Fuel injection, basic function
|
|
Fuel injection, basic function
|
|
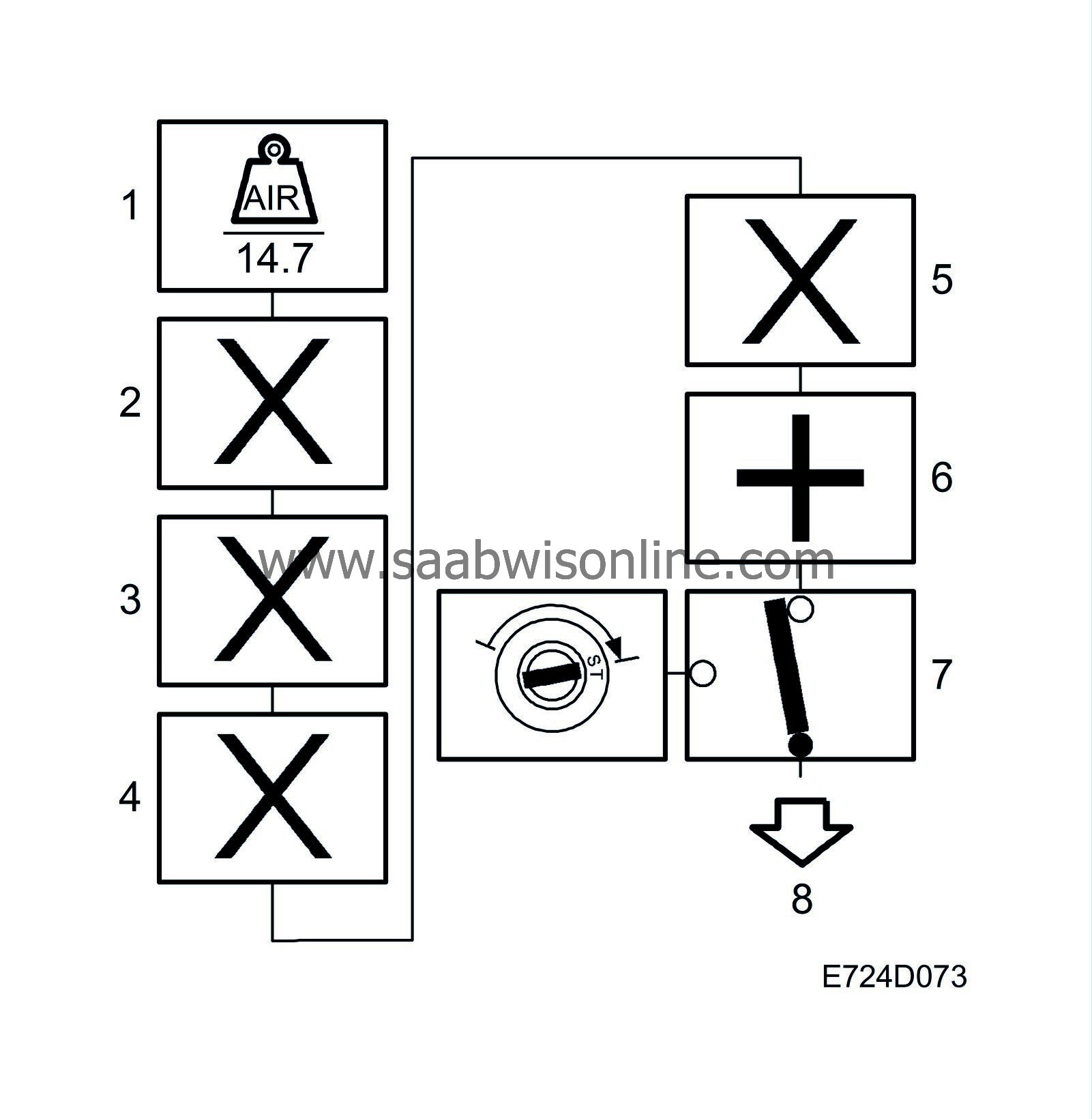
1.
|
Basic calculation of fuel mass/combustion
The current air mass/combustion is divided by 14.7 and sent to box 2. The unit is now mg petrol/combustion.
|
|
2.
|
Compensation
In the case of a cold engine, shortly after starting, rapid load changes, knocking or a high load, the current value is multiplied by a compensation factor.
|
|
3.
|
Closed loop
The closed loop control system value is also used as a multiplier. The value is sent to box 4.
|
|
4.
|
Correction for purging
Multiply by the value for purging adaptation. The value is sent to box 5.
|
|
5.
|
Multiplicative adaptation
The multiplicative adaptation value is also used as a multiplier and the new value sent to box 6.
|
|
6.
|
Additive adaptation
The additive adaptation value is added and the new value sent to box 7.
