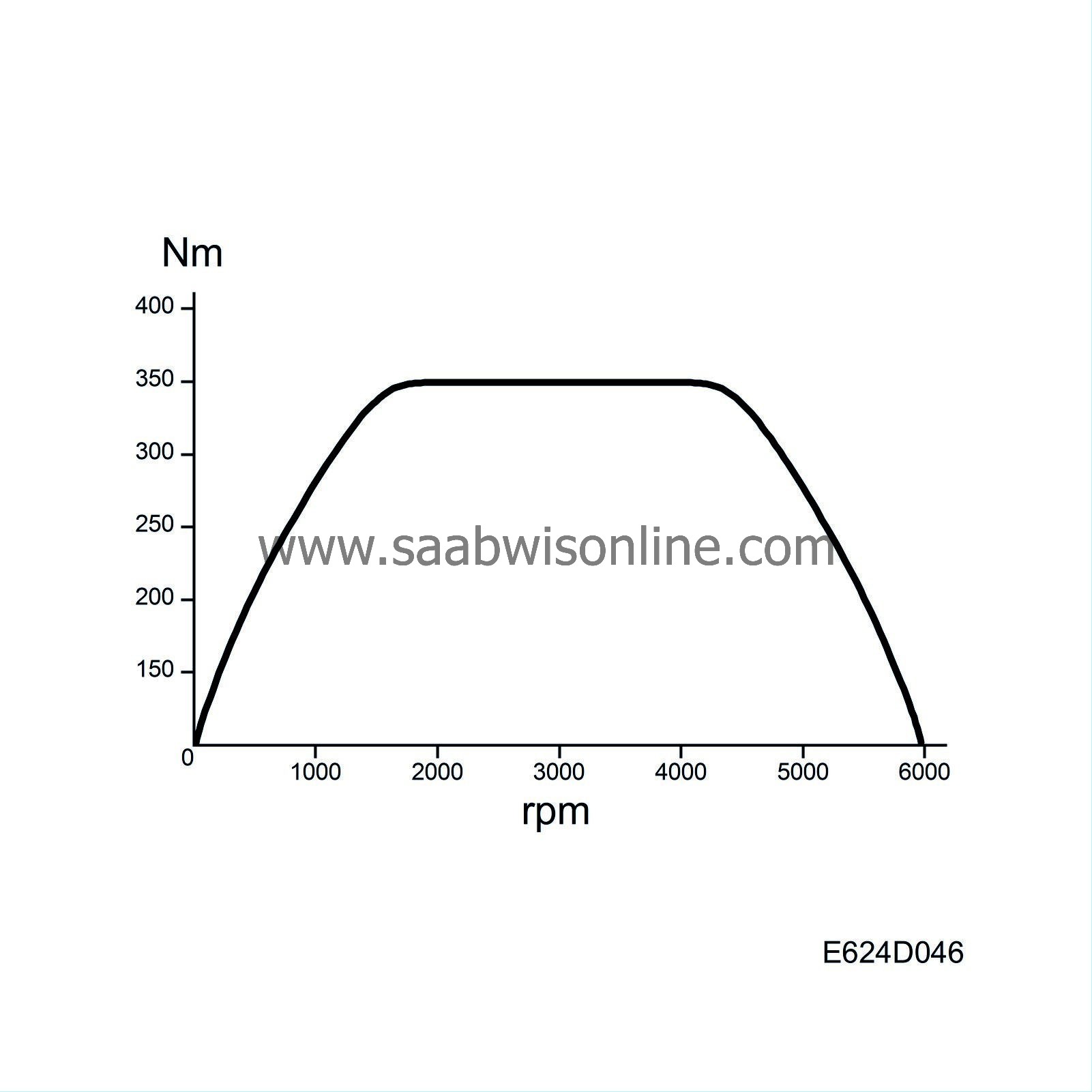
Air mass limitation
| Air mass limitation |
| Maximum engine torque |
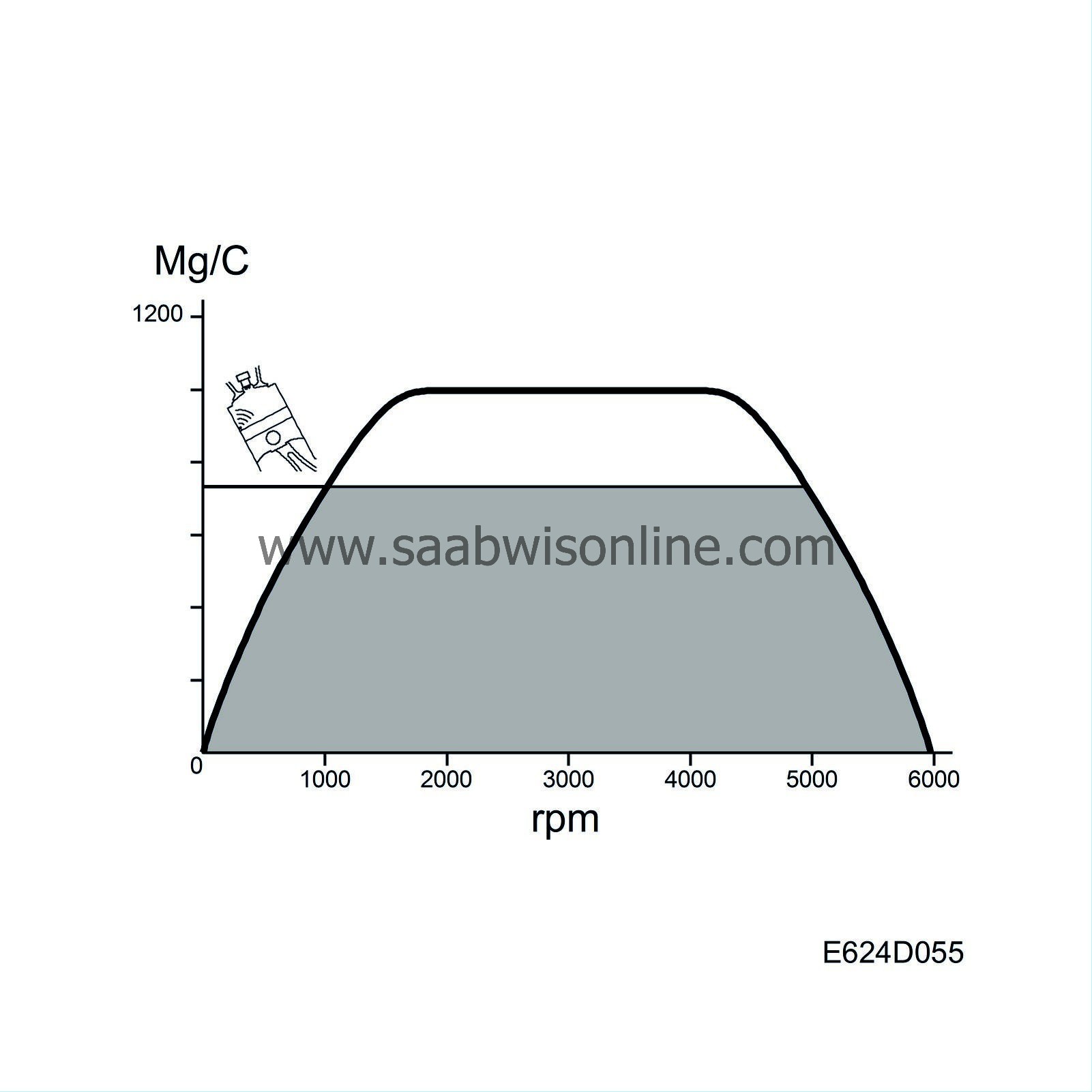
The engine torque curve is stored in the control module memory. The torque curve shows the engine's maximum torque at various rpm.
The torque is directly proportional to air mass/combustion.
The torque curve unit Nm is converted to mg air/combustion.
The curve value is the maximum air mass/combustion value that the engine variant allows.
| Automatic transmission, stall limitation |

For reasons of strength, maximum torque must be limited when the car is stationary with the brake pedal depressed.
Engine torque is limited to 200 Nm.
