Turbo control
| Turbo control |
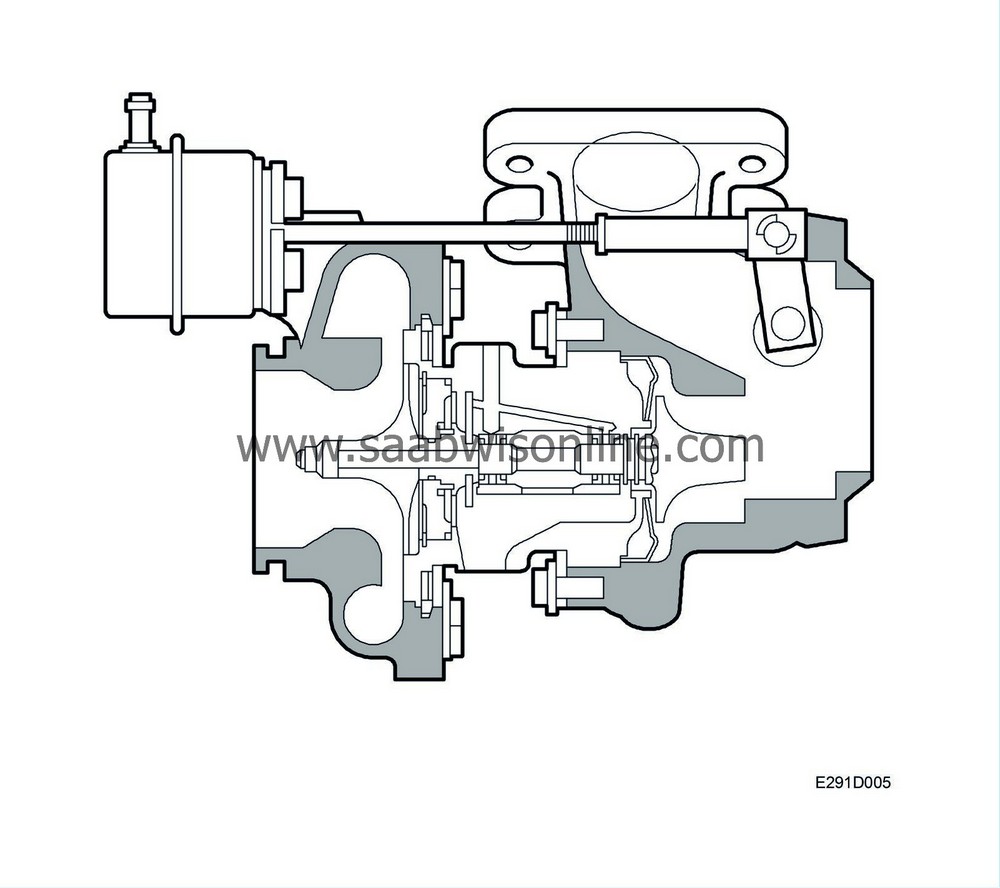
The turbo pressure in the inlet manifold depends mainly on the engine speed and load. However, at higher loads, the turbo pressure is limited by the wastegate valve.
The wastegate valve is a flap valve that closes and opens a bypass duct in parallel with the turbine wheel. The flap valve is actuated by a rod connected to a diaphragm in a housing located near the compressor housing. There is a spring in the diaphragm housing that closes the flap valve.
The wastegate valve for the turbo pressure is closed at low and normal engine loads. As the load increases and the turbo pressure approaches its maximum value, the load that the spring exerts on the diaphragm is balanced and then exceeded and the wastegate valve opens the bypass duct. This causes the turbo rpm to drop and the pressure is reduced.
The air flow from the turbo compressor is controlled by a solenoid valve which controls the wastegate valve pneumatically. The engine control module (ECM) ensures that the current air mass/combustion complies with that requested and sends PWM signals to control the solenoid valve.
For further information about turbo control and the solenoid valve see Group 2 “Engine control system, Trionic 4-cyl.”, Technical description, Turbo control
 .
.