Knock control
| Knock control |
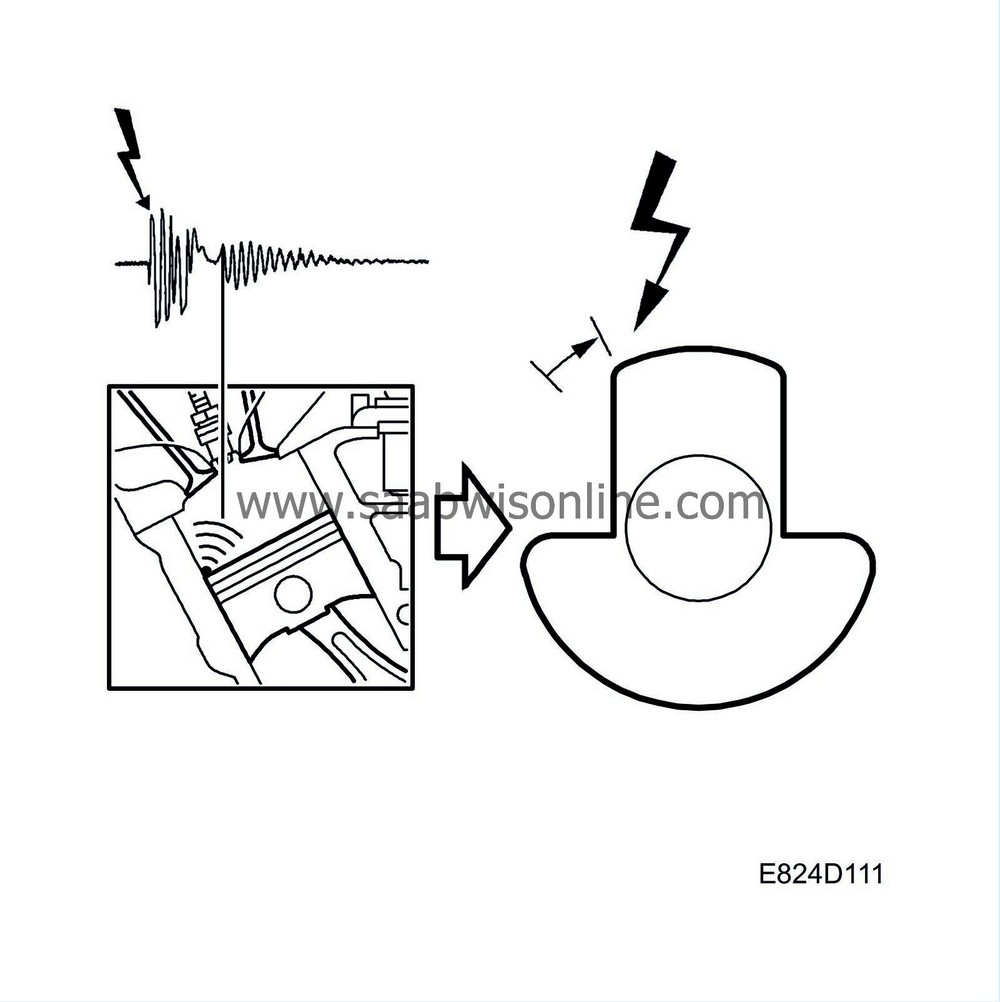
Trionic T7 does not have a conventional knock sensor. Instead, the ignition discharge module analyses the ionization flow across the spark plug gaps for all the cylinders in the relevant cylinder bank and sends a knock signal from each cylinder to control module pin 38 (Bank 1) or pin 62 (Bank 2).
From the combustion signals, the control module knows which cylinder has fired and if at the same time a knock signal above a certain level is registered by the control module, the control module retards the ignition in steps for the cylinder concerned until the knocking stops. Timing correction then gradually returns to zero.
If the mean value of ignition retardation on all cylinders exceeds a certain level, fuel enrichment takes place. If the mean value of ignition retardation on all cylinders rises further despite fuel enrichment, the maximum permitted mass air flow/combustion will be limited.
Since the control module expects the knock signal to have a certain level as the spark is produced, actual knock detection in the cylinder concerned begins only after a spark has been produced.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
If an open or short circuit occurs in the knock lead between the ignition discharge module for bank 1 and the control module, diagnostic trouble code P0327 is generated.
|
|
| • |
If an open or short circuit occurs in the knock lead between the ignition discharge module for bank 2 and the control module, diagnostic trouble code P0332 is generated.
|
|