Brief description
| Brief description |
| Description |
The exhaust emission control system comprises the following sub-systems:
| • |
Catalytic converters
|
|
| • |
Particle trap
|
|
| • |
Crankcase ventilation
|
|
| • |
Broadband oxygen sensor (Z19DTR)
|
|
| • |
EGR system
|
|
Catalytic converters
A catalytic converter is fitted directly after the turbocharger inlet. The proximity to the turbocharger means that the catalytic converter is heated quickly after starting. A second catalytic converter is built into the particle trap. The catalytic converters reduce the emissions of HC and CO.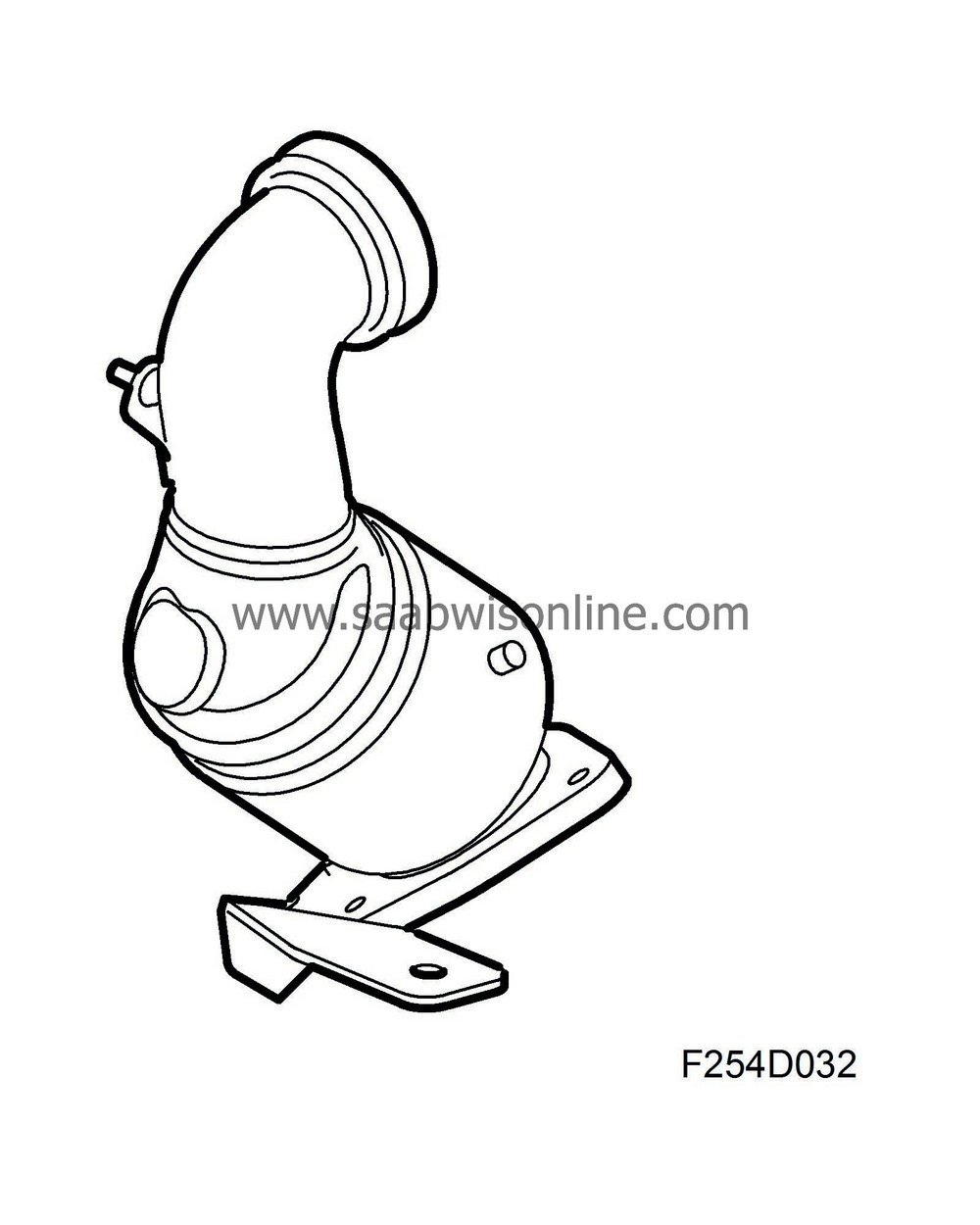
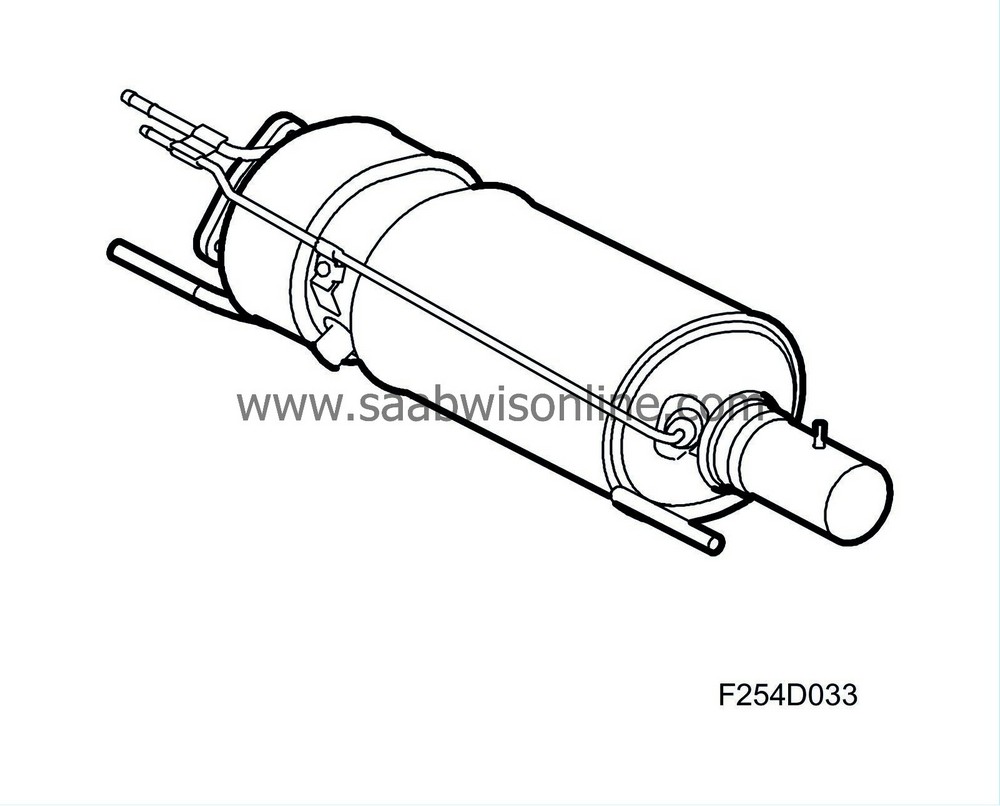
Particle trap
The function of the particle trap is to capture soot particles in the exhaust gases. When the particle trap is full of particles they are combusted. This is called regeneration.In principle, the particle trap comprises a ceramic body similar to a catalytic converter with a large number of small channels in which particles of soot fasten. A differential pressure sensor measures the drop in pressure across the particle trap and when it exceeds a certain limit, the particle trap is considered to be full and is regenerated. This is normally done fully automatically without the driver noticing. Principally, regeneration is a process where an extra dose of fuel is injected during the exhaust stroke to drastically raise the temperature of the exhaust gas entering the particle trap. The high exhaust temperature burns off the soot and "cleans" the particle trap. This process can take up to 15 minutes to complete. Regeneration can also be activated with the diagnostic tool.
