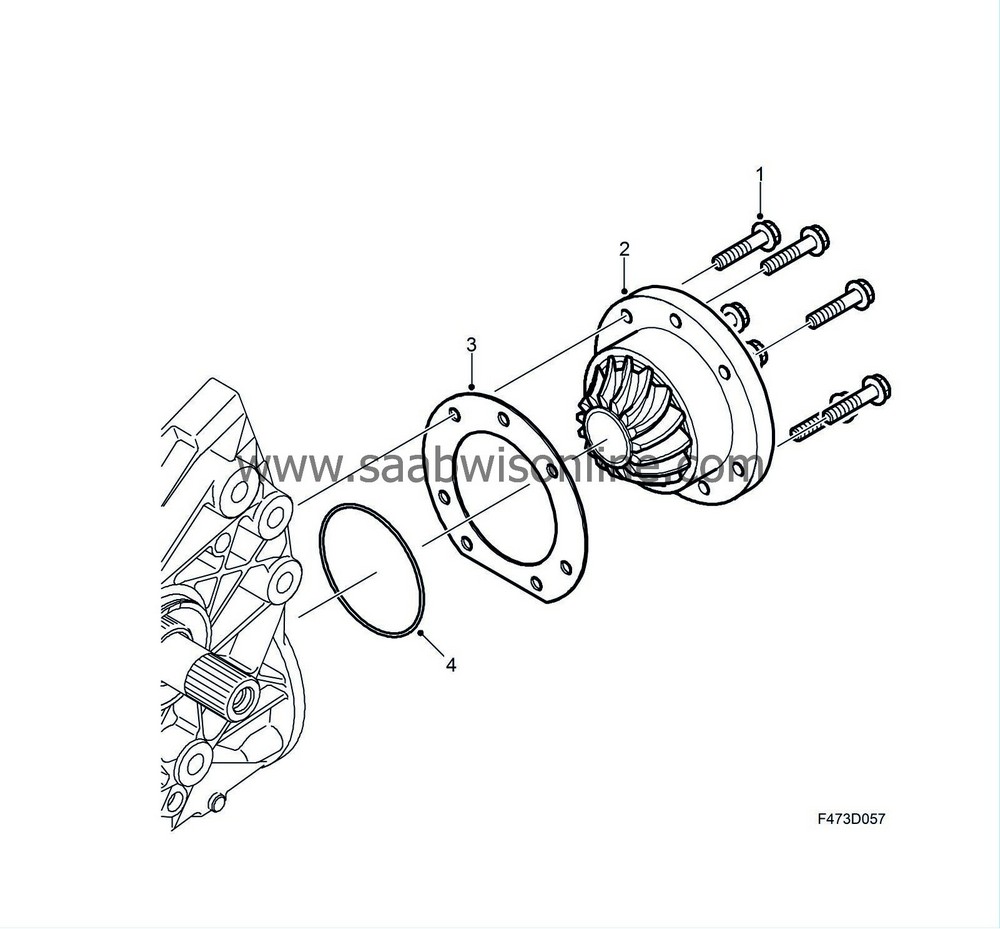
The pinion unit (2) is bolted to the housing with seven bolts (1) and sealed to the housing with an O-ring (4). A shim (3) guides the pinion gear insert into the crown wheel. There are bearing races in the housing for the input shaft and the crown wheel shaft, there is a shim behind the bearing races to provide the correct bearing preload.
There are bearing races (1) in the cover for the input shaft, crown wheel shaft as well as a support bearing for the intermediate shaft for the right-hand front wheel. The oil filler plug is fitted in the cover (2).

The transfer case cover has a neck through which the intermediate shaft for the right-hand front wheel runs. The neck serves partly as a holder for the intermediate shaft's support bearing, and partly as an attachment point for the transfer case to the engine. The intermediate shaft support bearing is a single-row sealed permanently-lubricated groove ball bearing and is locked with a circlip in the housing.
