Purging and leak diagnosis (321-588), E39
|
|
Purging and leak diagnosis (321-588), E39
|
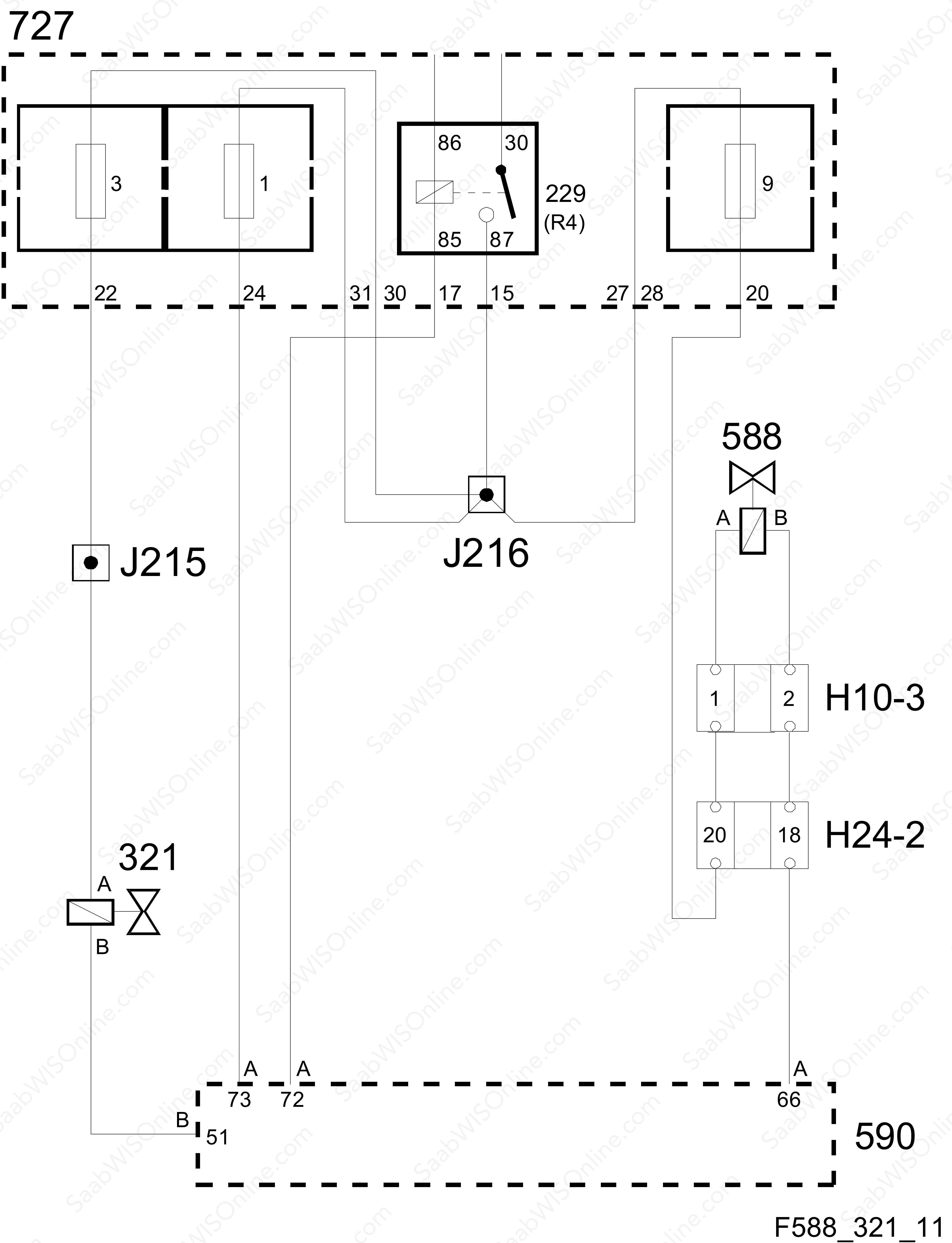
Purging (321-588) is done so that both the return of fuel fumes (ORVR) and leak diagnosis will show a leak in the purging system.
Fuel evaporating in the tank is led to an evaporative emission canister and when the engine is started, surrounding air is drawn through it via an evap canister purge valve (321) in the intake manifold. Fuel fumes are drawn in with it and burned in the engine.
The leak diagnosis detects a leak in the purge system and makes it possible to create negative pressure in the fuel tank through the shut-off valve (588). When this is closed, the negative pressure is maintained with the EVAP canister purge valve (321). A leak is detected by the EVAP differential pressure sensor (585) and the ECM control module, E39 (590), sets a DTC.
The EVAP canister purge valve solenoid (321) is in a closed position when unexcited. It is powered from the engine management system main relay (229) in the petrol engine management system fuel box (727), via fuse 3, and is PWM grounded by the ECM control module, E39 (590), through pin 51(B).
The EVAP shut-off valve solenoid (588) is open when unexcited. It is powered as above through fuse 9 and is PWM grounded by ECM through pin 66(A).
|
321 pin no.
|
Signal type
|
Description
|
|
A
|
Power supply
|
Via crimp connection J215, fuse 3 in the engine management system fuse box, E39 (590), and crimp connection J216 from the engine management system main relay (229).
|
|
B
|
Ground
|
Connected to ECM pin 51(B); pulse width modulated.
|
|
588 pin no.
|
Signal type
|
Description
|
|
A
|
Power supply
|
Via fuse 9 in the engine management system fuse box, E39 (590), and crimp connection J216 from the engine management system main relay (229).
|
|
B
|
Ground
|
Connected to ECM pin 66(A); pulse width modulated.
|