Brief description, anti-theft alarm
| Brief description, anti-theft alarm |
| General |
The theft protection on the car consists of two different functions, the immobilizer which is standard on all cars, and the anti-theft alarm which is an option. The theft protection functions are controlled by TWICE.
| Immobilizer |
The immobilizer prevents the car starting if the wrong key is used. The fuel supply is shut off and the starter motor relay blocked. The car key contains a transponder with a unique identification code which is received by a receiver unit. The receiver is located in the ignition lock.
The receiver, which is connected to TWICE, sends the code to TWICE which is programmed to recognize the car keys. If the right key is inserted in the ignition (ignition position ON), the engine can be started. If a faulty transponder or one which does not belong to the car is used, “KEY NOT ACCEPTED” appears on the SID display.
In the event of a fault on the receiver unit or transponder, the remote control can be used instead to mobilise the car. The car can be mobilised by pressing a button on the remote control after the ignition key has been turned to the ON position.
| Anti-theft alarm |
The anti-theft alarm can be factory-fitted or installed as an accessory.
The anti-theft alarm is armed/disarmed using the remote control. On US/CA/LA markets, it can also be armed/disarmed using the key in the driver's door or tailgate (disarm). If the anti-theft alarm is armed and the key placed in the ignition and turned, the alarm is disarmed when the correct identification code is received from the transponder.
The anti-theft alarm has the following inputs for tripping the alarm:
| • |
Door switches
|
|
| • |
Luggage compartment switch
|
|
| • |
Bonnet switch
|
|
| • |
Ignition lock (position ON with incorrect key)
|
|
| • |
Glass breakage sensor
|
|
| • |
Angle sensor (accessory)
|
|
A tripped alarm is indicated by:
| • |
Direction indicators
|
|
| • |
Siren
|
|
The behaviour of the anti-theft alarm depends on the market.
Door switches
The door switches are mounted in the frame of the door concerned and grounded through the switch mounting screw to the bodywork. The switches are supplied with a pulse width-modulated (approx. 3.5%) voltage via a 1 kohm pull-up in TWICE. When a door is opened, the switch is closed and the control module input is grounded.TWICE sends out information on the door position to the bus, where it is used by DICE for example for interior lighting. The anti-theft alarm also uses the door switch.
Luggage compartment switch
The luggage compartment switch is fitted in the tailgate lock. The switch is supplied with a pulse width-modulated (approx. 3.5%) voltage via a 1 kohm pull-up in TWICE. When the tailgate is opened, the switch is closed and the control module input is grounded.TWICE sends out information on the tailgate position to the bus, where it is used by DICE for example for the luggage compartment lighting. The anti-theft alarm also uses the switch.
Key switch, luggage compartment disarm
The luggage compartment switch is fitted in the tailgate and is grounded through the switch via the bodywork. The switch is supplied with a pulse width-modulated (approx. 3.5%) voltage via a 1 kohm pull-up in TWICE. When the key is turned in the lock, the switch is closed and the control module input is grounded. The tailgate is disarmed.Bonnet switch
The bonnet switch is placed at the rear left of the engine bay. The switch is supplied with a pulse width-modulated (approx. 3.5%) voltage via a 1 kohm pull-up in TWICE. When the bonnet is opened, the switch is closed and the control module input is grounded.TWICE uses the bonnet switch to trip the anti-theft alarm if the bonnet is opened when the alarm is armed.
Glass breakage sensor
The glass breakage sensor is located in the rear roof light and is powered from TWICE.The glass breakage sensor reacts to the sound of breaking glass. The sensor is of the active type and makes its own assessment and decision on whether the glass has been broken.
The sensor can be disconnected by pressing the NIGHT PANEL button on the SID unit when the key is not in the ignition.
Angle sensor
The angle sensor is placed under the right front seat and is powered from TWICE.The sensor reacts to the car's angle and sets off the alarm if the car is raised on one side, just before the wheel is lifted off the ground.
It does not react for example if the car is buffeted by a strong wind. The sensor should however be disconnected if the car is to be transported on a ship as the anti-theft alarm may trip.
The sensor can be disconnected by pressing the NIGHT PANEL button on the SID unit when the key is not in the ignition.
Siren
The siren is placed on the front edge of the front left wheel housing. The siren has two piezo-electric sound emitters and is equipped with batteries so that it can sound in the event of a power failure from the car's ordinary battery or if someone cuts the leads to the siren.Direction indicators
The car's direction indicators are activated via bus information from TWICE which DICE uses to turn on the direction indicators.LED (Light Emitting Diode)
The LED is placed on the top of the dashboard and is powered from TWICE.The LED is used to indicate the status of the anti-theft alarm:
| - |
A double flash means that the car is immobilized.
|
|
| - |
A flash every 3 seconds means that the anti-theft alarm is armed.
|
|
| - |
A fast flash during the delay time means that a door or the bonnet or tailgate is open.
|
|
| - |
A continuous light during the delay time means that everything is OK.
|
|
| Remote control |
The remote control is used to operate the central locking and to arm and disarm the anti-theft alarm.
