Charge air solenoid valve (179a), E39
| Charge air solenoid valve (179a), E39 |
| Location |
Charge air solenoid valve (179a), E39
Located in engine bay on the turbo vacuum box.
| Main task |
The airflow from the turbo compressor is regulated with the charge air control valve (179a), which controls the exhaust turbine wastegate pneumatically.
| Type |
Pulse width modulated (PWM) solenoid valve where R is closed in an unexcited state, and C and W are always open and connected to each other.
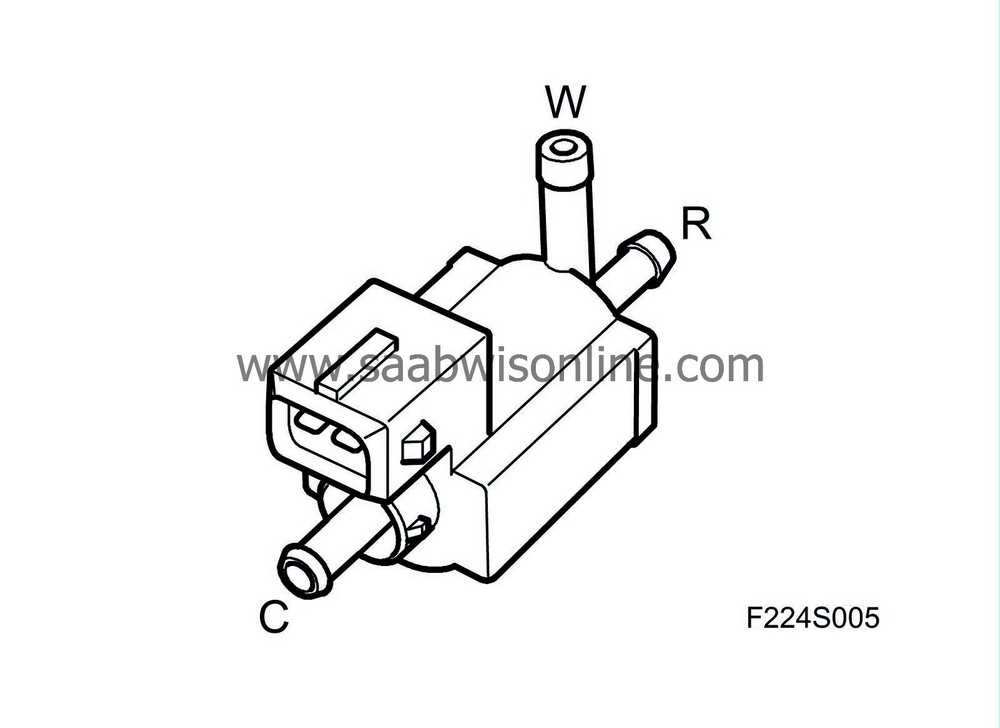
| Connection |
| 179a pin no | Signal type | Description |
| 1 | Power supply, B+ | The solenoid valve is powered from fuse 7 in the petrol engine management system fuse box (727) via crimp connection J215. |
| 2 | Control | Solenoid valve control lead. The solenoid valve is grounded, pulse width modulated, from the ECM control module, E39 (590), pin 71(B). |

Compressor flow increases as the pulse ratio increases.
When the requested airmass/combustion is too large to be regulated by the throttle alone, turbo control must provide for the remaining need. The remaining portion is converted to a pulse width modulated signal (PWM) that controls the charge air control valve, which will then guide the wastegate in an opening direction. Flow through the exhaust valve is limited due to exhaust flow through the wastegate.
The value for atmospheric absolute air pressure and the temperature of intake air are used to correct the conversion. With low atmospheric pressure or high intake air temperature, a greater PWM ratio is needed to maintain the same airmass/combustion.
The ESM control module, E39 (590), then checks that the actual airmass/combustion matches that requested. If necessary, the PWM ratio is adjusted by multiplying it by a correction factor.
The correction factor (adaption) is stored in the control module memory and is always included when calculating the PWM ratio.
The purpose is to have the actual airmass/combustion equal the request as quickly as possible after a load change. The adaption limit is 100 per cent.