|
|
7.
|
Starting fuel quantity
If the engine has not yet started, starting fuel is selected. The value is sent to box 7.
|
|
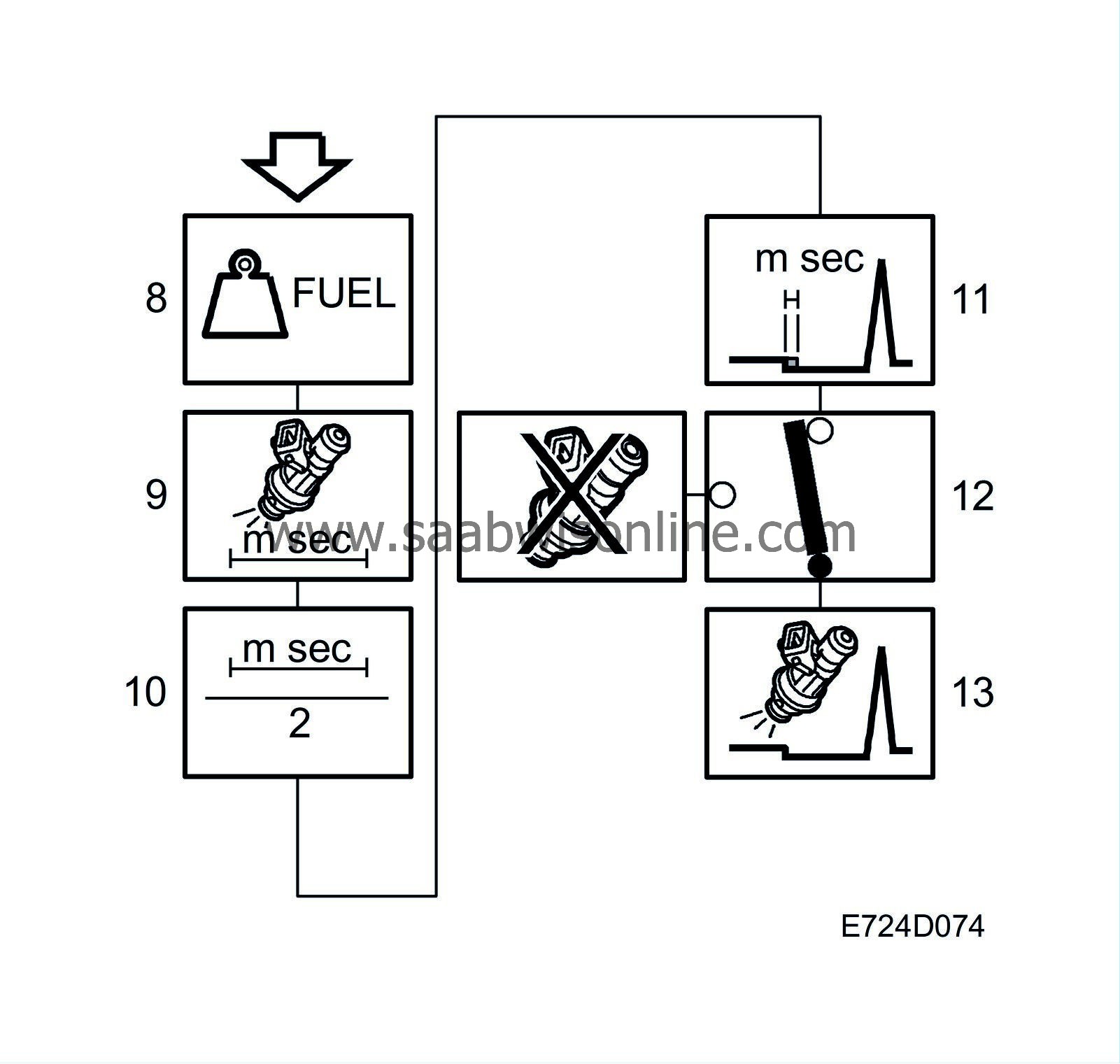
8.
|
Fuel mass/combustion to be injected
Fuel mass/combustion is the petrol mass that is to be supplied to the engine. The value is sent to box 9.
|
|
9.
|
Injector opening duration
Converts the value into the time the injector must be open and the new value is sent to box 10.
|
|
10.
|
Injection twice/combustion
Before the camshaft position is found, injection takes place twice per combustion. The injection duration is then divided by two. The current value is sent to box 11.
|
|
11.
|
Voltage-dependent needle lift time added
Add the injector's time delay, which is voltage-dependent. The value is sent to box 12.
|
|
12.
|
Fuel shut-off
If fuel shut-off is not active, the value will be sent to box 13.
|
|
13.
|
Activation of injector
At a specific crankshaft angle, the microprocessor will control the transistor for the injector that is next in the firing order.
|




