Crankshaft position sensor (345), T8
|
|
Crankshaft position sensor (345), T8
|
Crankshaft position sensor (345)
The control module receives information on crankshaft position and speed from the crankshaft position sensor.
Rpm is used to:
|
•
|
indicate engine operating point (together with the engine load). The operating point indicates which values are to be used in matrices and tables.
|
Crankshaft angle is used to calculate when angle-related functions are to be activated. These include ignition, injection and knock detection.
A perforated disc with 58 ribs is mounted on the crankshaft. The sensor is inductive and is mounted in the engine's crankcase wall. The distance between the sensor and the perforated disc is 0.4-1.3 mm and cannot be adjusted.
|
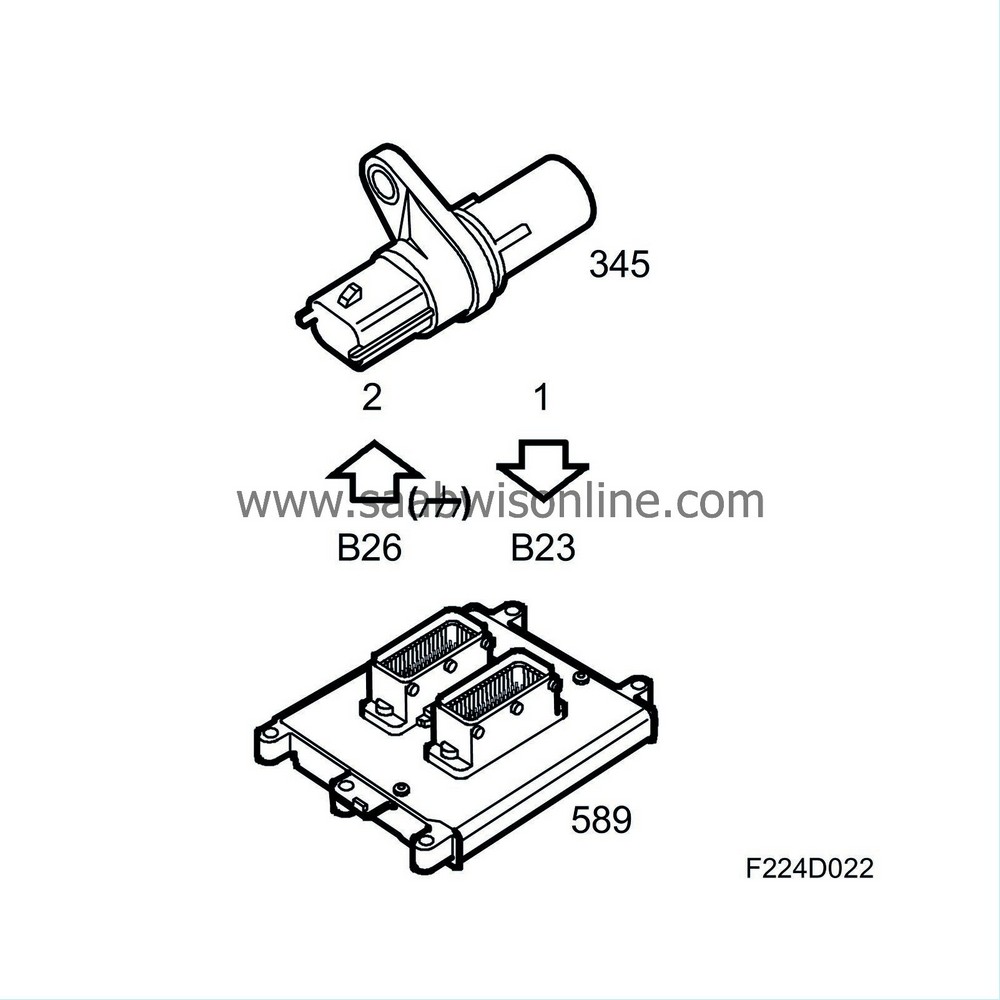
Pin No.
|
Signal type
|
Description
|
|
1
|
Signal
|
Connected to ECM pin 26(B).
|
|
2
|
Signal
|
Connected to ECM pin 23(B).
