Ignition discharge module
| Ignition discharge module |
| Ignition |
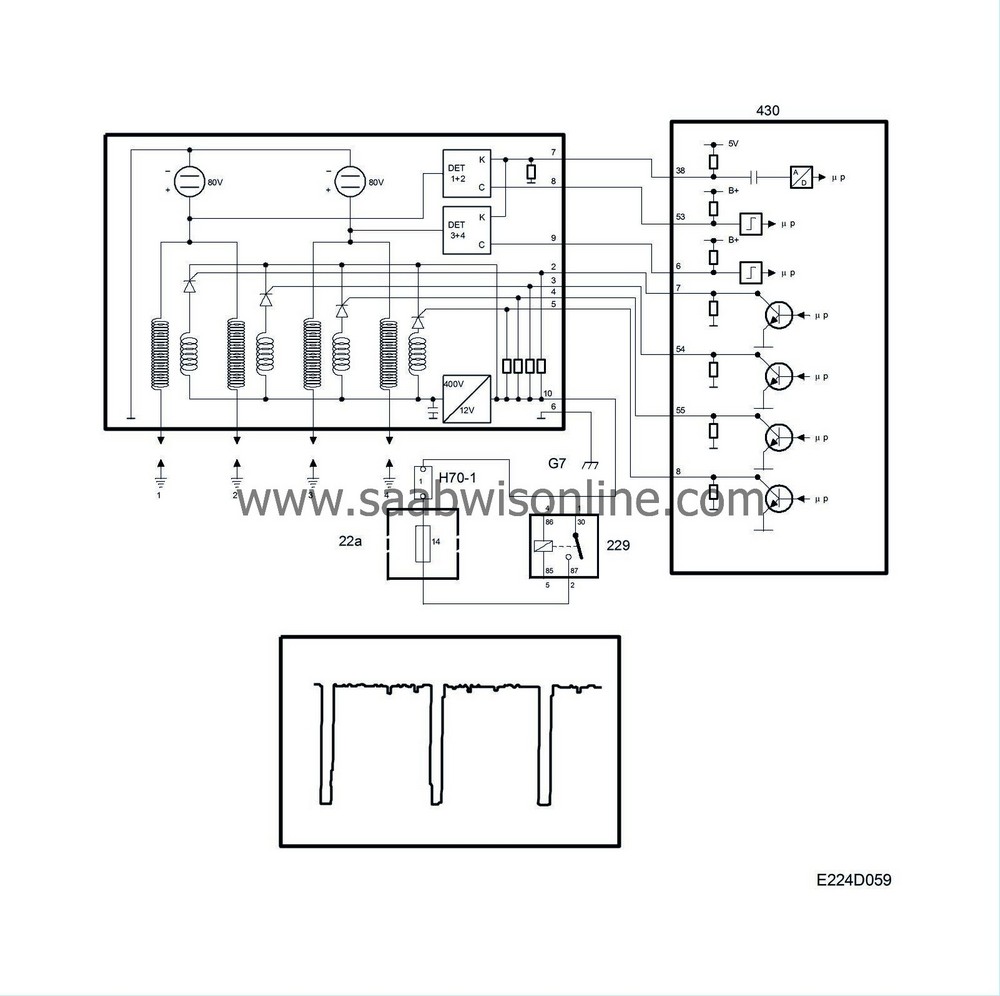
The ignition discharge module is located on the camshaft cover above the spark plugs. It contains 4 ignition coils, the secondary winding of which are connected to the spark plugs.
The ignition discharge module is powered with B+ from the main relay and is grounded to grounding point G7.
When the main relay operates, B+ is fed to the ignition discharge module, which converts the 12 V to 400 V DC and stores it in a capacitor. The 400 V is connected to one of the poles of the primary winding on each of the 4 ignition coils.
There are 4 trigger leads running from the control module to the ignition discharge module connected as follows:
| • |
Cylinder 1 is connected to control module pin 7.
|
|
| • |
Cylinder 2 is connected to control module pin 54.
|
|
| • |
Cylinder 3 is connected to control module pin 55.
|
|
| • |
Cylinder 4 is connected to control module pin 8.