The torque value is converted into mg air/combustion and constitutes the maximum air mass/combustion value allowed by the automatic transmission.
| Automatic transmission, limitation in reverse |
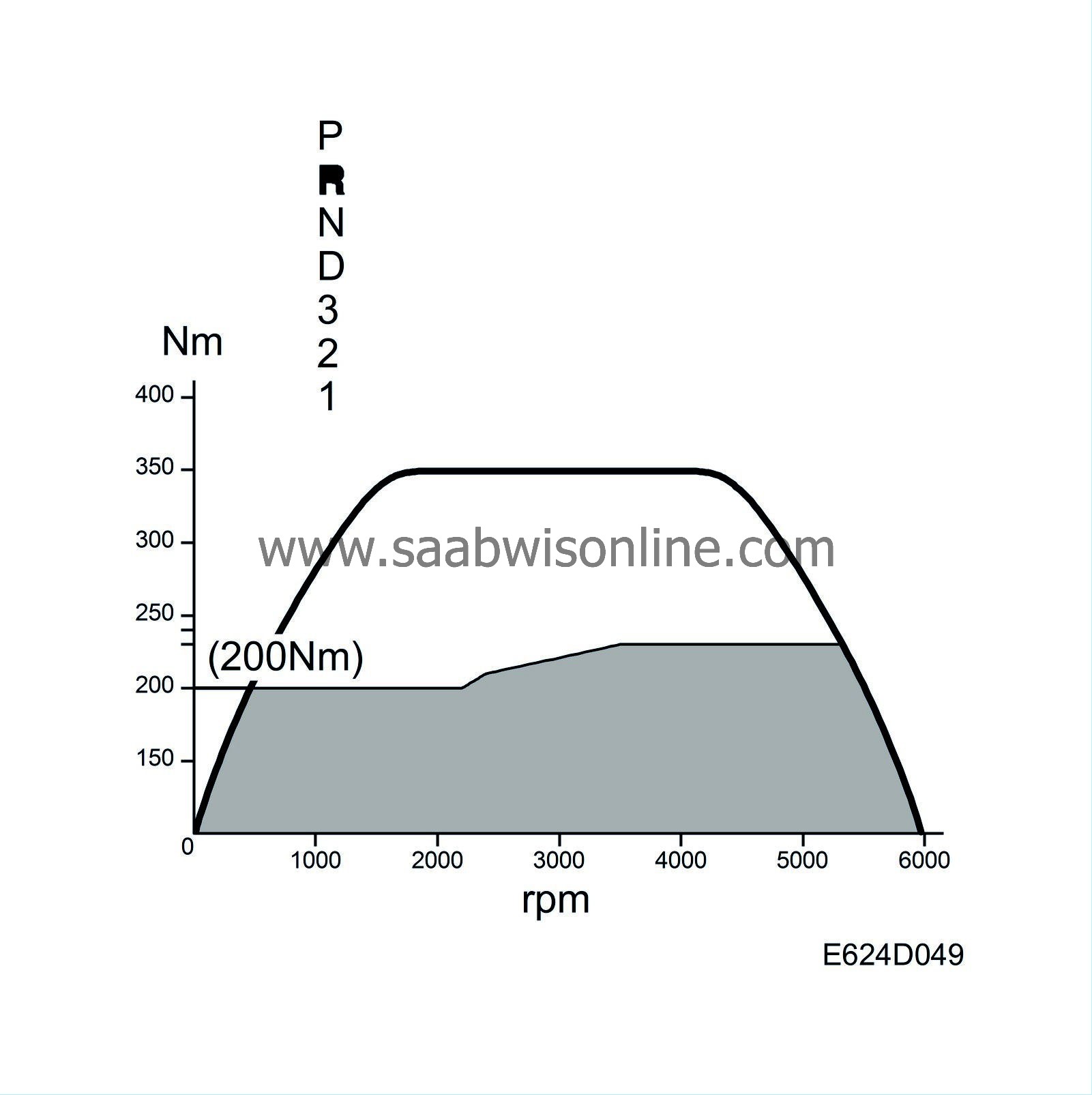
When selector position R is selected, an engine speed-dependent torque limitation takes place. This is to reduce the load on the power train mountings.
