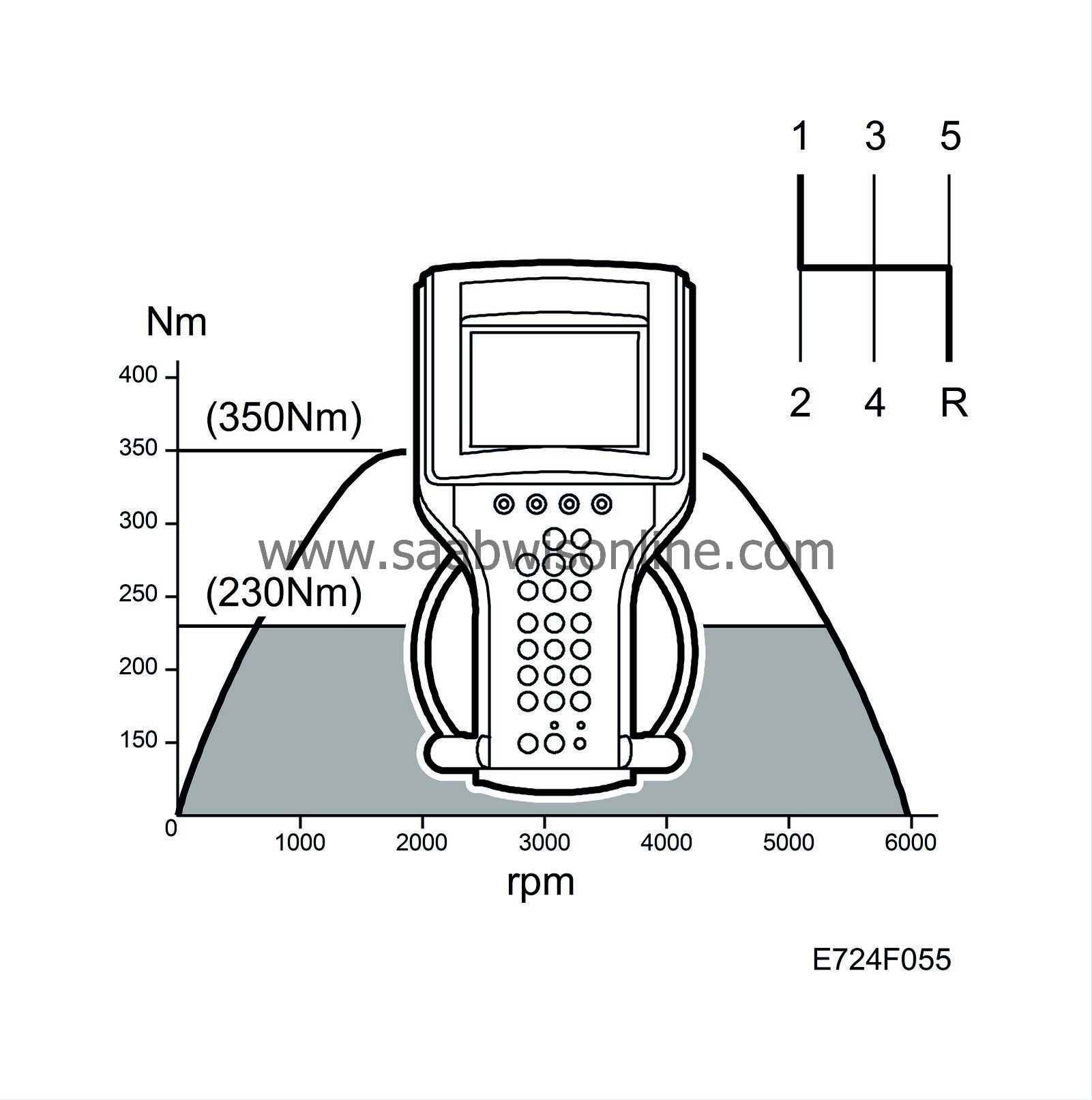
Power too low.
Read the instructions below then
start the fault diagnostic procedure.
Symptom: Low power.
Fault symptoms
Low power.
Conditions
The following conditions apply for the fault symptom concerned:
|
•
|
No diagnostic trouble codes for a car with this symptom description.
|
|
•
|
Pedal cable is adjusted correctly.
|
|
•
|
Brakes are not applied.
|
Diagnostic help
First, check that the three pressure sensors do not deviate more than 10 kPa from each other when the engine is stationary. This must be done because the mass air flow is later compared with the intake pressure and must therefore be correct. If the mass air flow does deviate, check first for air leaks before suspecting a defective mass air flow sensor.
Then, check the charge air control, knock control and fuel supply. Knock control is a normal engine function.
It is difficult to determine the degree of knocking to allow as it depends on the circumstances.
The following factors increase the tendency of knocking:
|
•
|
High coolant and outdoor temperatures.
|
Diagnostic tool functions related to this fault:
|
•
|
Atmospheric absolute pressure, unit kPa.
|
|
•
|
Charge air absolute pressure, unit kPa.
|
|
•
|
Intake manifold absolute pressure, unit kPa.
|
|
•
|
Air mass, deviation from requested, unit %.
|
|
•
|
Air mass, deviation from calculated, unit %.
|
|
•
|
Engine torque used at actual RPM, unit %.
|
|
•
|
Charge air adaptation, unit %.
|
|
•
|
All values in the group ”AIR MASS REQUEST”.
|
|
•
|
Activation of charge air control valve.
|
Refer also to the description of readings and
activations in ”Fault diagnosis, general” for more information.
Check the wiring
Jiggle the wiring harness at several points and in different directions to check if there are intermittent breaks and short-circuits in the leads. Observe the multimeter, test lamp or diagnostic instrument during the test.