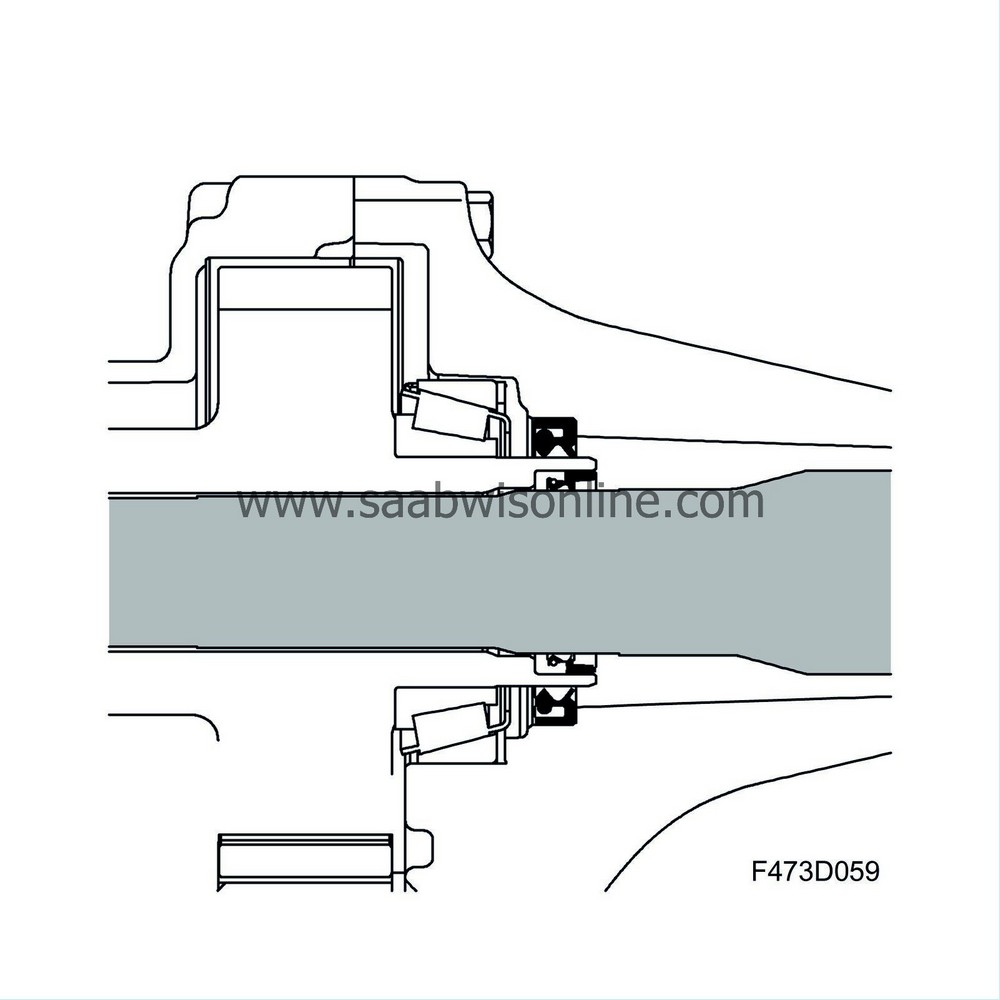
A radial seal is fitted in the cover at the input shaft so that the oil from the transfer case does not seep out at the neck of the cover. Inside the input shaft is a radial seal that seals against the intermediate shaft to avoid oil from the gearbox seeping out at the neck of the cover.
