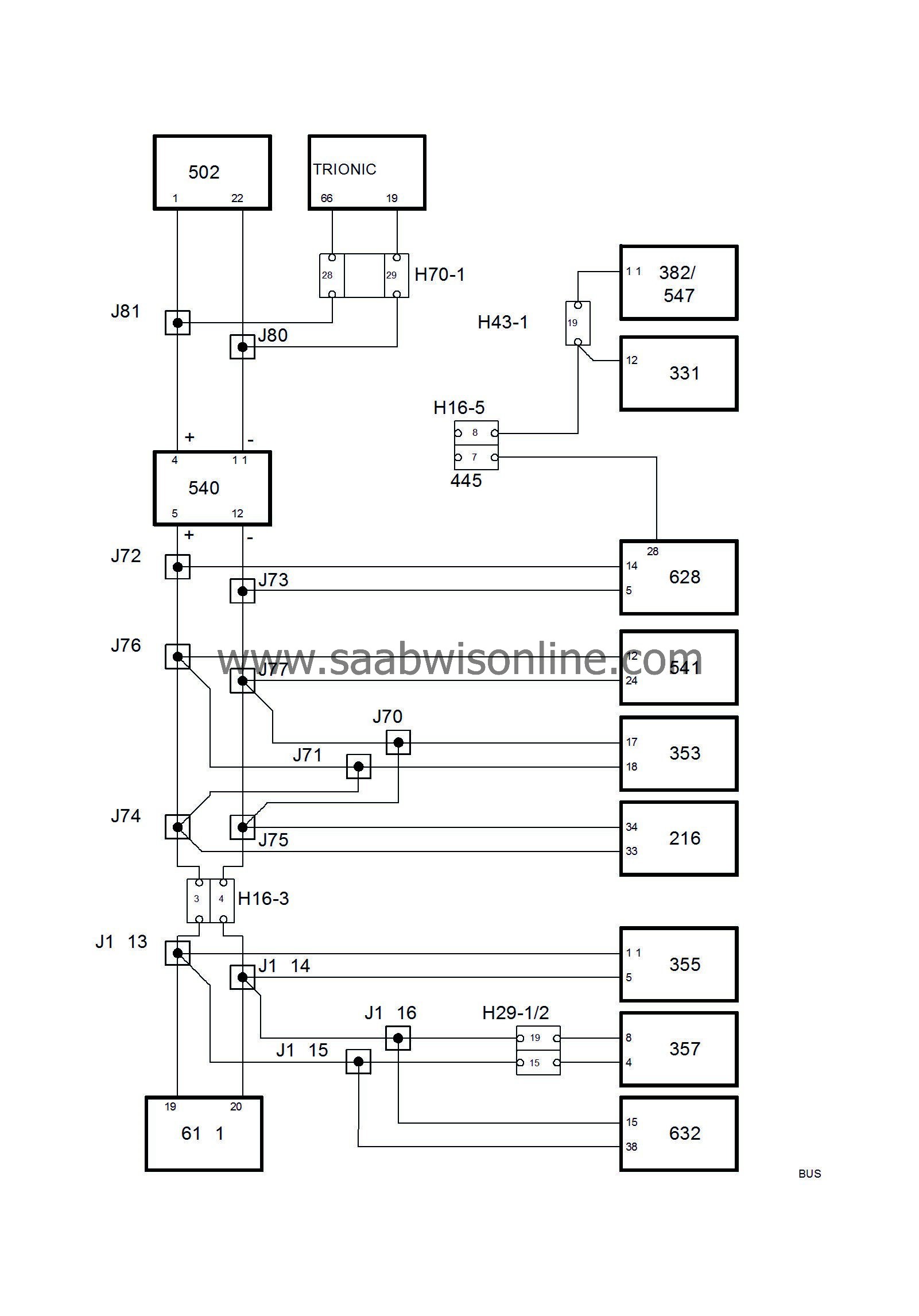
Bus communication
| Bus communication |
| • |
Trionic, engine management system (TRIONIC)
|
|
| • |
TCM (Transmission Control Module), control module for automatic transmission (502)
|
|
| • |
P-bus (Powertrain bus)
|
|
| • |
MIU (Main Instrument Unit) (540)
|
|
| • |
I-bus (Instrument bus)
|
|
| • |
SID (Saab Information Display) (541)
|
|
| • |
TWICE (Theft Warning Integrated Central Electronics) (632)
|
|
| • |
ACC (Automatic Climate Control) (216)
|
|
| • |
Audio system, main unit (353)
|
|
| • |
CDC (CD changer) (355)
|
|
| • |
PSM (Power Seat Memory) (357Dk)
|
|
| • |
PMM (Power Mirror Memory) (611)
|
|
| • |
DICE (Dashboard Integrated Central Electronics) (628)
|
|
| • |
Data link connector (H16-5/445)
|
|
| • |
Airbag (SRS) (331)
|
|
| • |
ABS (Anti Block System) (547)/TC-ABS (382)
|
|
| P-bus and I-bus |
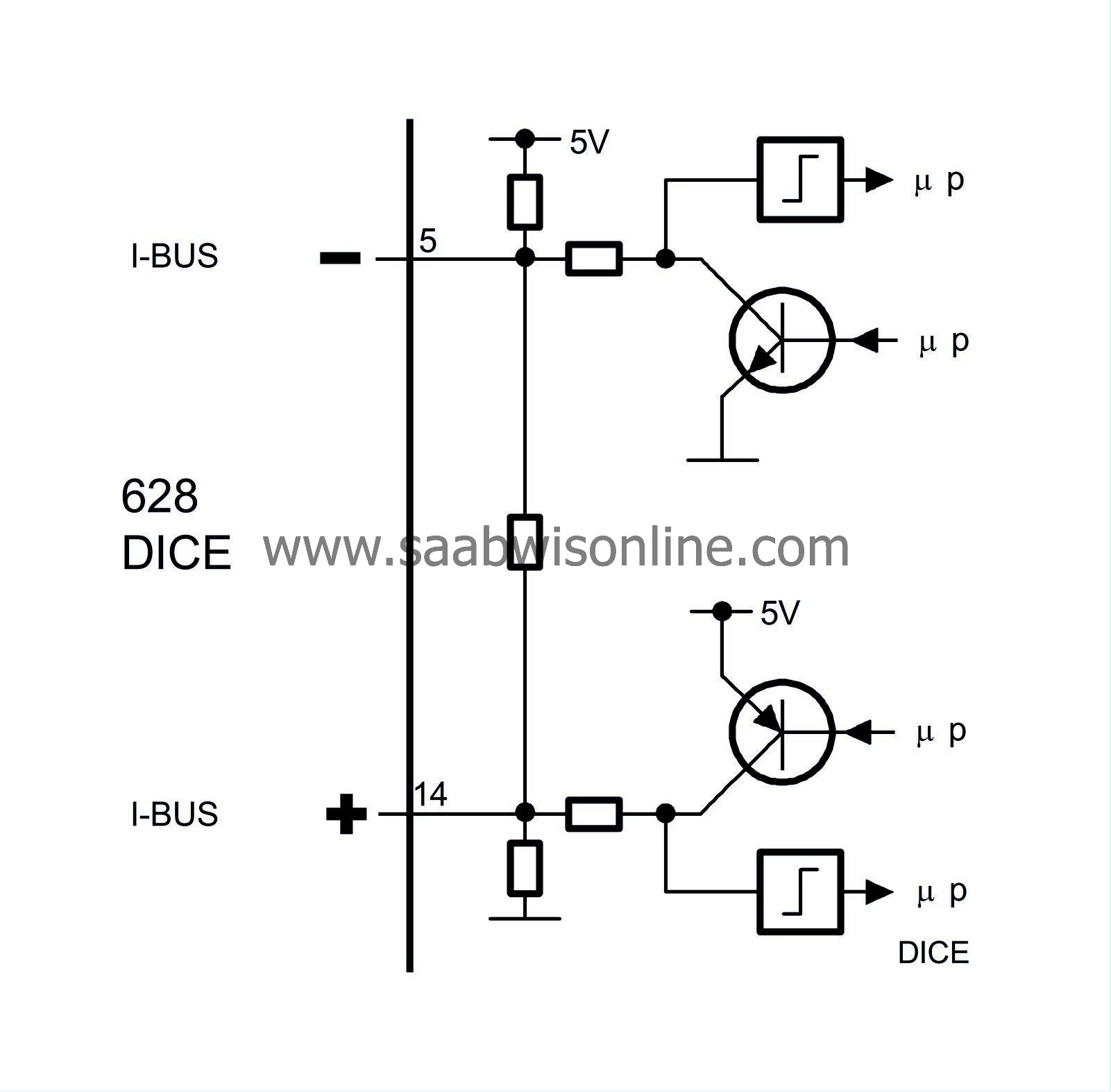
