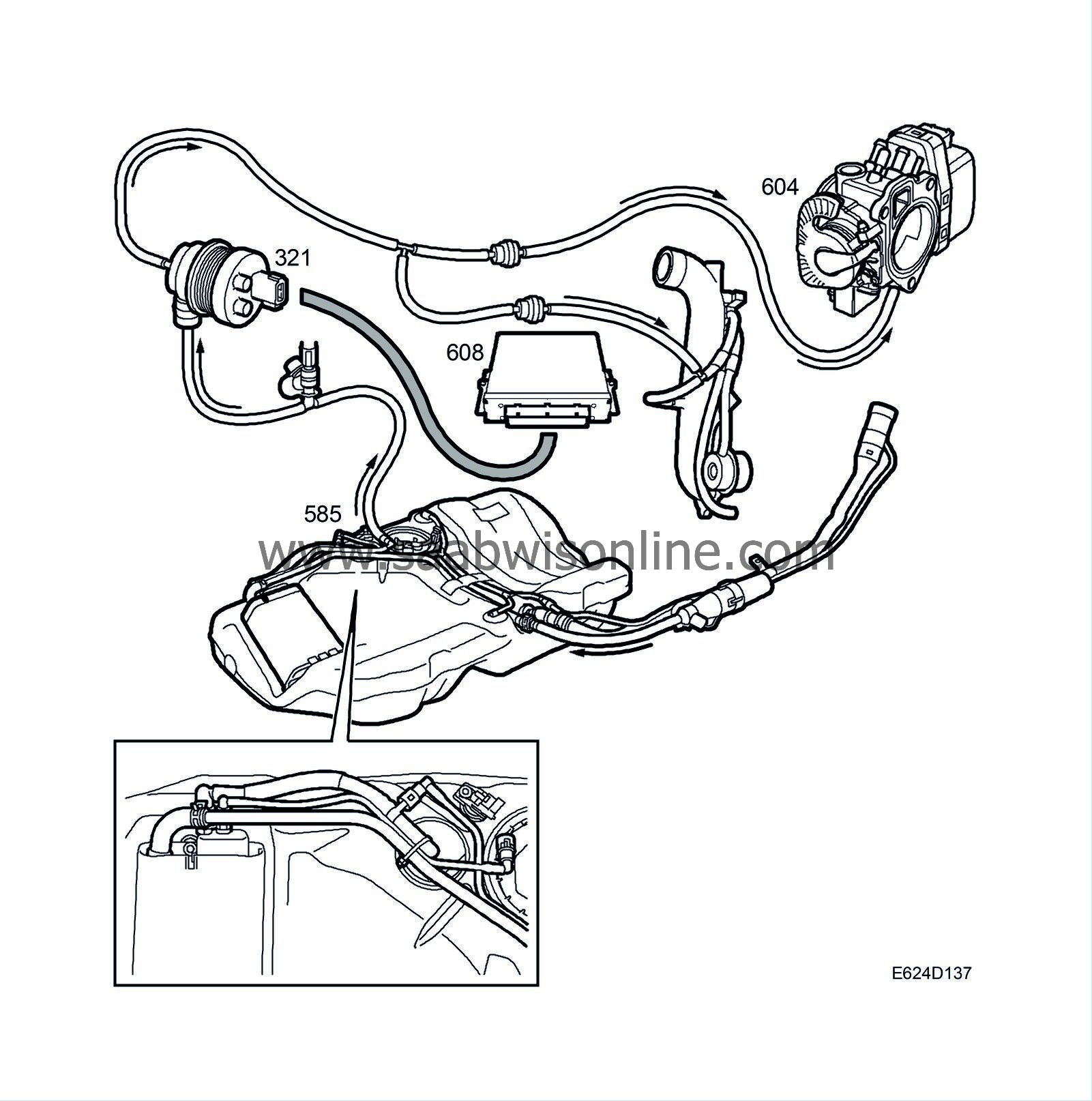
Purging
| Purging |
When not supplied with current, the purge valve is closed. It is supplied with current from the main relay and controlled with a 8 Hz PWM signal from control module pin 27.
