Brief description
| Brief description |
| General |
A connection for a mobile phone is a standard feature in the car. It provides simultaneous power supply for charging the telephone battery. When the phone is in use, the sound emitted by a pre-selected source is automatically disconnected and changed to the sound of the telephone (line-in). The volume of the sound can be preset and adjusted during a call.
As an option, a mobile phone connection with a “handsfree” function is available. Handsfree means that a call can be taken without holding the receiver.
When a telephone is connected “handsfree”, the incoming telephone sound is fed into, and emitted by, the audio system. At the same time, the normal sound is disconnected. The outgoing telephone sound is emitted by a built-in microphone in the car.
The following unit in the audio system are used:
| • |
Main unit, Audio System
|
|
| • |
SID
|
|
| • |
Amplifier (Premium and Prestige only)
|
|
| • |
Speakers
|
|
| • |
Steering wheel switches
|
|
| • |
Telephone connection
|
|
| Main unit |
The main unit for the telephone system is the audio system main unit.
| Display |
The telephone system uses the SID to indicate that the telephone is active. The display information is sent on the bus from the audio system and read by SID.
| Amplifier |
The Premium and Prestige audio systems both have an external speaker to reproduce incoming telephone sound during a call.
| Speakers |
The audio system has side and centre speakers in the dashboard as well as in the front and rear doors. The Prestige system includes a bass speaker in the parcel shelf as well. These can reproduce incoming telephone sound during a call.
| Steering wheel switches |
The volume for the incoming telephone sound can be adjusted easily and safely with the steering wheel switches.
The switches are connected to SID which reads their positions and sends information to the main unit via the bus.
| P bus and I bus |
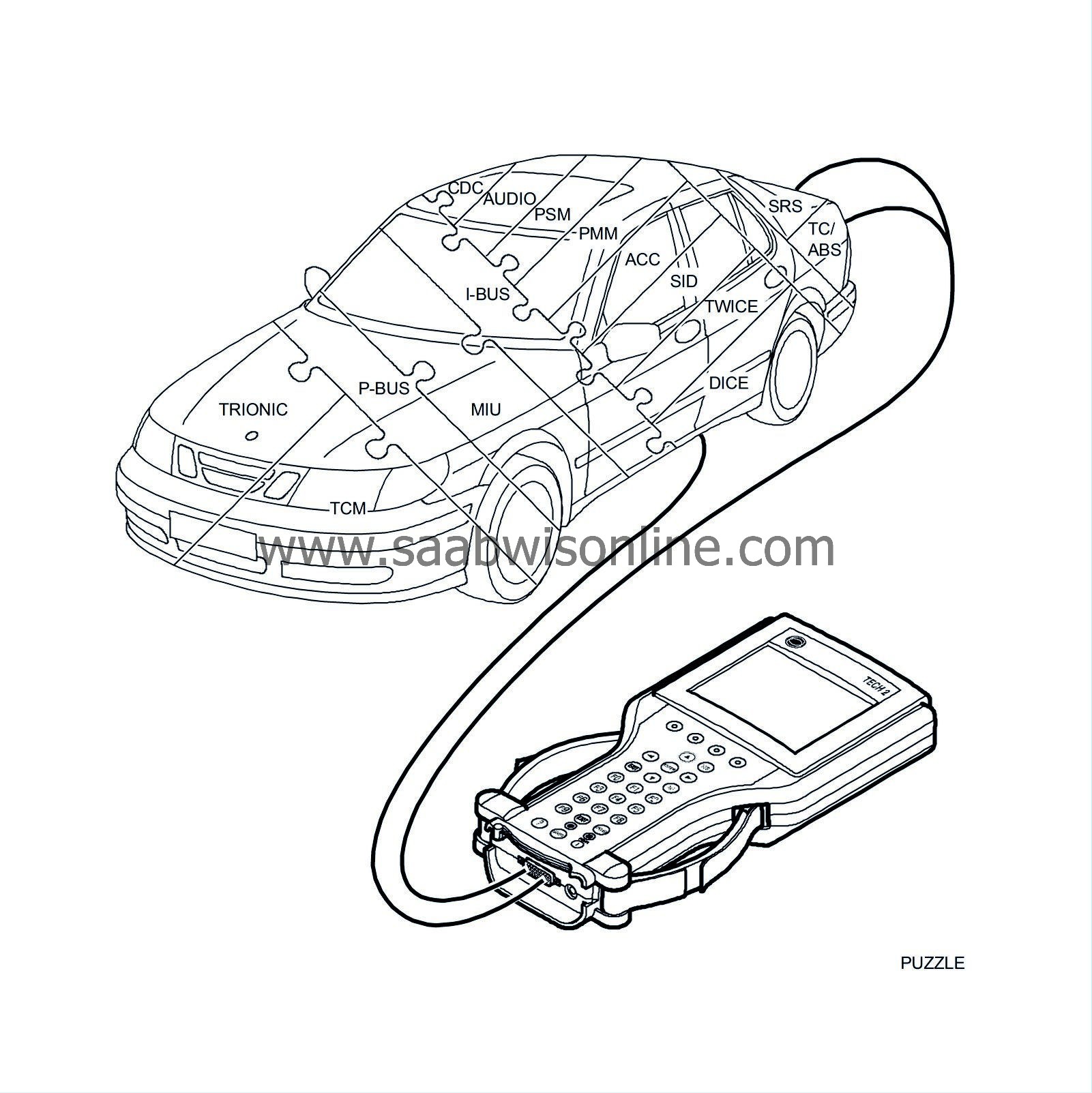
The two powertrain systems, Trionic and TCM, are not connected to the I bus, however. These systems need much faster communication facilities so that no delays will be noticeable, such as in connection with torque limitation when changing gear.
The Trionic and TCM are therefore connected by means of a separate bus called the P bus (Powertrain Bus). The communication speed (data transfer rate) of the P bus is ten times faster than that of the I bus.
In addition, the P bus is connected to the MIU. The MIU ensures that information which is available on one bus is also available on the other.
The diagnostic instrument is not connected directly to the bus but communicates via the DICE, one of the control modules connected to the I bus, and so has access to all control modules connected to the bus.
Vehi cle speed is an important item of information for many control modules. Since the ABS is not connected to a bus, the vehicle speed signal goes to the MIU via a cable of its own. The MIU then sends out the vehicle speed information on the buses.