The remote control is fitted with three buttons which have the following function:
| • |
Lock/arm anti-theft alarm
|
|
| • |
Unlock/disarm anti-theft alarm
|
|
| • |
Unlock tailgate/disarm anti-theft alarm on tailgate
|
|
When a button on the remote control is pressed, a code is sent to a receiver. The receiver is connected to TWICE which performs the required command.
| P bus and I bus |
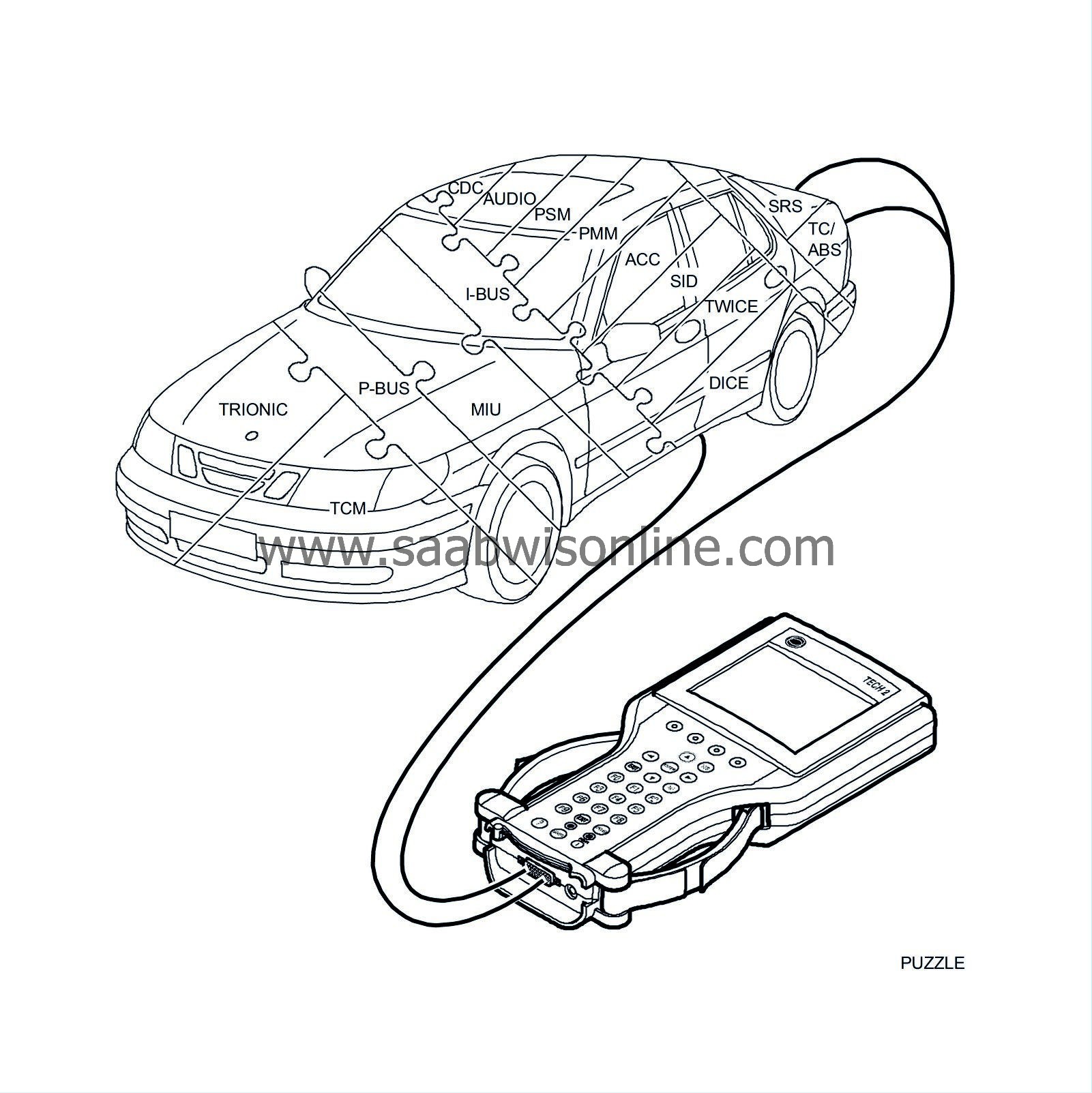
The buses are divided into the Powertrain bus (P-bus) and the Instrument bus (I-bus). Both buses are connected to the main instrument unit (MIU). The buses are electrically isolated from each other.
The data transfer rate on the P bus is ten times faster than on the I bus.
All the information sent from one control module is accessible for all other control modules on the bus. The MIU is responsible for ensuring that information available on one bus is also available on the other bus.