|
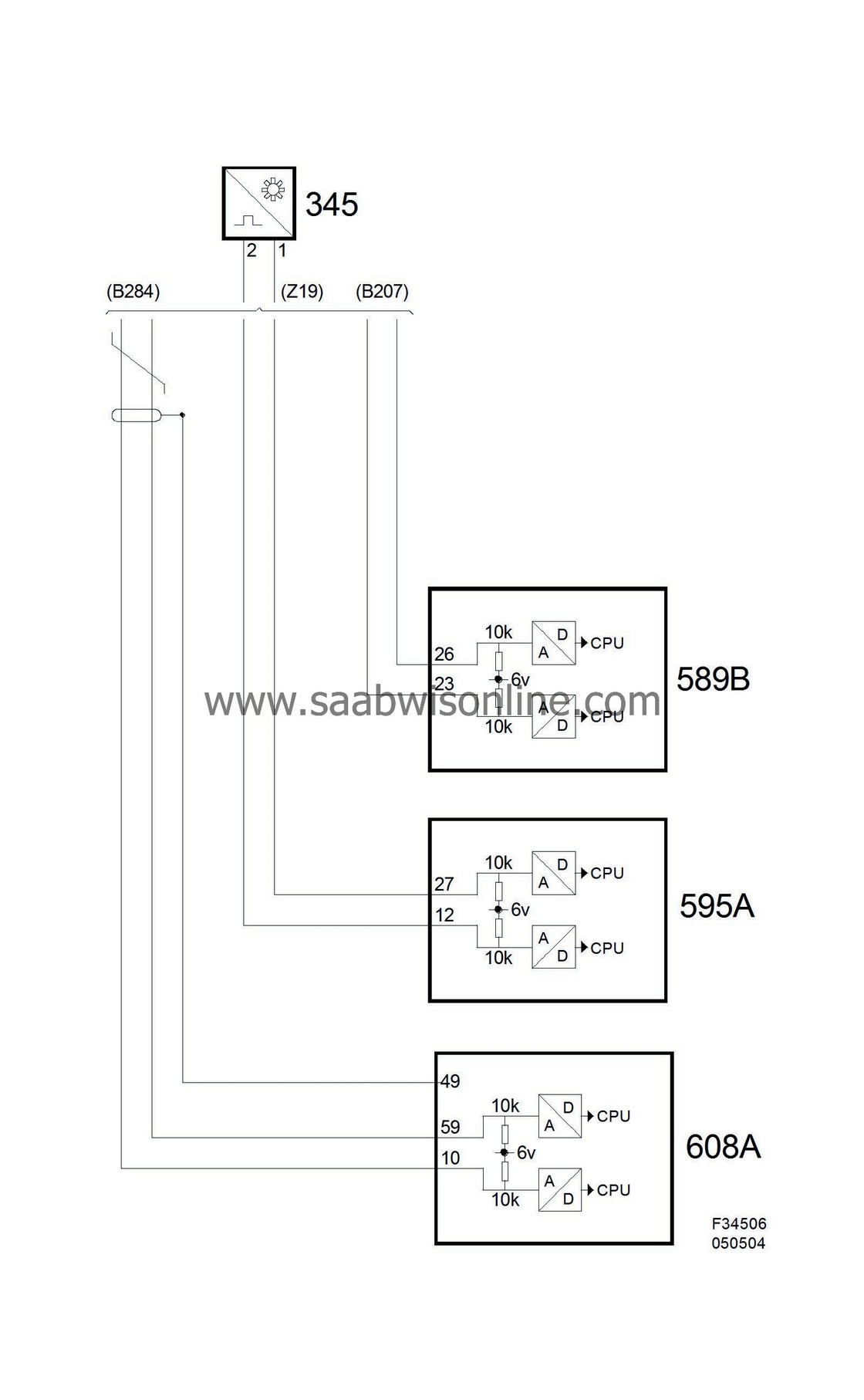
The sensor works like a generator and yields a sinusoidal AC. By measuring the frequency, the control module can determine engine speed. After the 58th rib of the perforated disc, there are 2 empty rib spaces. When rib 1 then passes the sensor, the control module knows that the crankshaft is 117° before top dead centre (BTDC).
Voltage from the crankshaft sensor varies with engine speed. When idling, voltage is 5-10 V (AC) and at 2500 rpm, it is approx. 15-20 V (AC). It is the frequency, not voltage, that is important to the control module. As soon as the control module receives pulses from the crankshaft sensor, it grounds the fuel pump relay. Sensor resistance is 860±90 Ohm.