A bus is understood to be the leads over which information is sent digitally and serially. Digital means that the voltage difference between the leads has only two values, roughly 0 V and 5 V. The information is coded so that different combinations of 0 V and 5 V pulses have different meanings.
Serial means that the information is sent in ”packets” which are transmitted one after the other in rapid succession.
All the control modules in the Saab 9-5 are connected to the bus except those for the ABS and SRS.
The bus consists of a P-bus (Powertrain Bus) and an I-bus (Instrument Bus). Both buses are connected to the MIU (Main Instrument Unit). The buses are electrically isolated from each other.
The diagnostic tool is not connected directly to the bus but communicates via the DICE, one of the control modules connected to the I-bus, and so has access to all control modules connected to the bus.
The data transfer rate of the P-bus is ten times faster than that of the I-bus. The reason for this is that the powertrain systems need information with the least possible delay, as for example when providing air mass compensation when the selector lever is moved from N to D or torque limitation in connection with gear changing.
All the information sent from one control module is accessible for all other control modules on the bus. The MIU is responsible for ensuring that information available on one bus is also available on the other bus.
The control modules send out information on the bus at regular intervals. The time between two transmissions depends on the information being sent and varies between 10 milliseconds (0.010 seconds) and 1 second. Information is also sent out by the control modules whenever the information changes.
The transfer of information between the control modules takes place on two leads, bus+ (green lead) and bus- (white lead). The leads are twisted to reduce susceptibility to electrical interference.
| Diagnostics |
In a bus system, all units must be able to communicate with each other. For example, the engine cannot start unless the TRIONIC control module can receive the immobilization information emitted by TWICE.
