Mass air flow control, basic function
| Mass air flow control, basic function |
| 1. |
Driver request
The control module reads pedal potentiometer 1 and converts the voltage into mass air flow/combustion (mg/c). The value is sent to box 3. |
|
| 2. |
Cruise control, request
When the cruise control is active, the mass air flow/combustion required to maintain the set speed is calculated. The value is sent to box 3. |
|
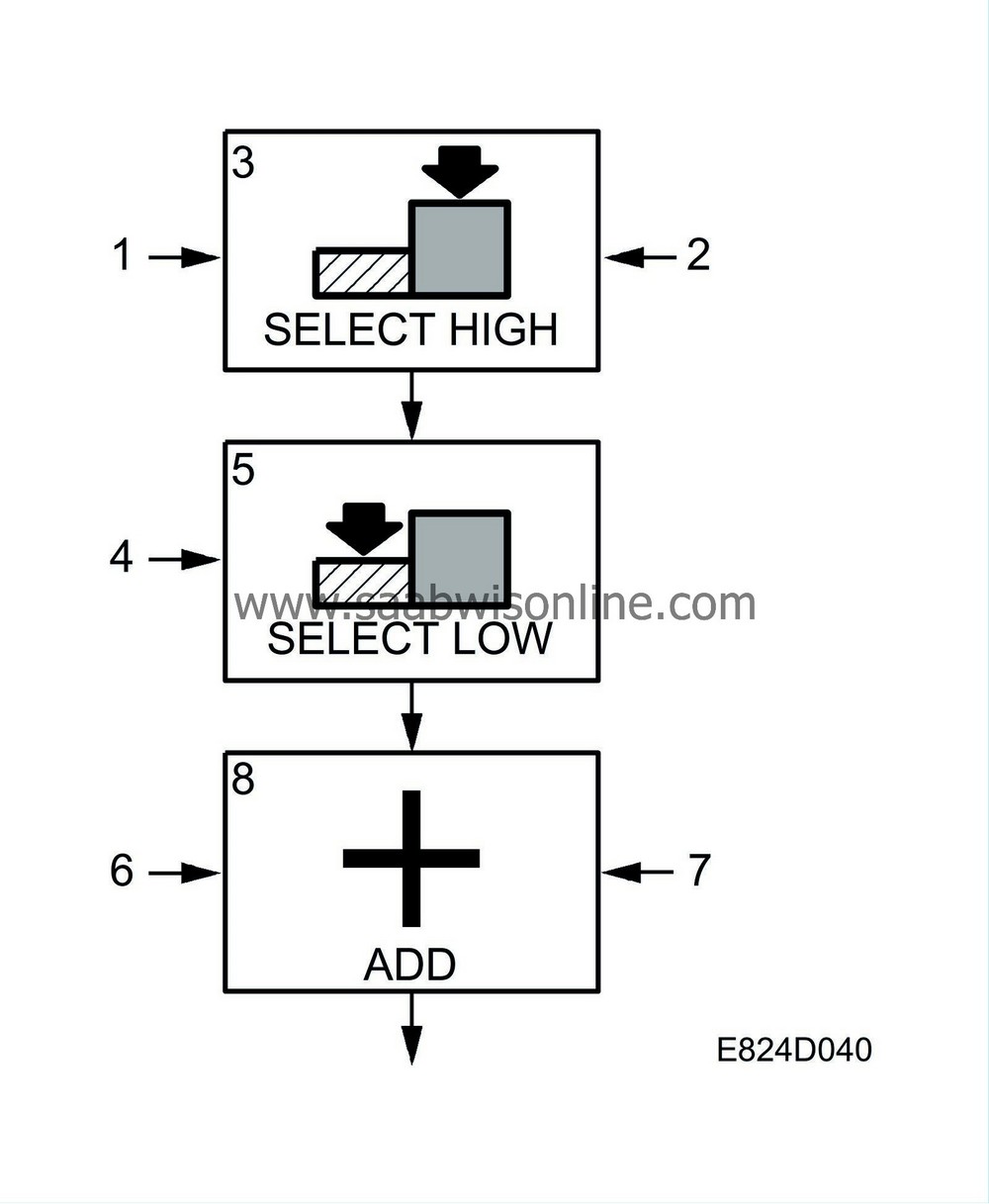
| 3. |
Select highest value
The control module selects the highest value. The value is sent to box 5. |
|
| 4. |
Torque limitation
Maximum permitted mass air flow/combustion varies depending on the engine variant. When driving, the maximum permitted mass air flow/combustion must also be limited to protect the engine, gearbox, brakes and turbo. Peripheral units such as the automatic gearbox or TC/ABS can also limit the maximum permitted mass air flow/combustion. Limitation can also take place if a system fault occurs. The control module selects the lowest value. The value is sent to box 5. |
|
| 5. |
Select lowest value
The control module selects the lowest value and sends this to box 8. |
|
| 6. |
Compensation request
When the A/C compressor is turned on, and when the electrically heated rear window or radiator fan is on, the mass air flow/combustion required to compensate for the increased engine load is calculated. The value is sent to box 8. |
|
| 7. |
Other air request
The control module calculates the mass air flow/combustion required for basic load, dashpot or idle speed control. The value is sent to box 8. |
|
| 8. |
Totalling of values