Crankcase ventilation, general
The combustion gases passing the piston rings collect in the crankcase and must be led out of the engine through the crankcase ventilation. The reason for this is partly to prevent excessively high pressure in the crankcase and ventilate off the water vapour and hydrocarbons left from the combustion. Since the crankcase gases contain hydrocarbons, they must not be released into the air and must be led back to the cylinders to be burned. This means the crankcase ventilation is a closed system.Crankcase ventilation, Z19DTH
Z19DTH (16V) has an external oil trap. Most of the oil mist coming from the crankcase gases is deposited in the oil trap. The oil passes back into the crankcase and the air is led into the engine induction system for combustion and to be rendered harmless.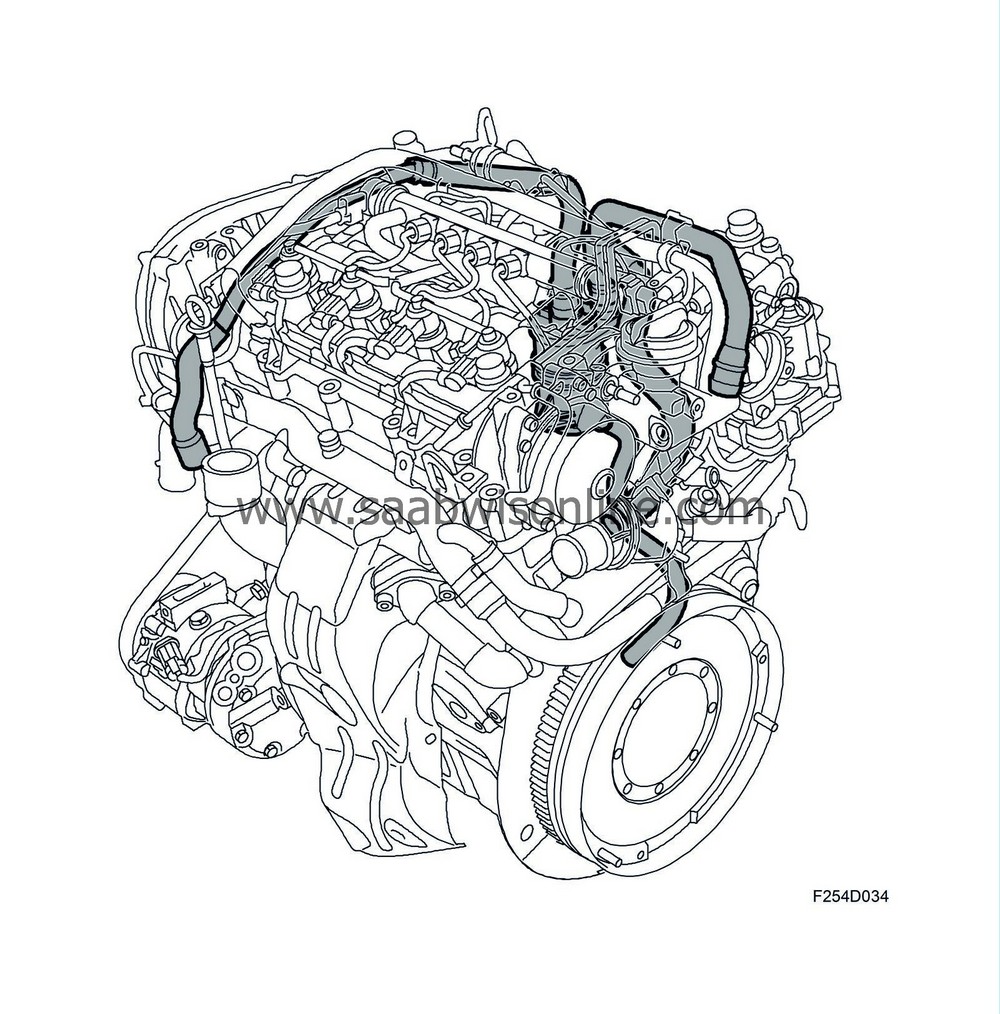
Crankcase ventilation, Z19DTR
Z19DTR has an external oil trap. Most of the oil mist coming from the crankcase gases is deposited in the oil trap. The gases are led from a duct between the cylinder head and the sump on the rear of the crankcase into the oil trap, where the oil is separated from the air. The oil passes back into the sump. The air passes into the compressor inlet and then into the crankcase. From there, it is led into the engine induction system for combustion and to be rendered harmless.Design differs compared to other engine variants.