|
|
When the control module grounds pin 7, the other pole on the primary winding of the ignition coil for cylinder 1 will be connected to the B+ input on the ignition discharge module. 400V is stepped up to maximum 40kV in the ignition coil for cylinder 1. Ignition takes place for cylinder 2, 3 and 4 in the same way.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
If there is an open circuit in the power supply to the ignition discharge module, the voltage on all the trigger leads will be 0V and diagnostic trouble code P1310 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If a break occurs in an individual trigger lead, no diagnostic trouble code will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
Fuel shut-off| Combustion signals, synchronization |
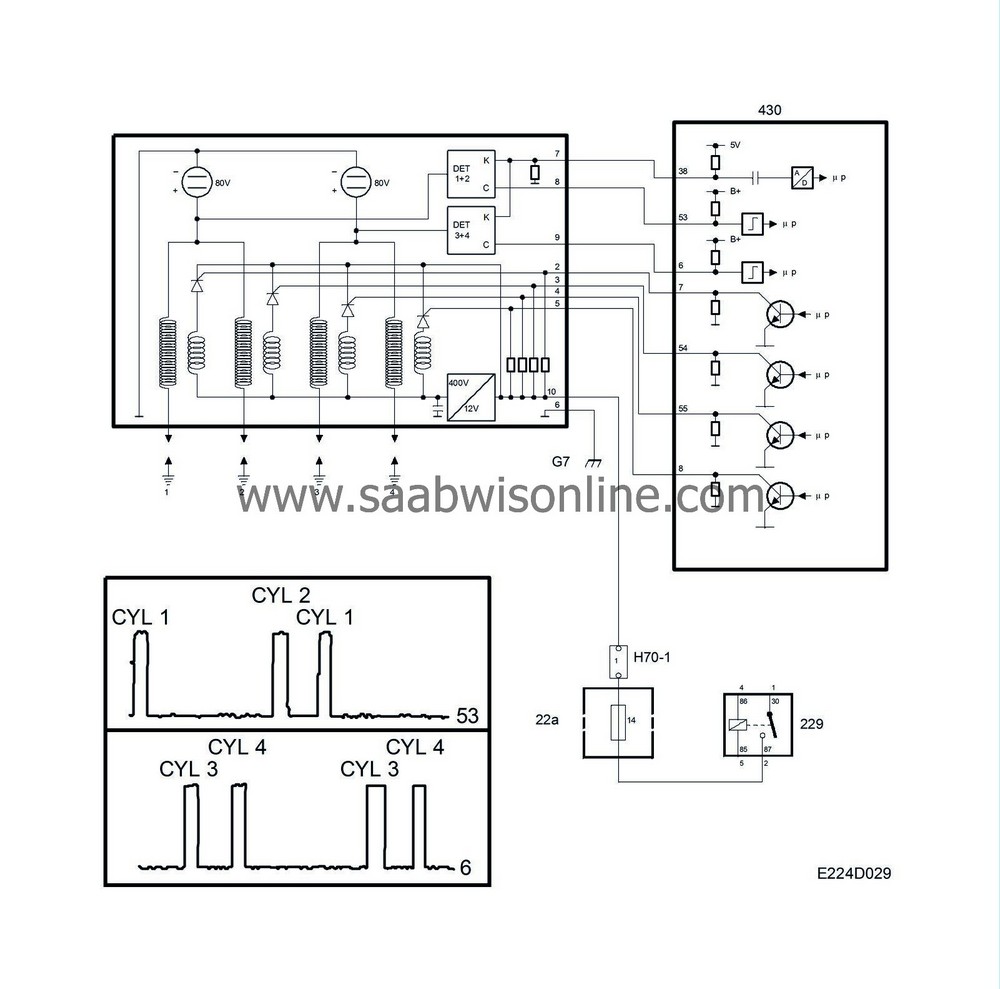
The Trionic T7 has no camshaft position sensor as normally required for sequential knock control and fuel injection.
On starting, the control module is not aware of which of the cylinders 1 or 4 that is in compression position. Consequently, ignition takes place in cylinders 1 and 4 simultaneously. Ignition in cylinders 2 and 3 takes place in the same way.
The control module must determine whether combustion occurs in cylinder 1 or 4 or in cylinder 2 or 3 when they are triggered. This is carried out as follows:
One pole of the secondary windings of the 4 ignition coils is normally connected to the relevant spark plug. The other pole is not grounded direct but connected to 80 V. This means that a voltage of 80 V is always present across the spark plug gap except just as the spark is produced.
When combustion takes place, the temperature in the combustion chamber is very high. The gases are ionized and begin to conduct current. This means that current passes between the spark plug electrodes without producing a spark.
As the circuit is completed between the spark plug electrodes, the current (80 V) flowing across the gap drops sharply. The voltage drop will be proportional to the pressure and temperature in the combustion chamber.
Two detectors measure the voltage drop across the cylinder pairs 1+2 and 3+4 respectively. If combustion takes place in cylinder 1 or 2, the ignition discharge module will send a B+ pulse to control module pin 53. In the same way, the ignition discharge module will send a B+ pulse to control module 6 if combustion takes place in cylinder 3 or 4.
If cylinders No. 1 and No. 4 are triggered and a B+ pulse is received on control module pin 53 at the same time, the control module knows that cylinder No. 1 has fired.
As soon as combustion signals are received on control module pins 53 and 6, both ignition and fuel injection are synchronized to the engine firing order.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
If ignition and the camshaft position are not synchronized, diagnostic trouble code P0340 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
If a break occurs in any of the leads to control module pins 53 and 6, no synchronization of the ignition or fuel injection will take place. Knock detection then takes place on cylinder Nos. 1+4 and cylinder Nos. 2+3 at the same time.