The control module totals all the values. The total is sent to box 9. |
|
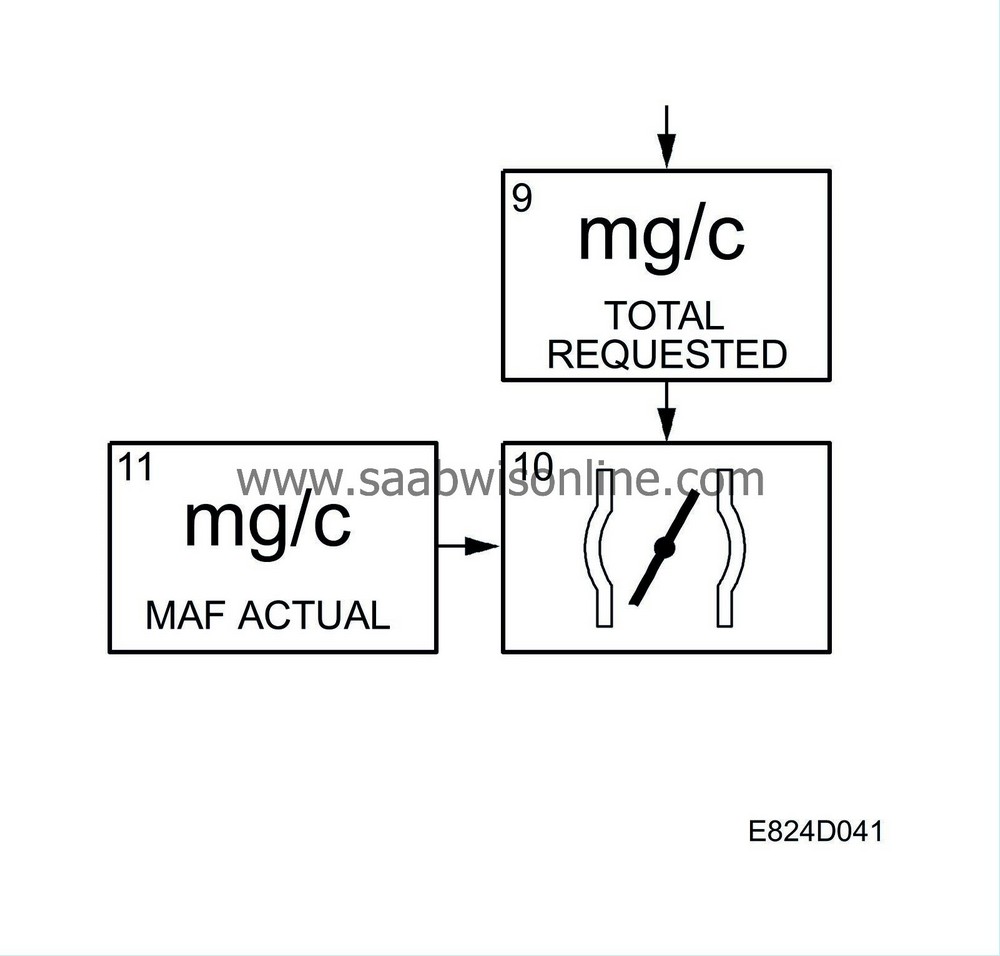
| 9. |
|
|
| 10. |
Total system air request
This value is the system's total air request. The value is sent to box 10. |
|
| 11. |
Throttle control
The requested mass air flow/combustion is converted to the requested voltage for throttle position sensor 1. The charge air pressure and intake air temperature are used to correct this conversion. The throttle motor turns the throttle valve until the current voltage for throttle position sensor 1 corresponds to the voltage requested.
|
|||||||
| 12. |
Current mass air flow/combustion
The requested mass air flow/combustion is also compared with the current mass air flow/combustion (current MAF value/combustion). If necessary, the requested voltage is finely adjusted for throttle position sensor 1. |
|
| Diagnostics |
Mass air flow/combustion is basically the same as engine torque. When carrying out fault diagnosis to determine the cause of poor performance, mass air flow control is therefore extremely important.
The diagnostic tool contains a special menu where relevant values can be displayed. The most important of these is the difference between requested and current mass air flow/combustion.
The current value should always, sometimes after a slight delay, follow the requested value. If this does not happen, a fault in the turbo function should be suspected. Faults in the throttle control are excluded as differences between the throttle position's actual and nominal values will put the throttle control into limp-home mode.