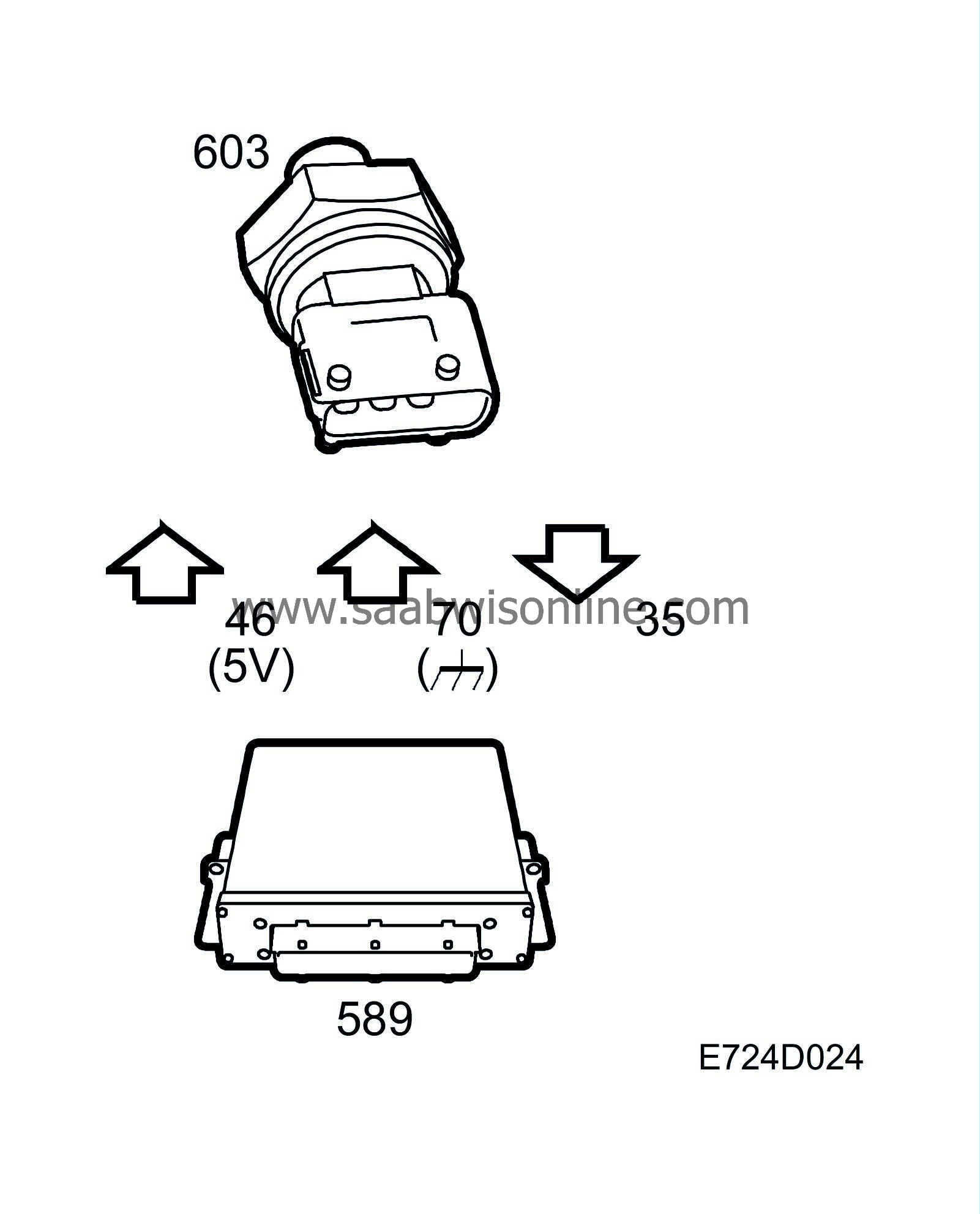
Charge air absolute pressure sensor
| Charge air absolute pressure sensor |
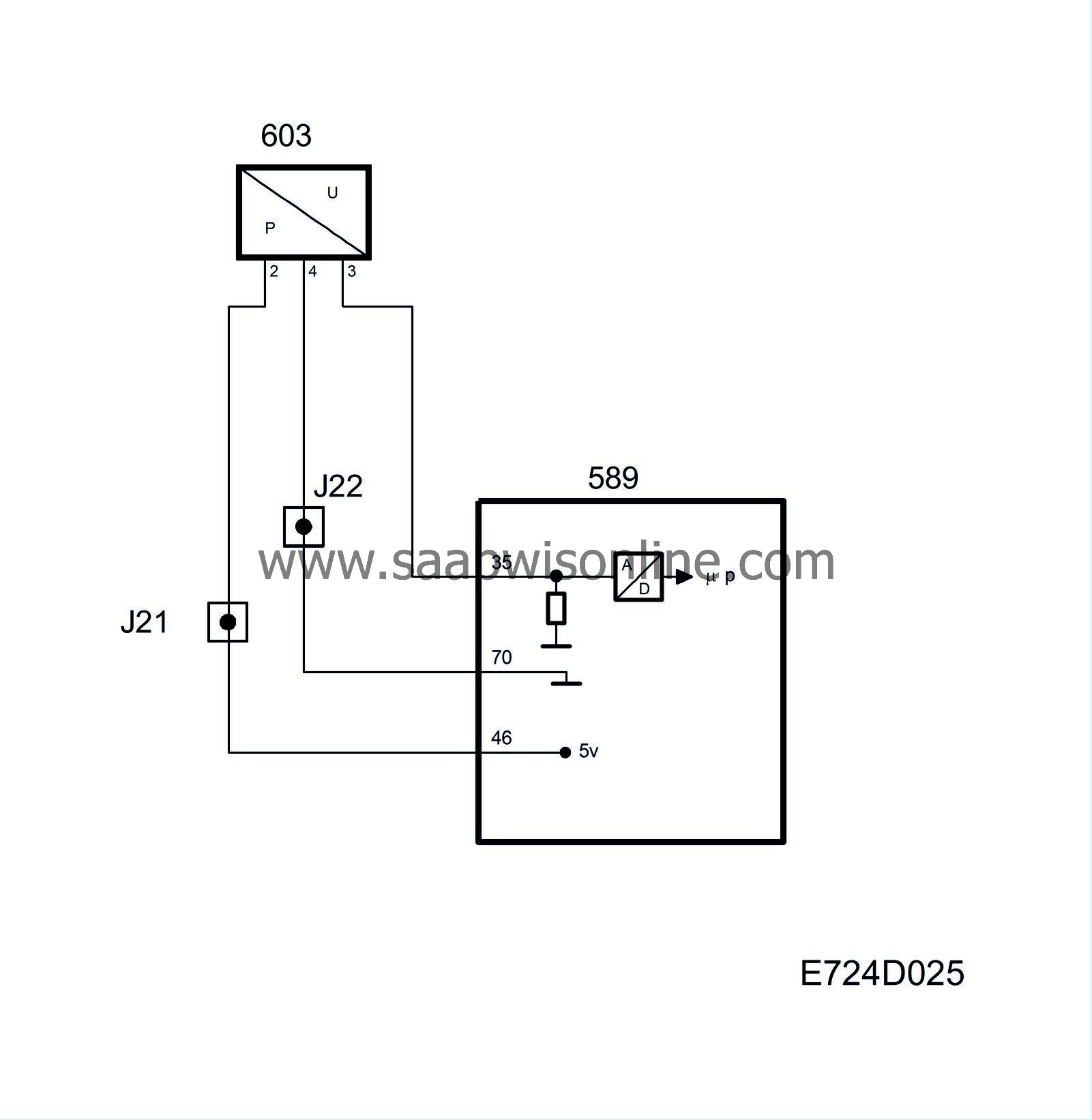
The pressure sensor contains two metal-coated ceramic discs mounted close together. The disc closest to the pressure connection is thinner and bends when it comes under pressure. This modifies the capacitance between the metal coatings of the discs as a function of the pressure. Built into the sensor is a circuit which converts the capacitance to an analogue voltage. The pressure sensor is connected to the engine's intake manifold via a hose before the throttle and is supplied with 5 V from control module pin 46 and grounded via control module pin 70.
Depending on the pressure in the charge air pipe, the pressure sensor applies a proportional voltage to control module pin 35.
The air mass control system determines which air mass/combustion is be drawn in during the cylinder's intake stroke. The value corresponds to the engine's torque.
The throttle control should set the throttle so that the actual air mass/combustion is the same as that requested.
If the density of the air before the throttle is high, a smaller throttle angle will be required than for low air density. The density of the air is therefore calculated by the control module from the charge air pressure and intake air temperature.
At normal atmospheric pressure, 100 kPa, the voltage from the sensor is about 2.1 V.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
If the sensor voltage is too low, diagnostic trouble code P1107 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If the sensor voltage is too high, trouble code P1108 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If the pressure value is implausible, diagnostic trouble code P1106 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If the hose to the sensor breaks, diagnostic trouble code P1105 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Density compensation of the throttle angle is blocked.
|
|