Crankcase ventilation, Z19DT
The engine's crankcase ventilation is fully closed. The ventilation comprises an oil trap integrated in the camshaft cover and a nipple in the engine block that is connected to the crankcase. From the nipple in the engine block there is a hose leading to the oil trap. In the camshaft cover is a connection to the oil trap for ventilating the cylinder head. Drops of oil from the crankcase gases are separated in the oil trap. From the oil trap there is a hose connected to the inlet pipe between the mass air flow sensor and the turbocharger.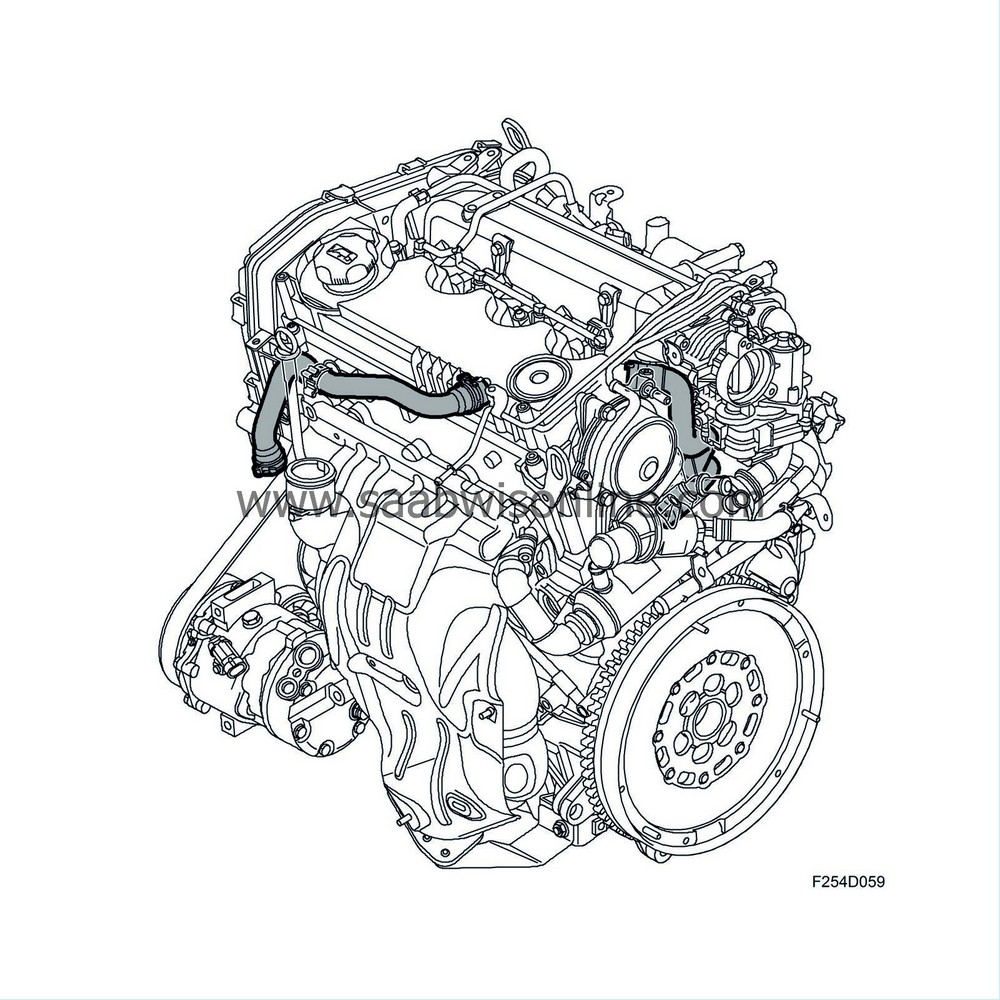
EGR system
To reduce NO x (nitrogen oxides) they must be prevented from arising altogether. This is done by reducing the temperature during combustion. By adding recirculated cooled exhaust gas to the intake air, the combustion temperature can be reduced and therefore also the level of NO x emissions.The following components are included in the EGR system:
| • |
An EGR valve to control the amount of exhaust gas being recirculated.
