Strategy Based Diagnostics
|
|
Strategy Based Diagnostics
|
The goal of Strategy Based Diagnosis is to provide guidance when you create a plan of action for each specific diagnostic situation. Following a similar plan for each diagnostic situation, you will achieve maximum efficiency when you diagnose and repair vehicles. Although each of the Strategy Based Diagnosis boxes is numbered, you are not required to complete every box in order to successfully diagnose a customer concern. The first step of your diagnostic process should always be Understand and Verify the Customer's Concern. The final step of your diagnostic process should be Repair and verify the Fix. Refer to the following chart for the correct Strategy Based Diagnosis.
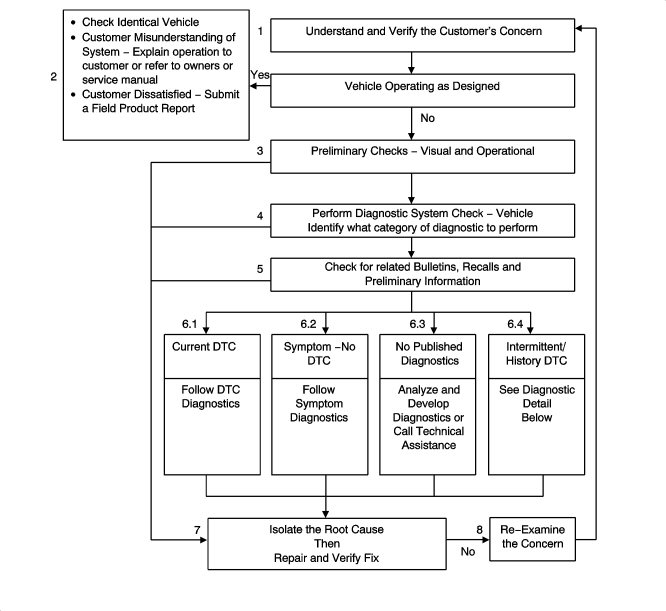
|
1.
|
Understand and confirm the customer's problem: The first part of this step is to obtain as much information as possible from the customer. Are there aftermarket accessories on the car? When does the problem occur? Where does the problem occur? How long does the problem persist? How often does the problem occur? To confirm the problem, the mechanic must be acquainted with the normal functions of the system and refer to the Owner's Manual or Service Manual for any additional information required.
|
|
2.
|
Car works as intended: This condition exists when it is confirmed that the car is working properly. The condition described by the customer may be normal. Compare with another like vehicle that is operating normally under the same conditions described by the customer. Explain your findings and the operation of the system to the customer. If the customer is dissatisfied submit a Field Product Report.
|
|
3.
|
Preparatory checks: Perform a thorough inspection. Review the service history. Detect unusual sounds or odors. Gather diagnostic trouble code (DTC) information in order to achieve an effective repair.
|
|
4.
|
Perform the published Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle:
Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle
checks that the system is working properly. This will lead the technician in an organized approach to diagnostics and identify what category of diagnostic to perform.
|
|
5.
|
Check for related Bulletins, Recalls and Preliminary Information (PI).
|
|
6.
|
Diagnostic categories:
|
|
|
•
|
Symptom - no DTC: Choose a suitable symptom diagnosis Follow the diagnostic steps or suggestions in order to complete the repair. Refer to
Symptoms - Vehicle
.
|
|
|
•
|
No published diagnosis: Analyse the problem: Develop a plan for the diagnostics. The service manual schematics will help you to see system power, ground, input, and output circuits. You can also identify splices and other areas where multiple circuits are tied together. Check component positioning to see whether components, connectors or wiring harnesses may be exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture or corrosive matter (road salt, battery acid, oil or other fluids). Use the wiring diagrams, the description of the system and its functionality and the description of the system circuits.
|
|
|
•
|
Intermittent/DTC history: An intermittent problem is a problem that does not occur continually, may be difficult to repeat and that only occurs under certain conditions. In general, an intermittent problem is caused by defective electrical connections and cable routings, malfunctioning components, electromagnetic/radio frequency disruptions, driving conditions or aftermarket equipment. The following approaches/tools may prove to be beneficial in locating and repairing an intermittent condition or history DTC.
|
|
|
-
|
Combining technicians knowledge with the available service information.
|
|
|
-
|
Use the available scan tool, digital multimeter, or J 42598-B with data capturing capabilities.
|
|
7.
|
Isolate the base cause, repair and check results: Once the base cause has been isolated, perform the repair work and evaluate whether correct functionality has been restored by performing
Diagnostic Repair Verification
. A road test of the car may be required to verify that the DTC or symptoms have been remedied.
|
|
8.
|
Re-evaluate the problem: If a technician cannot successfully find or isolate the problem, a re-evaluation is necessary. Re-verify the concern. The concern could be an intermittent or normal condition.
|