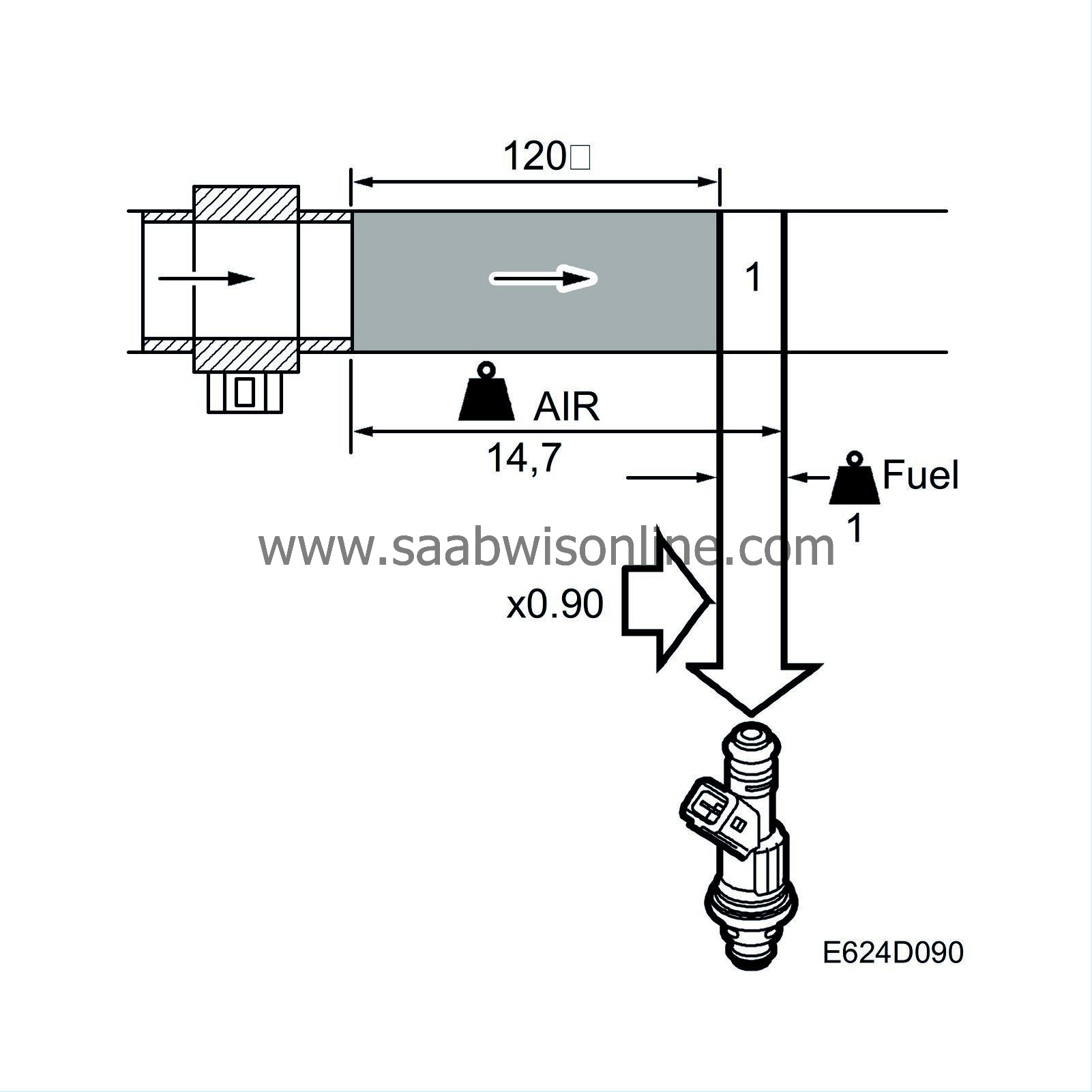
The flow is controlled by the pulse ratio so that it always constitutes a specific proportion of the total flow consumed by the engine.
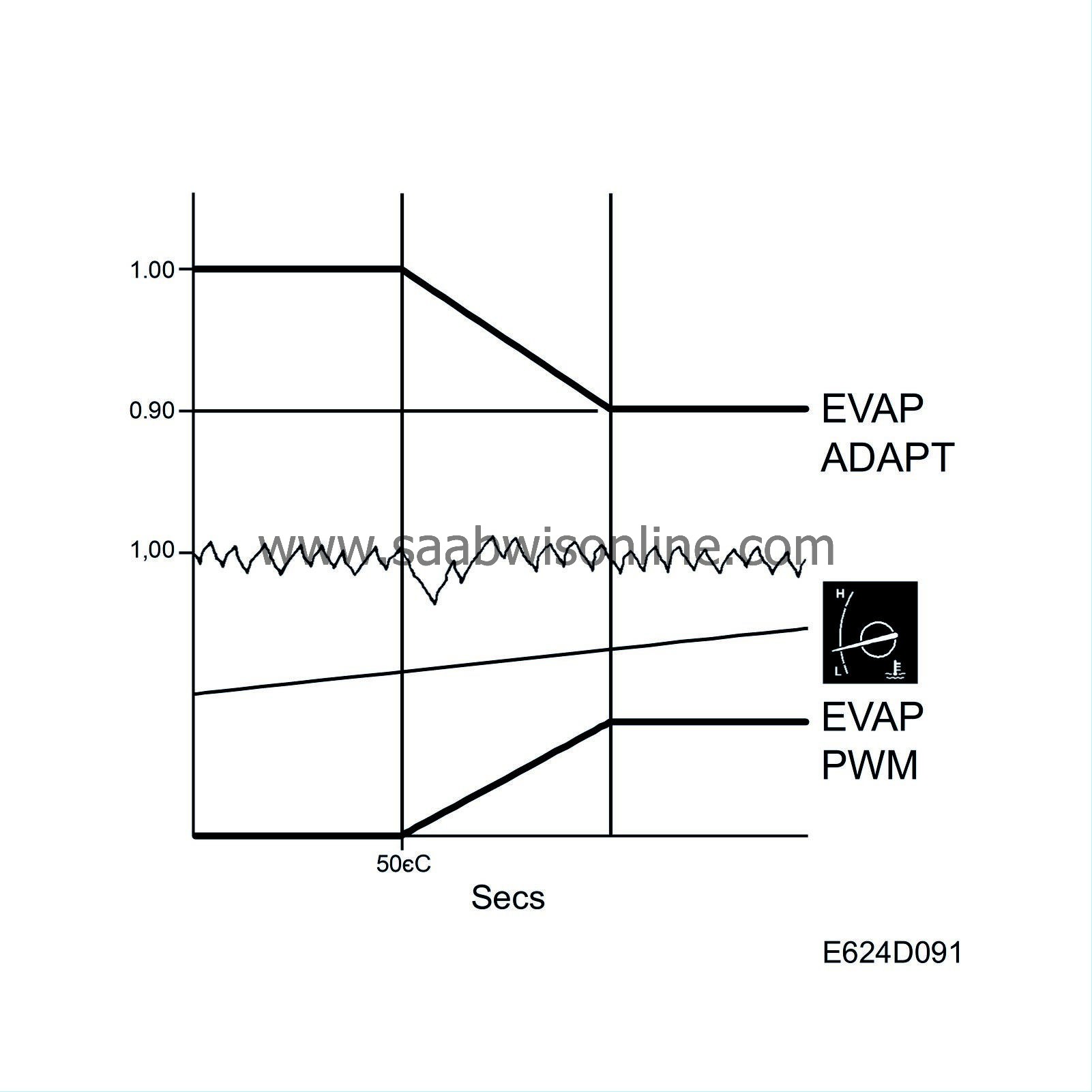
If the flow has a fuel/air ratio other than 14.7:1, the closed loop control system will be affected. However, since it is not the closed loop system's function to correct for the additional purge air, the purging function has a correction factor that is affected by the closed loop system as soon as purging starts. The closed loop system's entire departure from 1.00 is added to the purge correction factor, which means that the closed loop system fluctuates round 1.00 (0%) even if the purge air contains large quantities of hydrocarbons or consists of pure air.
When purging is not active the factor 1.00 is used and the entire fuel fault is corrected by the closed loop and the multiplicative adaptation and additive adaptation.
The limits for purging adaptation are 0.75 and 1.25.

The following conditions must be fulfilled for purging to be engaged:
| • |
Closed loop active.
|
|
| • |
No fuel adaptation in progress; this takes place for 30 seconds every 5 minutes.
|
|
| • |
Engine coolant temperature exceeds 50°C.
|
|
| • |
If the engine coolant temperature is below 5°C when the engine is started, the vehicle speed must exceed 10 km/h.
The function is active during the entire driving cycle and reduces the risk of valve noise. It makes more noise when cold. |
|
The diagnostic tool shows 25% when the correction factor is 1.25 and -25% when the correction factor is 0.75.
| Diagnostics |
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P0444 will be generated in the event of a break or short-circuit to ground.
|
|
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P0445 will be generated in the event of a short-circuit to B+.
|
|
| • |
If there is an internal leak in the valve, diagnostic trouble code P0441 will be generated.
|
|||||||
| Integrity diagnosis |

The on-board diagnostics must be able to detect a leak in the purge system corresponding to a hole with diameter 1 mm.
