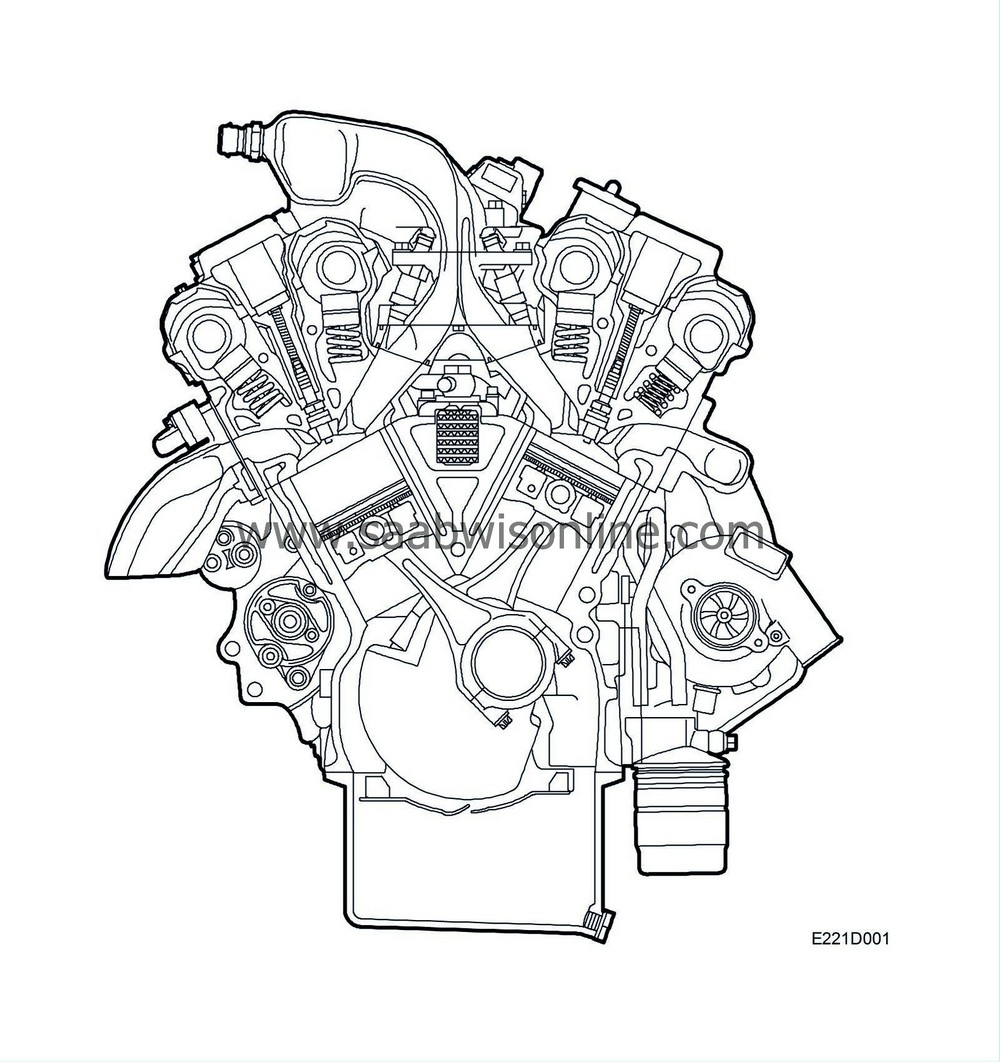
Engine block
| Engine block |
The camshafts are driven by an internally cogged belt and the engine features automatic purging of the air in the oilways supplying oil to the tappets, an integral heat exchanger for the engine oil and a torque member which stabilizes the block round the main bearings.
The heat exchanger has a dual function, namely to heat the oil when starting from cold and to cool the oil at working temperature.
The V6t Ecopower is a compact and lightweight engine developing high torque at low rpm. It is characterized by low emission levels and low fuel consumption. This is the result of a number of engineering solutions such as asymmetric turbocharging, the Saab Trionic engine management system and four-valves-per-cylinder technology.
The V6t Ecopower is the first engine in the world to feature asymmetric turbocharging. The exhaust gases from one of the V6 engine's cylinder rows drive a turbocharger which supercharges both rows of cylinders. Asymmetric turbocharging was developed to combine the superior torque, low fuel consumption and environmental advantages of the turbo engine with the smoother running and balanced sound of the V6 engine.