| Input shaft |
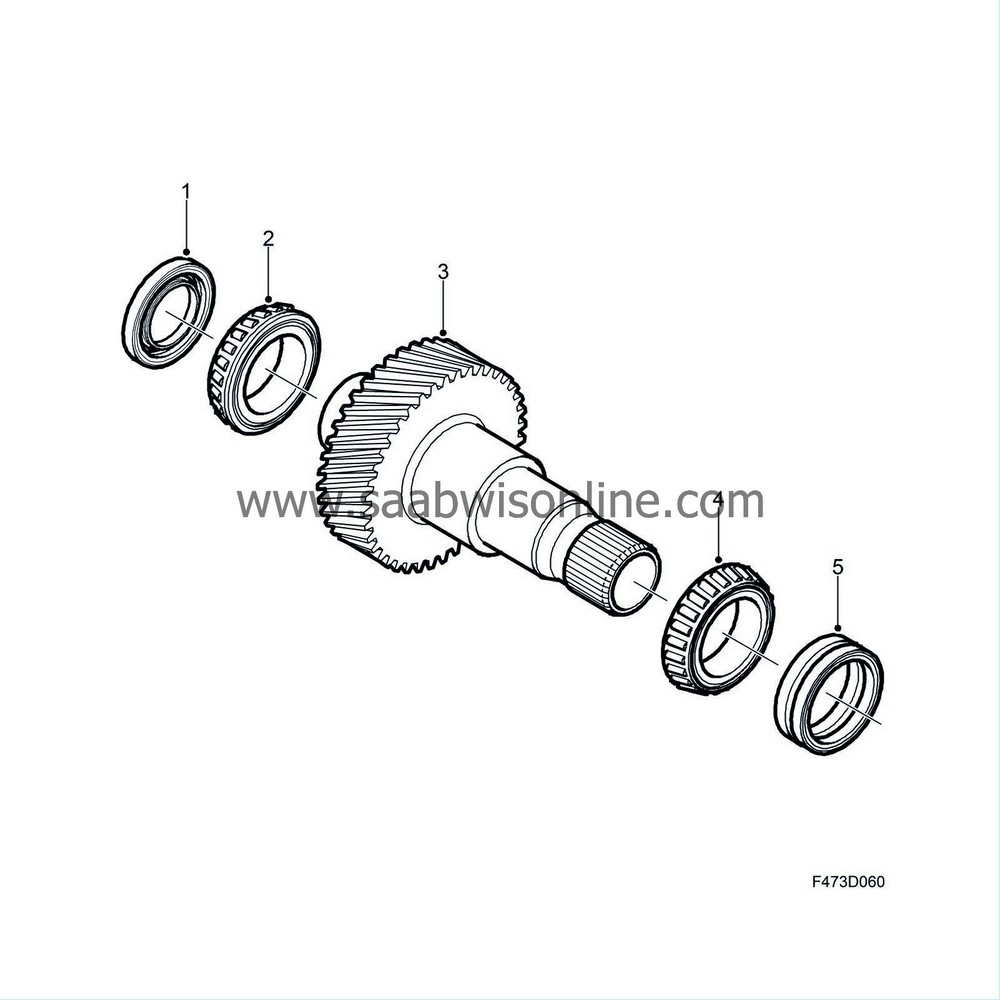
The function of the input shaft (3) is to transfer power from the transfer case. In one end the shaft is equipped with splines which are inserted into the gearbox differential housing. Consequently the speed of the input shaft is the same as the gearbox crown wheel. Fitted in the transfer case housing are two opposite radial seals (5) to seal the input shaft. The other end of the input shaft is equipped with an internal radial seal to seal against the right-hand front wheel's intermediate shaft which runs inside the input shaft. Externally the shaft is sealed with a radial seal (1).
There is a gear on the shaft with helical teeth in order to reduce noise and to increase the engagement area of the teeth. The gear is engaged with a gear wheel on the crown wheel shaft.
