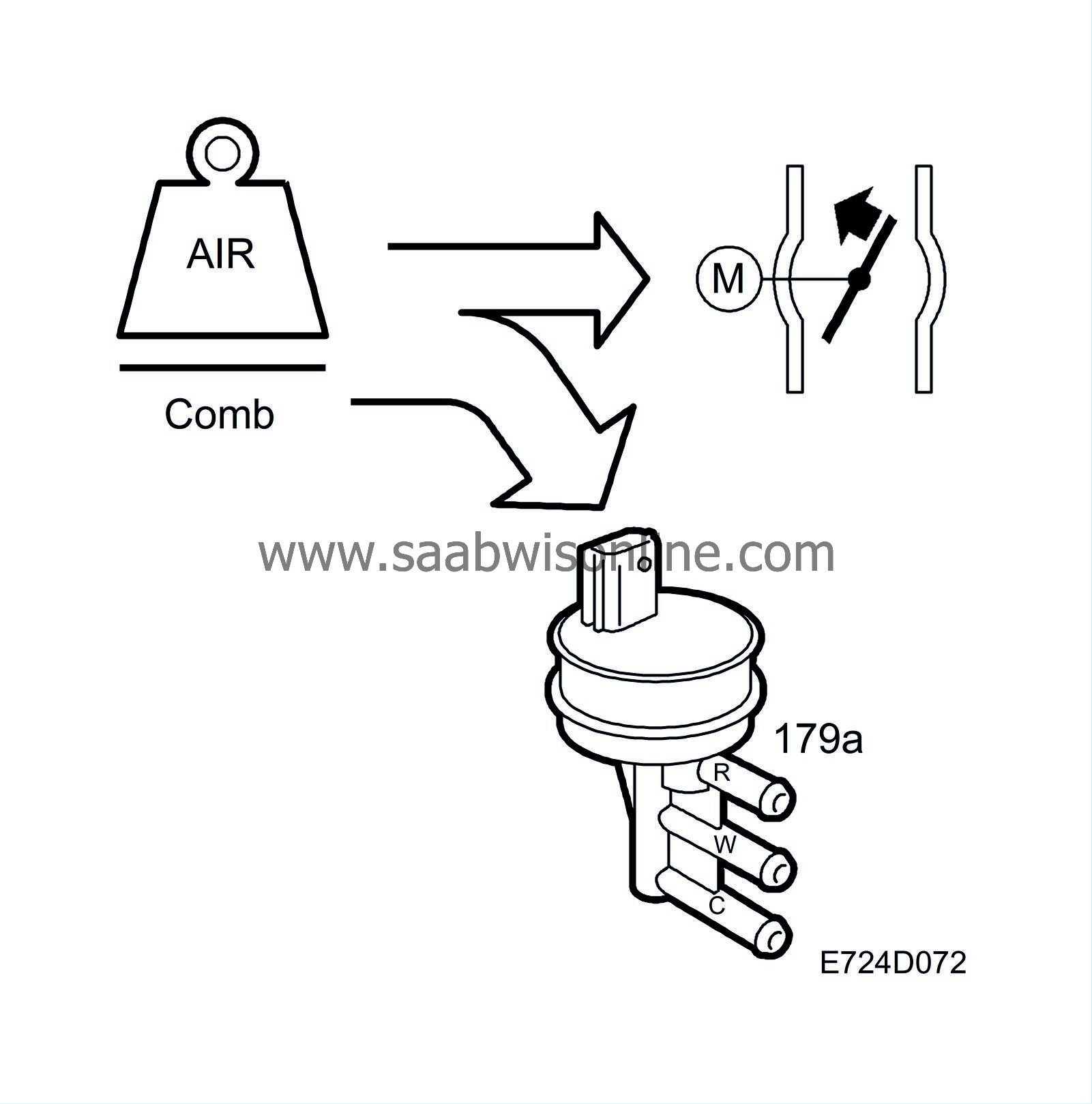
Turbo control
| Turbo control |
The solenoid valve is supplied with current from +15 and is grounded from control module pin 13 with a 32 Hz PWM signal. The compressor flow increases with the pulse ratio.
When the requested air mass/combustion is too great to be governed only by the throttle, the turbo control must provide the exceeding requirements. The exceeding portion is converted into a PWM signal, which governs the charge air control valve.
The values for the absolute atmospheric pressure and the intake air temperature are used to correct the conversion. At low atmospheric pressures or high intake air temperatures, a greater PWM ratio will be required to obtain the same air mass/combustion.
The control module then checks that the current air mass/combustion corresponds to that requested. If necessary, the PWM ratio is finely adjusted by multiplying it with a correction factor.
The correction factor (adaptation) is stored in the control module memory and is always included in the calculation of the PWM ratio.
This is so that the current air mass/combustion will equal the requested as soon as possible after a load change has occurred. The adaptation limit is 100%.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P1662 will be generated in the event of a break or short-circuit to ground.
|
|
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P1663 will be generated in the event of a short-circuit to B+.
|
|
| • |
If the air mass per combustion is greater than the requested, diagnostic trouble code P1549 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Charge air adaptation is blocked.
|
|
| • |
The requested air mass per combustion is limited to 600 mg/c.
|
|
| • |
|
|||||||