Due to asymmetric turbocharging, the engine already develops its maximum torque, 310 Nm, at 2100 rpm. As a result, the engine runs very quietly and is relaxing to drive since it doesn't need revving up to give of its best.
| Cylinder block |
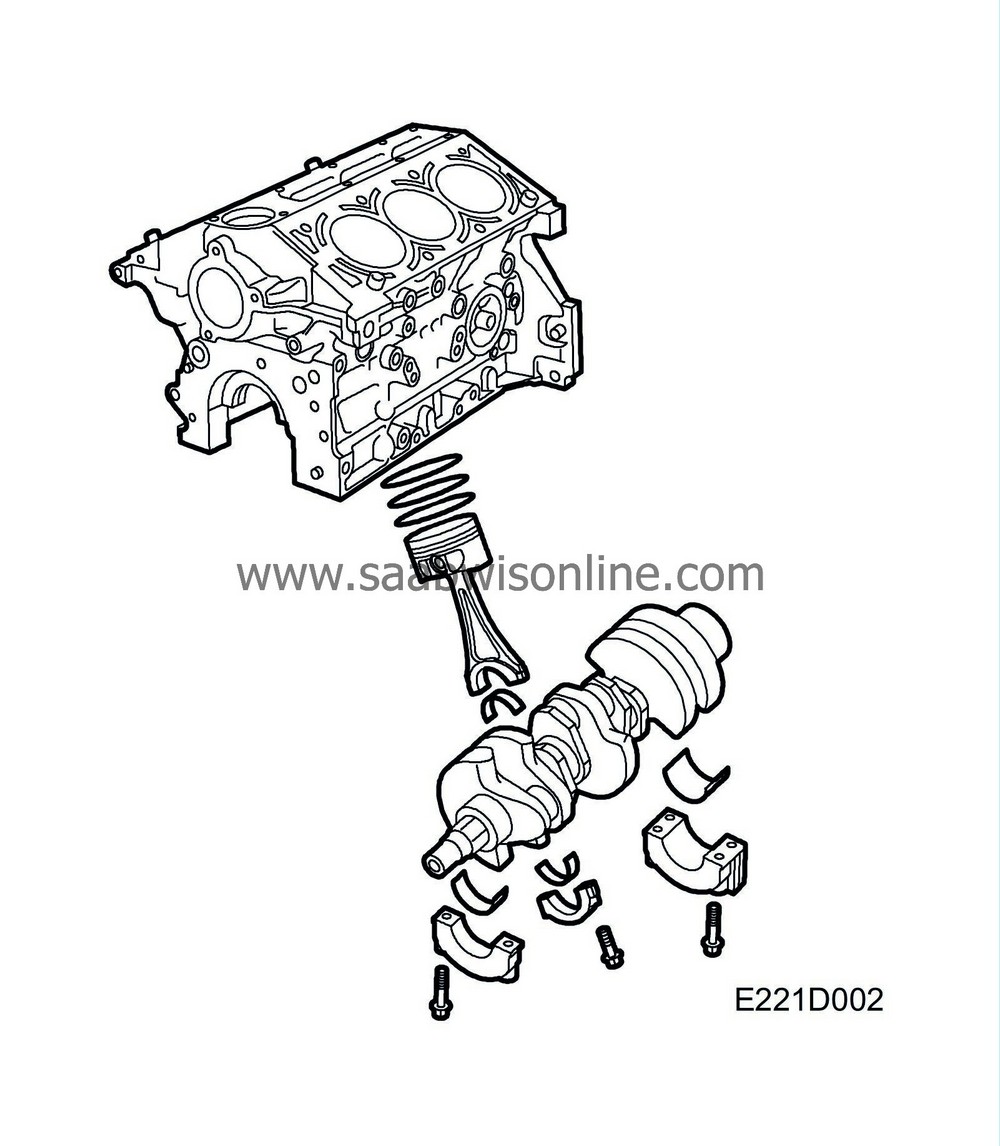
The cylinder block is a special one-piece casting with the cylinder bores drilled directly into the block. Special oilways for the lubricating system are also drilled into the block.
| Pistons |
The pistons are made of light alloy and have grooves for two compression rings and one oil scraper ring.
The top compression ring is flat and molybdenum coated. The lower compression ring has an oil scraper function and is somewhat wider than the upper one. The actual oil scraper ring is in three parts.
