Turbo control
| Turbo control |
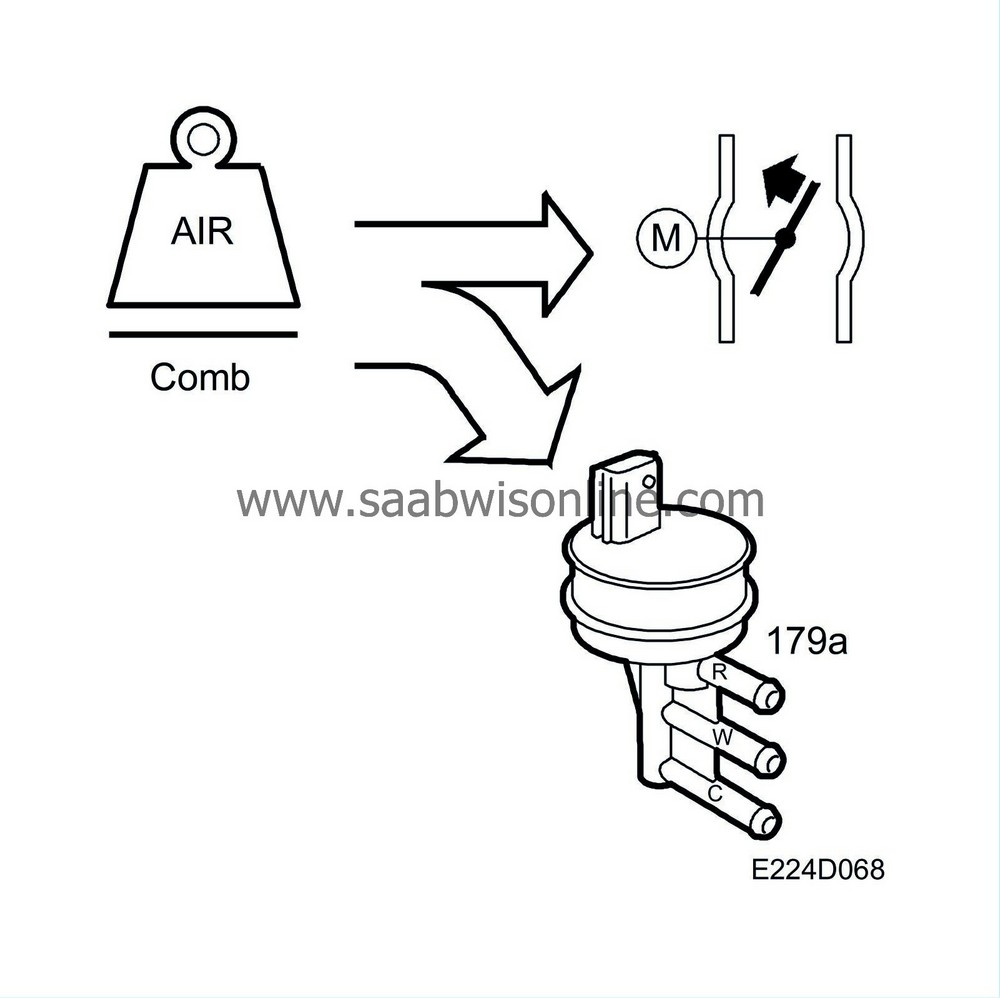
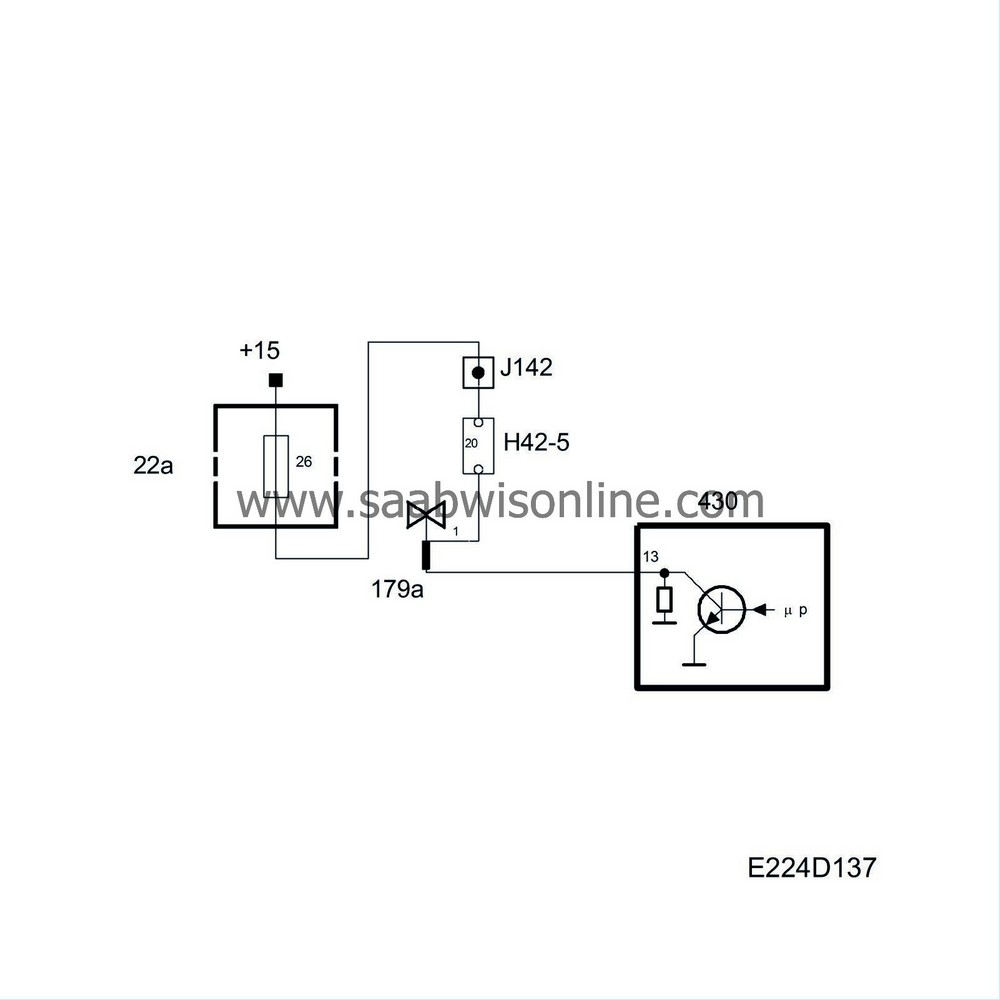
The airflow from the turbocharger is regulated by a solenoid valve, which controls the exhaust turbine wastegate pneumatically.
The solenoid valve is powered from +15 and is grounded from control module pin 13 with a 32 Hz PWM. The turbocharger flow increases as the pulse ratio increases.
When the requested air mass/combustion is too great to be regulated by the throttle alone, the turbo control must supply the excess requirement. The excess is converted to a PWM, which controls the charge air control valve.
The absolute barometric pressure and temperature of the intake air are used to correct the conversion. At low barometric pressure or high intake air temperature, a higher PWM ratio is required to achieve the same mass air flow/combustion.
The control module therefore makes sure that the current air mass/combustion corresponds with the requested. If necessary, the PWM ratio is finely adjusted by multiplying it with a correction factor.
The correction factor (adaptation) is stored in the control module memory and is always included in the calculation of the PWM ratio.
This is to ensure that the current air mass/combustion will correspond with the requested as soon as possible after a change in load. The limit for adaptation is 100%.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
If there is an open circuit or short circuit to ground, diagnostic trouble code P1662 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If there is a short circuit to B+, diagnostic trouble code P1663 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Charge air adaptation is blocked.
|
|
| • |
In regard to other turbo control system faults, the diagnostic tool will be of great help in obtaining a readout of charge air adaptation.
|
|||||||