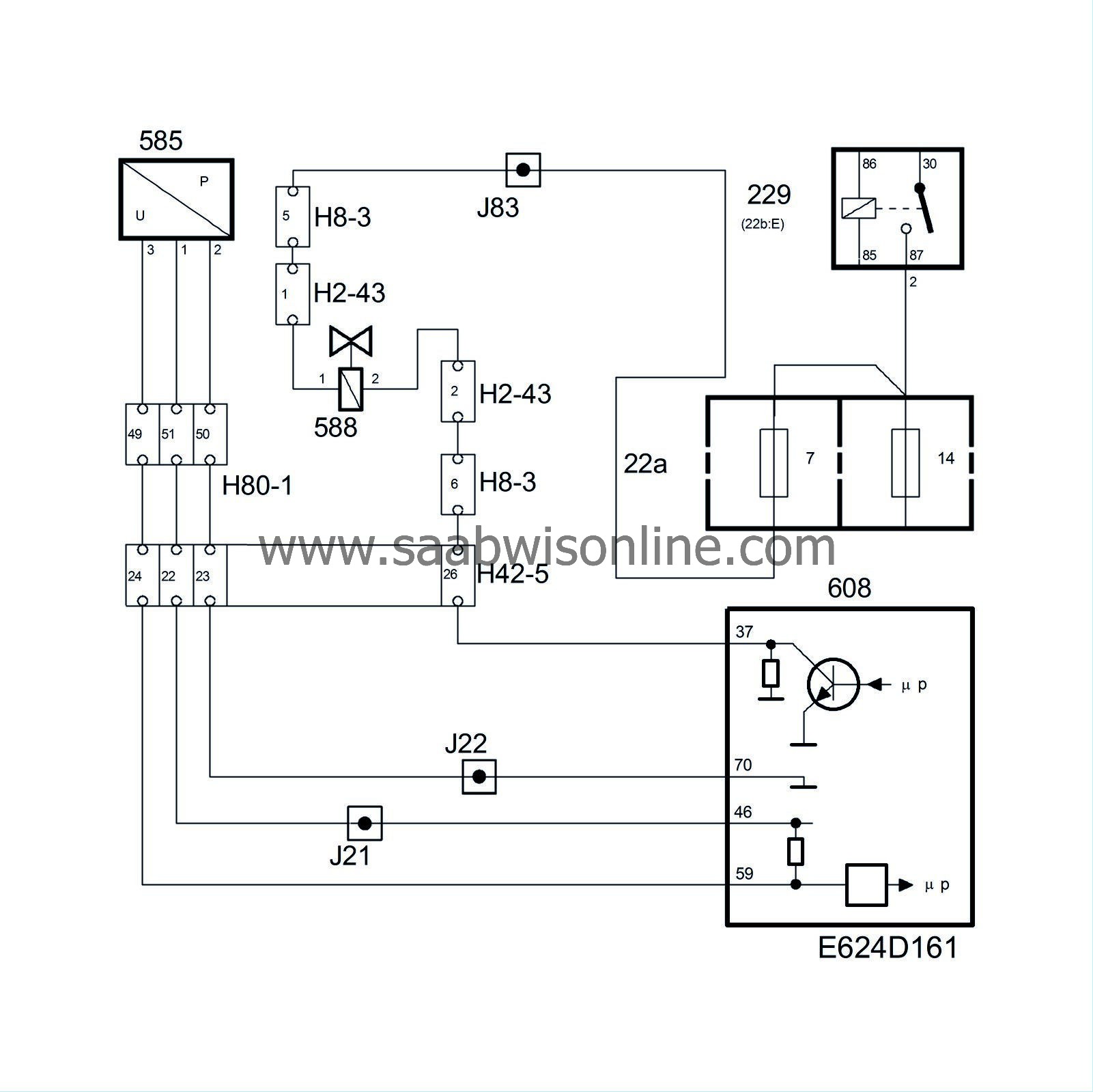
For this reason, there is a differential pressure sensor fitted to the tank and a shut-off valve on the EVAP canister atmospheric connection. When the shut-off valve is closed, it should be possible to create and maintain a vacuum in the tank using the purge valve. Otherwise, the system is leaking and a diagnostic trouble code will be generated. The diagnosis is performed once per driving cycle.
The pressure sensor voltage is fed with 5 V from the control module pin 46 and is grounded from control module pin 70.
Depending on the pressure difference between the tank and atmosphere the pressure sensor passes a proportional voltage to control module pin 59.
The pressure sensor value is adapted to 0 kPa at ignition provided the coolant temperature is under 40°C and the fuel level is under 50 litres.
The shut-off valve is open in a de-energized state. It is powered from the main relay and is controlled from control module pin 37.
| Diagnostics |
Pressure sensor
| • |
If the sensor voltage is too low, diagnostic trouble code P0452 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If the sensor voltage is too high, diagnostic trouble code P0453 will be generated.
|
|
| • |
If the pressure value is implausible, diagnostic trouble code P1451-P1453 will be generated.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Integrity diagnosis is blocked.
|
|
| • |
Fuel adaptation and purging blocked on P1452.
|
|
Shut-off valve
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P1444 will be generated in the event of a break or short-circuit to ground.
|
|
| • |
Diagnostic trouble code P1445 will be generated in the event of a short-circuit to B+.
|
|
System reaction to a fault
| • |
Fuel adaptation and purging are blocked.
|
|
Integrity
| • |
A minor leak will generate diagnostic trouble code P0442.
|
|
| • |
A major leak will generate diagnostic trouble code P0455.
|
|