The gudgeon pins are of fully-floating type, being free to turn in both piston and connecting rod. Axial movement of the gudgeon pin is limited by circlips in the gudgeon pin holes.
| Connecting rods |
Each connecting rod is manufactured in one piece. There is a fractural impression at the big end where the connecting rod is “snapped” into two parts, one of which forms the big-end bearing cap.
The big-end bearing caps are bolted to the connecting rods. The connecting rods are marked with “protuberances” to prevent them being turned the wrong way round. They are not numbered.
| Crankshaft assembly |
The crankshaft has ground journals which are hardened by an induction hardening process. This provides a hard-wearing surface finish.
There are four main bearings, which are all replaceable.
The slotted ring for the engine management system is bolted to the crankshaft.
| Cylinder head |
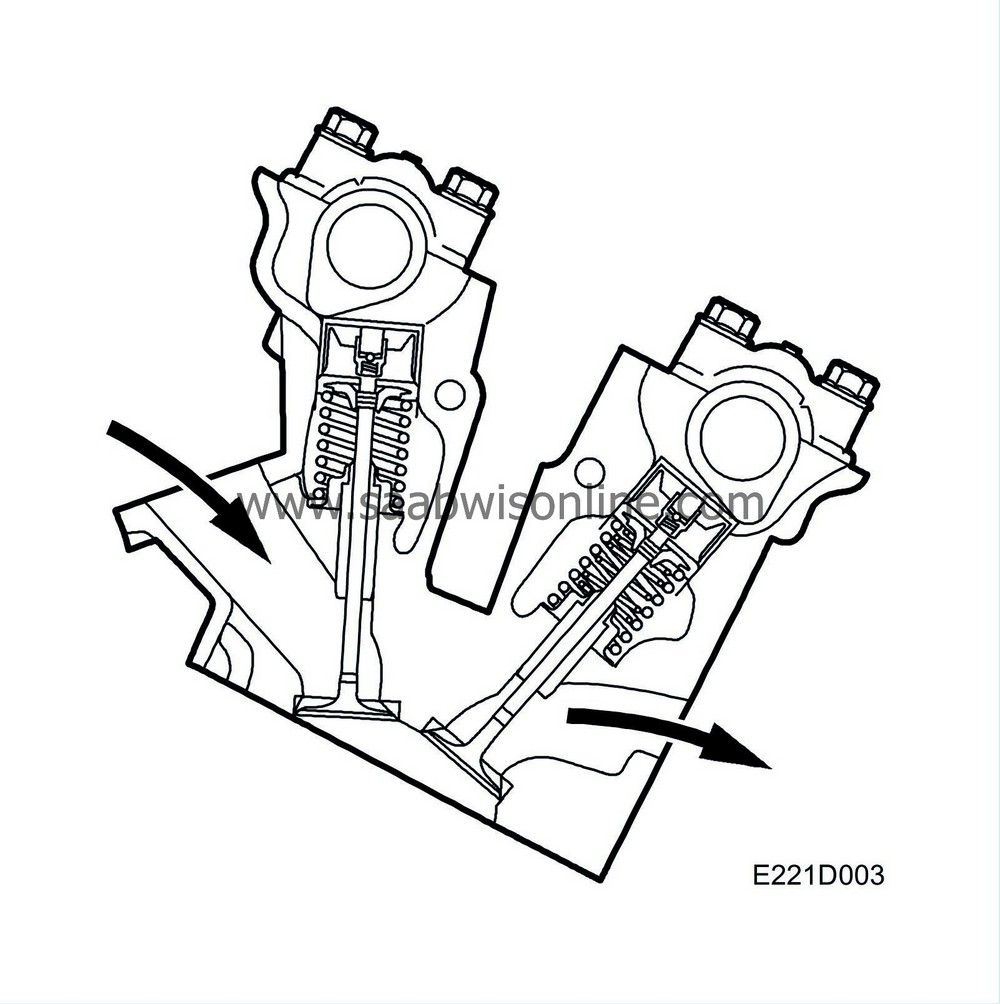
The engine has two cylinder heads, called the rear cylinder head (cylinders 1-3-5) and the front cylinder head (cylinders 2-4-6).
Each cylinder head is precision cast in light alloy and fitted to the cylinder block with bolts. The combustion chambers are hemispherical with four valves per cylinder and the spark plugs in the centre. This improves the flow of gases in the cylinders and also ensures effective combustion of the fuel-air mixture, which makes for a high-efficiency power unit.
The valve springs for the front cylinder head's exhaust camshaft are of “double spring type” while other valve springs are of “single spring type”.