The shaft is mounted in two conical roller bearings (2, 4). The bearings are given the correct preload at manufacture by means of shims being fitted behind the bearing races in the housing and cover respectively.
| Crown wheel shaft |
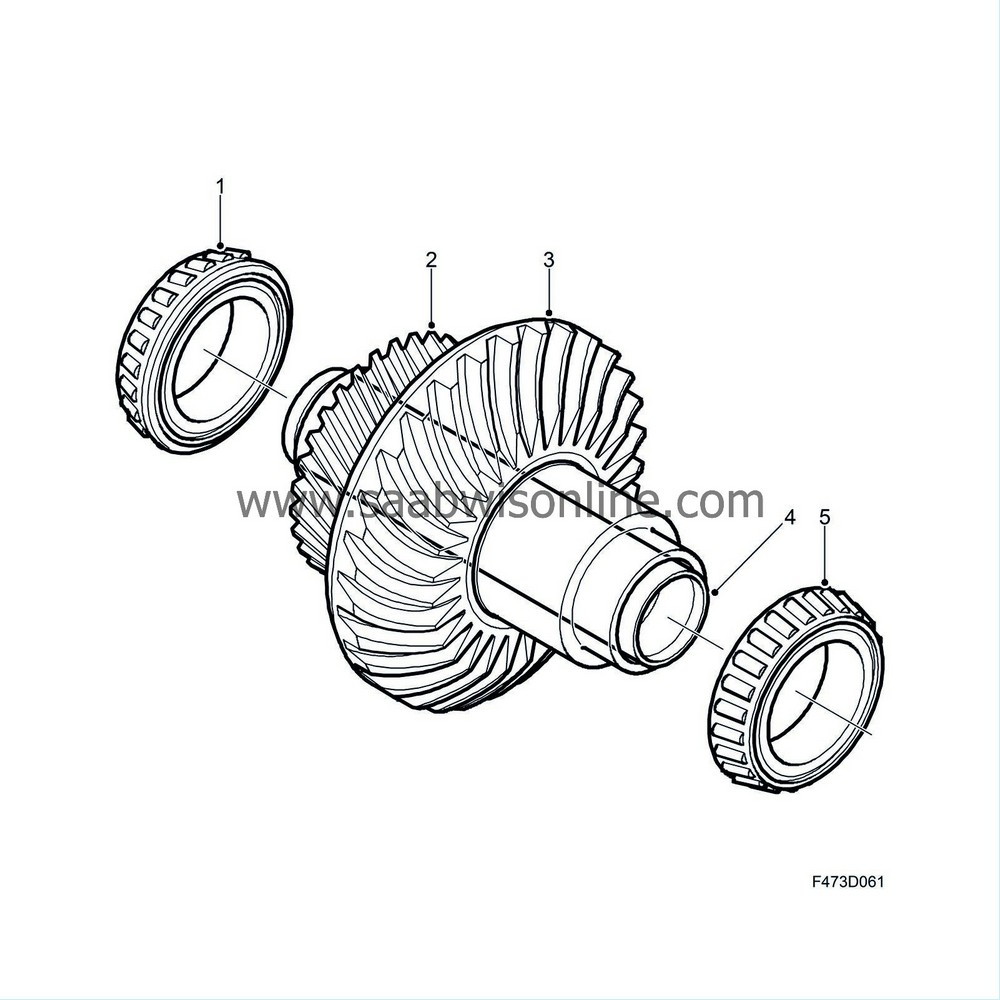
The crown wheel shaft is located under the input shaft and is driven by the gear on the input shaft. The shaft has a relatively large diameter and is hollow.
The crown wheel shaft consists of a helical gear wheel (2) and a crown wheel (3). The helical gear wheel is driven by the input shaft. In turn the crown wheel drives the pinion. The crown wheel and pinion are matched to each other.