Permanent bus faults
All communication between Tech 2 and the bus-connected systems goes via DICE. Irrespective of which system is being contacted, Tech 2 and DICE will check to see that all the bus-connected systems in the car are activated and communicating. If any bus-connected control module is missing, Tech 2 will detect this. This means that all the bus-connected control modules are communicating correctly if there is no warning from Tech 2.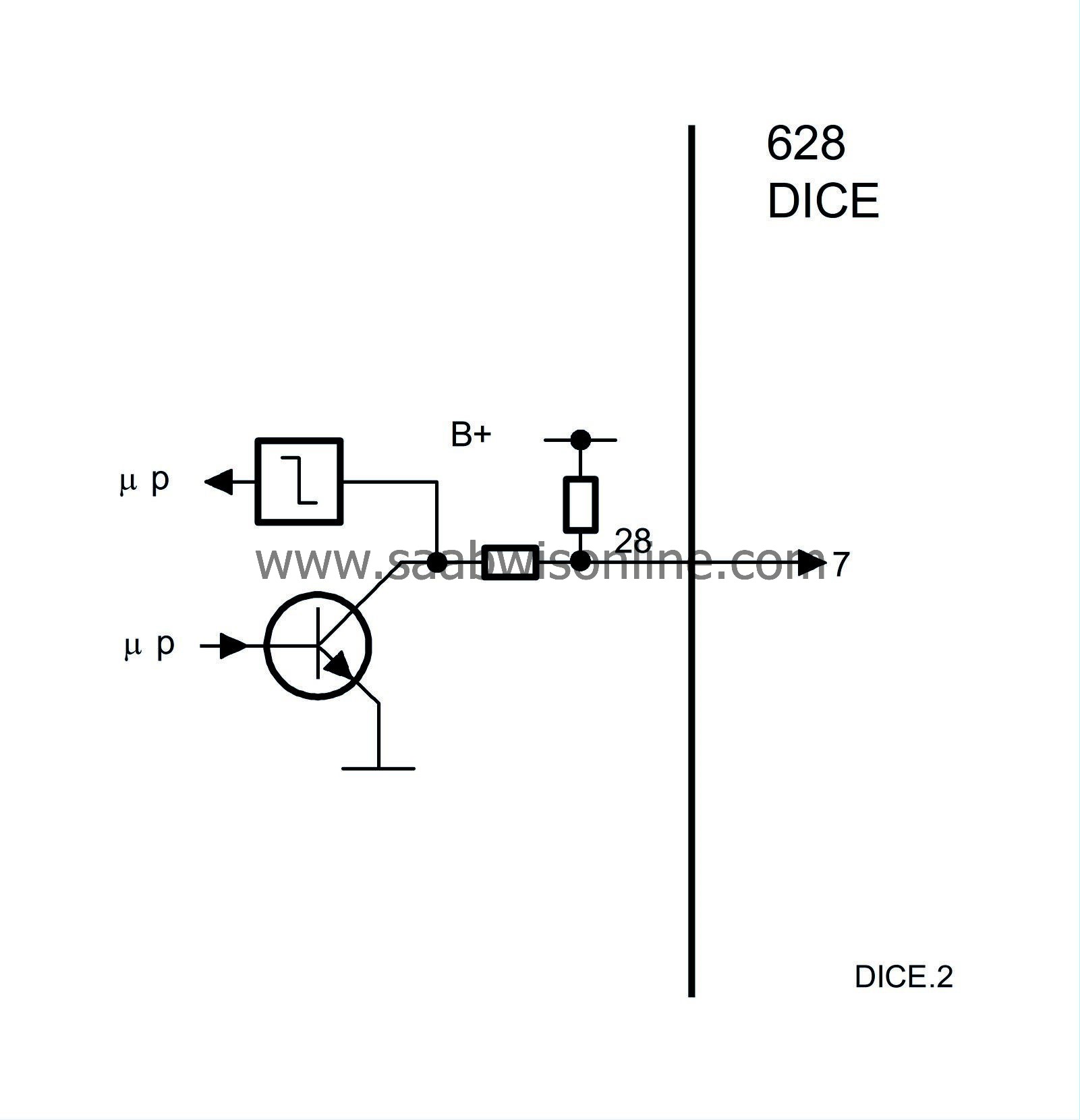
Intermittent bus faults
The Trionic control module and the transmission control module always check that all control modules from which they obtain information are communicating properly. If intermittent faults occur in bus communication, diagnostic trouble codes will be generated in the Trionic and transmission control modules. The cause of the fault may be that the control module concerned has lost its power supply or that one of the bus leads is disconnected.Incorrect values on the bus
Diagnostic trouble codes are set in Trionic and TCM if any information they receive from the bus has an incorrect value. The trouble code readout will refer to the faulty system.For further information on the bus, see Bus and diagnostics communication
| DICE uses the following information |
| DICE sends the following information |