Pistons
| Pistons |
| General data |
| Different makes of piston must not be fitted in the same engine. |
| Piston class and cylinder travel |
Piston class is stamped on piston crown.
| Classification codes | Piston diameter | |
| Category A | mm | 81.920 - 81.930 |
| Category B | mm | 81.930 - 81.940 |
| Category C | mm | 81.940 - 81.950 |
| Oversize | mm | 0.4 |
| Piston clearance | mm | 0.1 |
The possible cylinder classes are
| Classification codes | Cylinder bore | |
| Class A | mm | 82.000 - 82.010 |
| Category B | mm | 82.010 - 82.020 |
| Category C | mm | 82.020 - 82.030 |
| Oversize | mm | 0.1 |
| Cylinder bore conicity | mm | < 0.005 |
| Cylinder bore ovality | mm | ± 0.05 |
| Max weight difference between pistons | g | 5 |
| Piston rings |
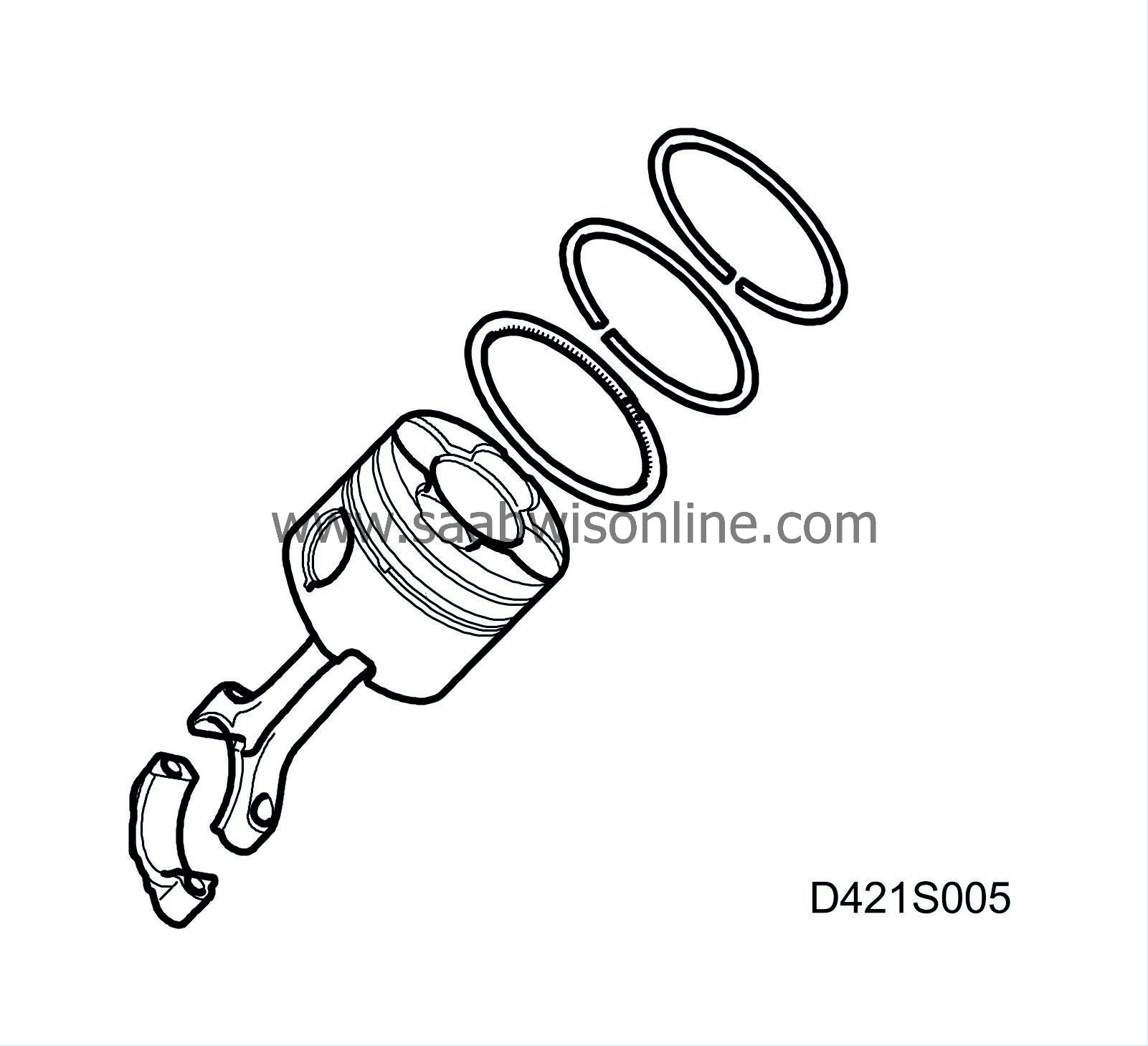
| Upper compression ring | Lower compression ring | Oil scraper ring | ||
| Piston ring gap | mm | 0.20 - 0.35 | 0.60 - 0.80 | 0.25 - 0.50 |
| Piston ring play in groove | mm | 0.0985 -0.130 | 0.025 -0.070 | 0.030 -0.070 |
| Piston ring thickness | mm | 1.970 - 1.995 | 1.970 - 1.990 | 1.970 - 1.990 |
| Piston ring, groove in piston | mm | 2.080 - 2.100 | 2.020 - 2.040 | 2.020 - 2.040 |
They can all occur in the same cylinder block.
The piston ring working gaps must be displaced 120° to each other.


