Throttle control (TAC), system description, E39
|
|
Throttle control (TAC), system description, E39
|
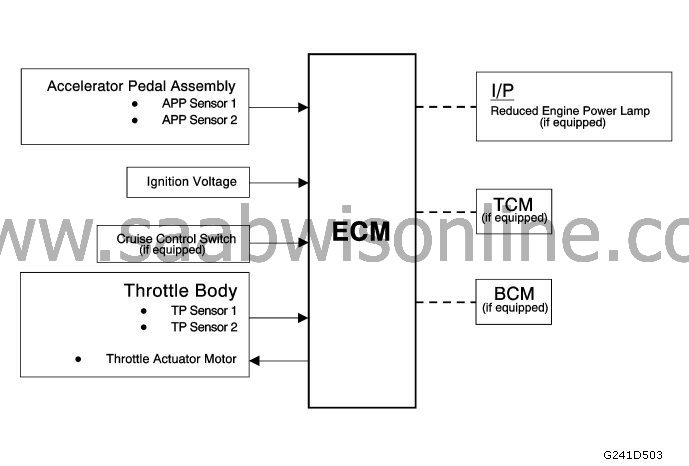
The engine control module (the ECM) controls the throttle control system (TAC) and assesses the driver's intentions on the basis of input data from accelerator position sensors, and then calculates the correct acceleration response on the basis of information from the throttle position sensors.
The ECM achieves the throttle position by sending a pulse width modulated voltage to the throttle regulator motor. The throttle blade is spring loaded in both directions, and slightly open is the default position.
Normal mode
When the TAC system is operational, a number of modes, or functions, are regarded as normal. The following modes can be implemented during normal operation:
|
•
|
Minimum pedal value -- When the ignition key is turned, the ECM updates the minimum pedal value learned.
|
|
•
|
Minimum throttle position values -- When the ignition key is turned, the ECM updates the minimum throttle position value learned. To learn the minimum throttle position value, the throttle blade is moved to closed position.
|
|
•
|
Ice breaking mode -- If the throttle blade is unable to reach the predetermined minimum throttle position, ice breaking mode is enabled. Under ice breaking mode, the ECM orders the maximum pulse width several times to the throttle regulator motor in the closing direction.
|
|
•
|
Minimum pedal value -- When the ignition key is turned, the ECM updates the minimum pedal value learned.
|
|
•
|
Battery saving mode -- After a predetermined time without engine speed, the ECM switches to battery saving mode. Under battery saving mode, the TAC module removes the power from the engine's control circuits, which removes the power used to maintain idle mode and allows the throttle to return to the spring loaded standard position.
|
Reduced engine output mode
If the ECM discovers a problem with the TAC system, the ECM can switch to reduced engine output mode. Reduced engine output mode can lead to one or more of the following conditions:
|
•
|
Acceleration restriction -- The ECM continues to use the accelerator for throttle control, but the car's acceleration is restricted.
|
|
•
|
Throttle restriction mode -- The ECM continues to use the accelerator for throttle control, but the maximum opening of the throttle is restricted.
|
|
•
|
Standard throttle mode -- The ECM shuts off the throttle regulator motor and the throttle returns return to spring loaded standard position.
|
|
•
|
Forced idle mode -- The ECM undertakes the following actions:
|
|
|
-
|
Restriction of engine speed to idle by altering the throttle position or by regulating the fuel and ignition if the throttle is set to OFF mode.
|
|
|
-
|
Ignoring of input data from the accelerator.
|
|
•
|
Engine shutdown mode -- The ECM shuts off the fuel supply and kills the power to the throttle regulator motor.
|