The shaft is mounted in two conical roller bearings (1, 5). The bearings are given the correct preload at manufacture by means of shims being fitted behind the bearing races in housing and cover respectively.
| Pinion |
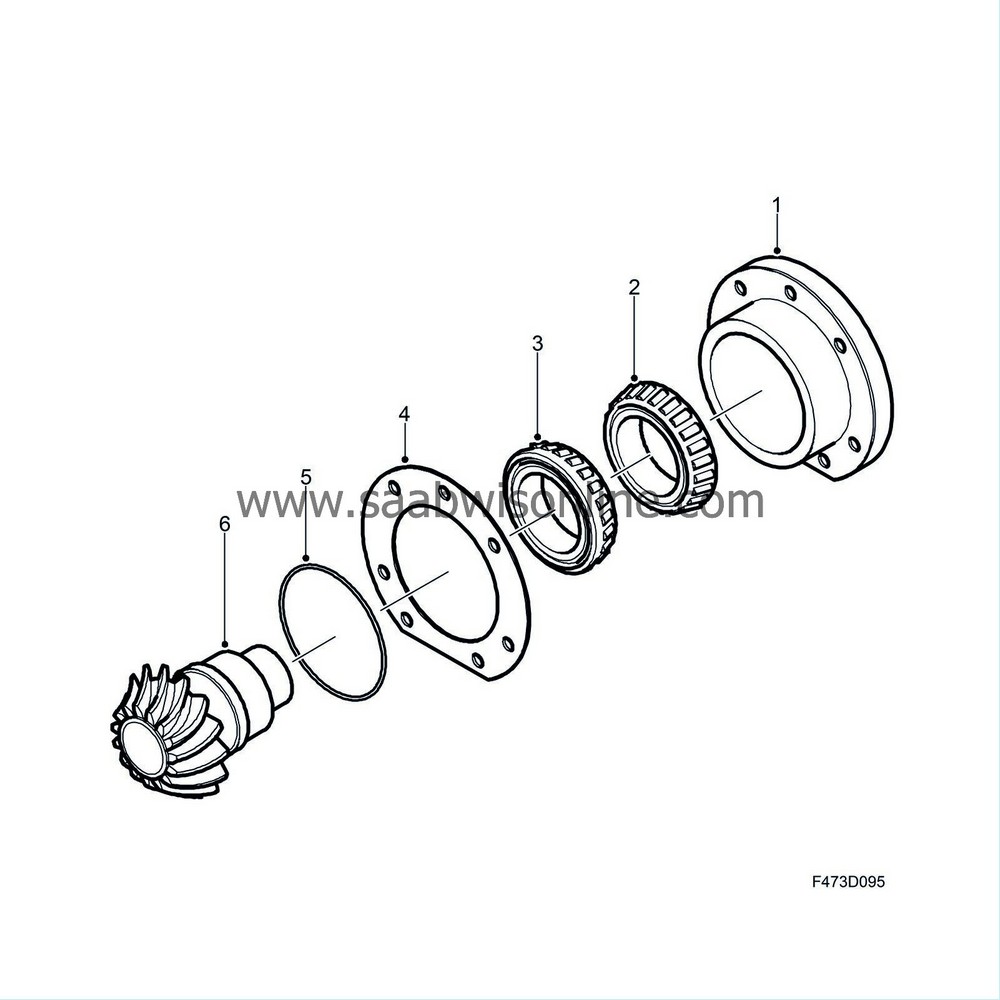
The pinion (6) with associated bearings (2,3) and radial seal (4) constitute one unit which is bolted (1) to the transfer case housing with seven bolts. A shim (5) provides the pinion with the correct gear contact to the crown wheel. The pinion is matched together with the crown wheel.
The pinion shaft, which together with the pinion gear (6) constitutes one unit, is mounted with two conical roller bearings (2,3), fitted towards each other. The bearing closest to the pinion gear absorbs forces that attempt to press the pinion gear from the crown wheel, while the farther bearing absorbs the forces that attempt to press the pinion gear into the crown wheel.
The pinion shaft is hollow and is equipped with internal splines in which the pin on the propeller shaft's front drive shaft universal joint is fitted.
The pin is equipped with a spring-loaded ring which locks it into a groove in the pinion shaft.