|
|
| • |
EGR cooler to cool down the exhaust gas.
16V: 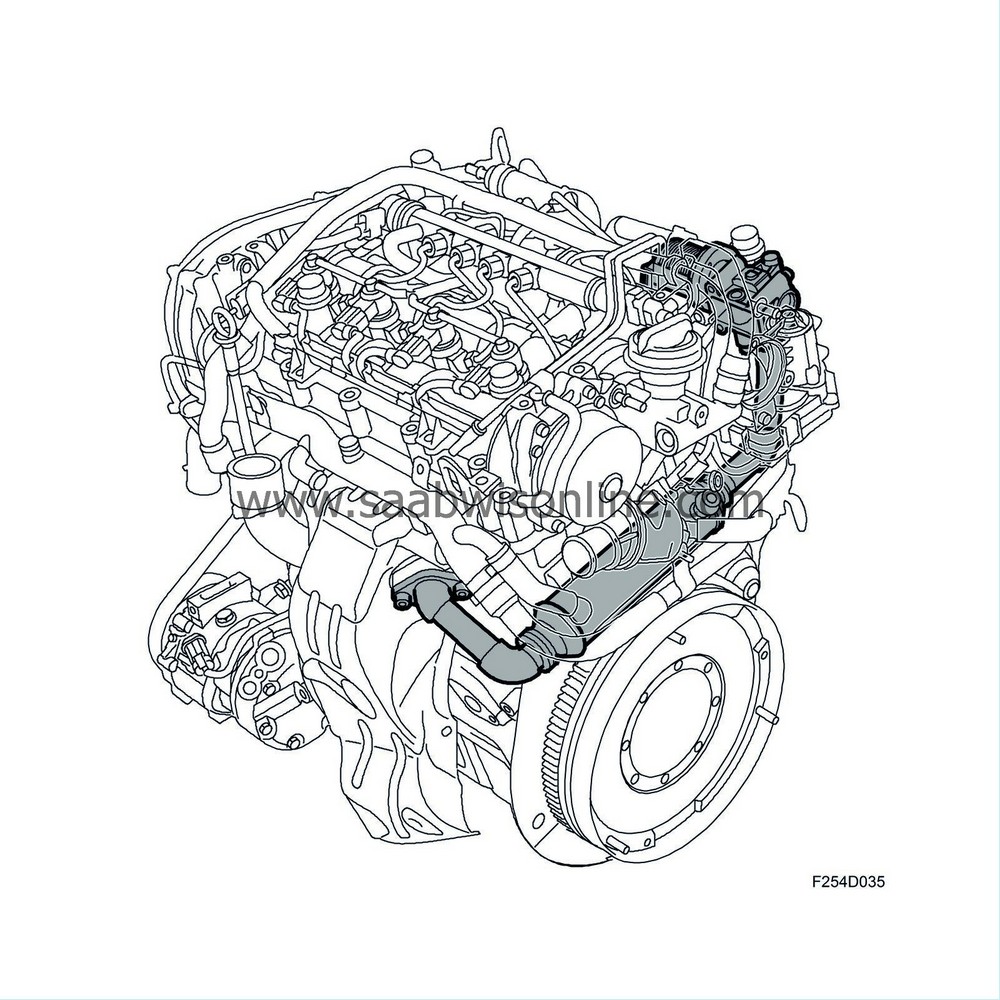
8V: 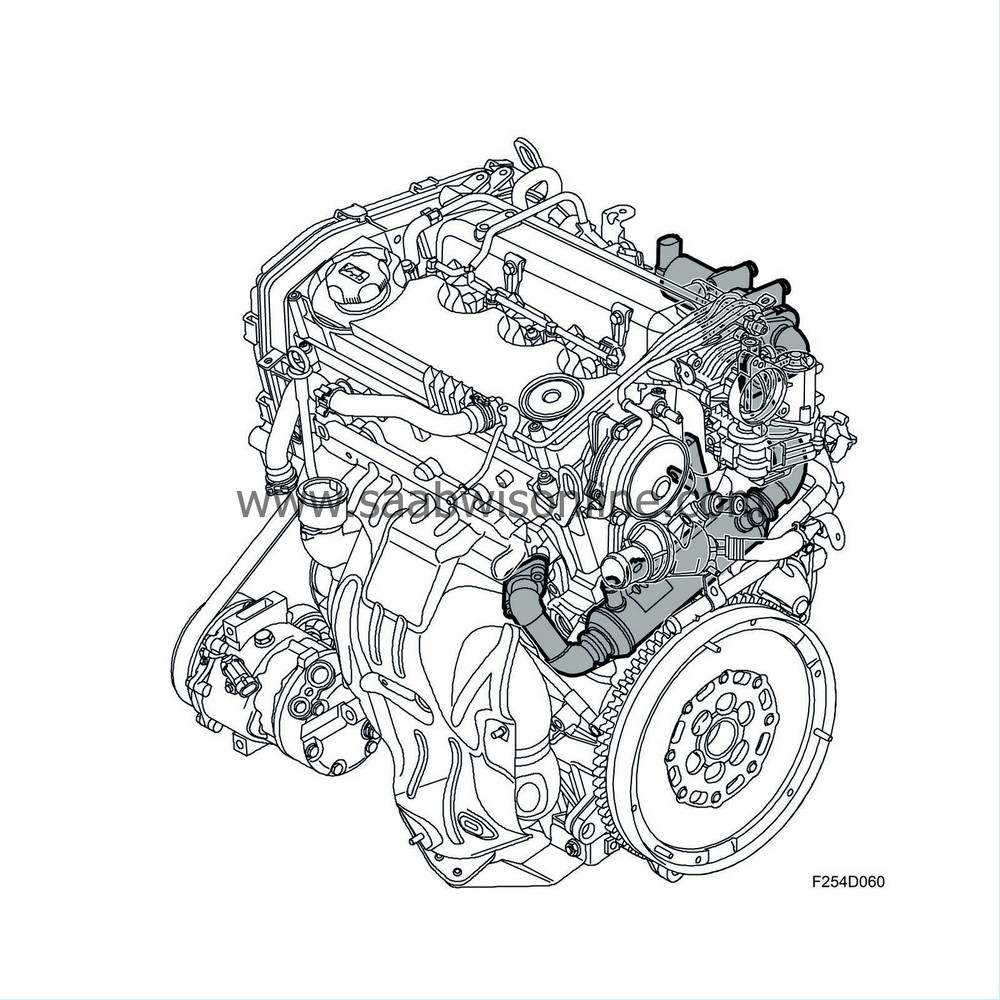
|
|
Z19DTR: The EGR system has a different design compared to other engine variants. The exhaust gases pass directly from the exhaust manifold into the cylinder head, where they are led towards the bypass valve for EGR cooling. The bypass valve can either send the exhaust gases into the EGR cooler and then on to the EGR valve or it can send them past the EGR cooler. The latter serves to reduce emissions when running a cold engine. The valve is operated by a vacuum unit that is regulated by a solenoid valve.
Z19DTR: The engine variant is equipped with a broadband oxygen sensor upstream from the front catalytic converter. The oxygen sensor monitors the composition of the exhaust gas, particularly the oxygen content. This enables it to ensure the proper functionality of components such as the mass air flow sensor and the injectors.