The torque value is converted into mg air/combustion and constitutes the maximum air mass/combustion value allowed by the automatic transmission.
| TCM, torque limitation |
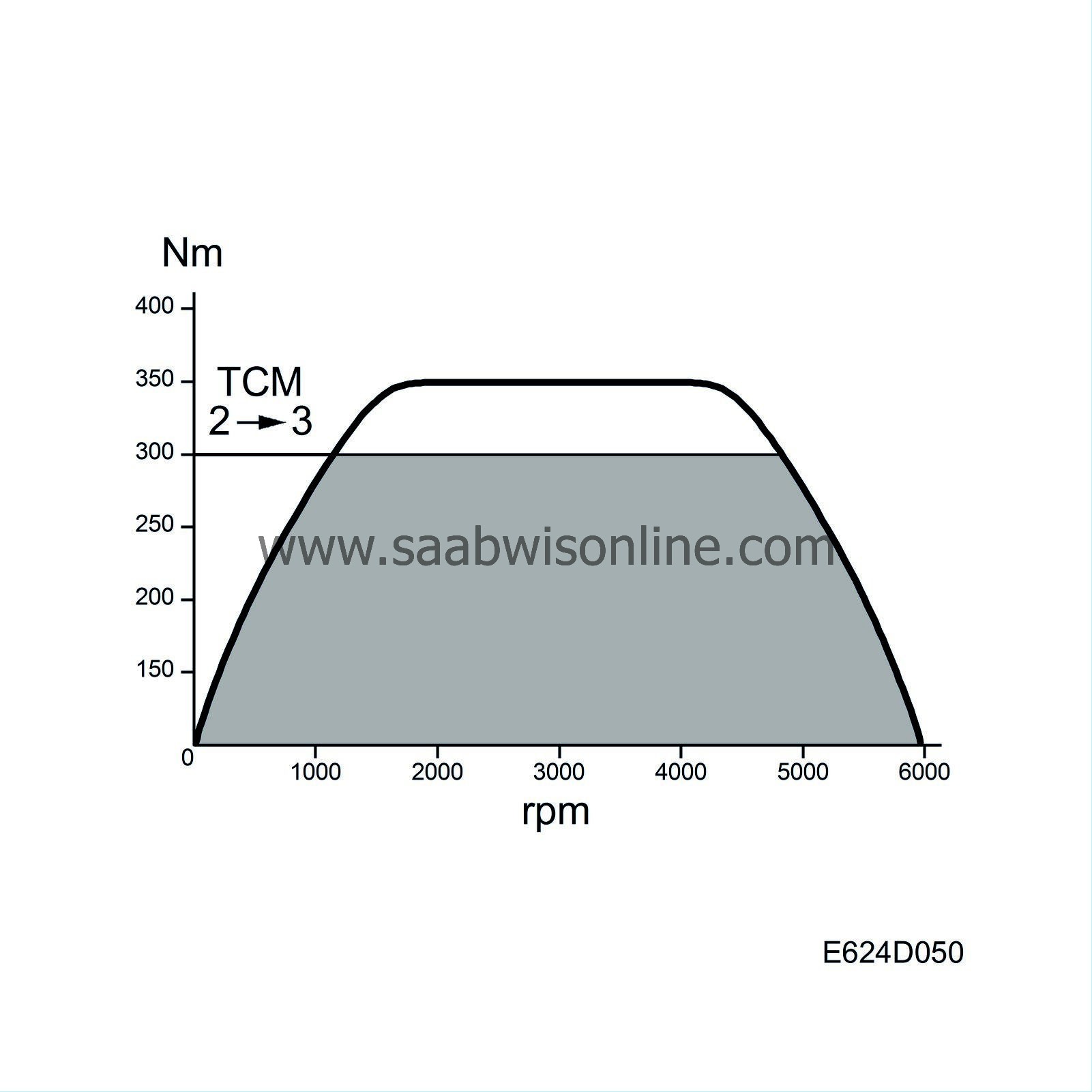
For reasons of strength, maximum torque must be limited when changing gear. The TCM continuously sends out information on the bus specifying maximum permitted torque.
The Trionic T7 converts Nm into mg air/combustion. The value comprises the maximum air mass/combustion value permitted by the automatic transmission.
| Braking |
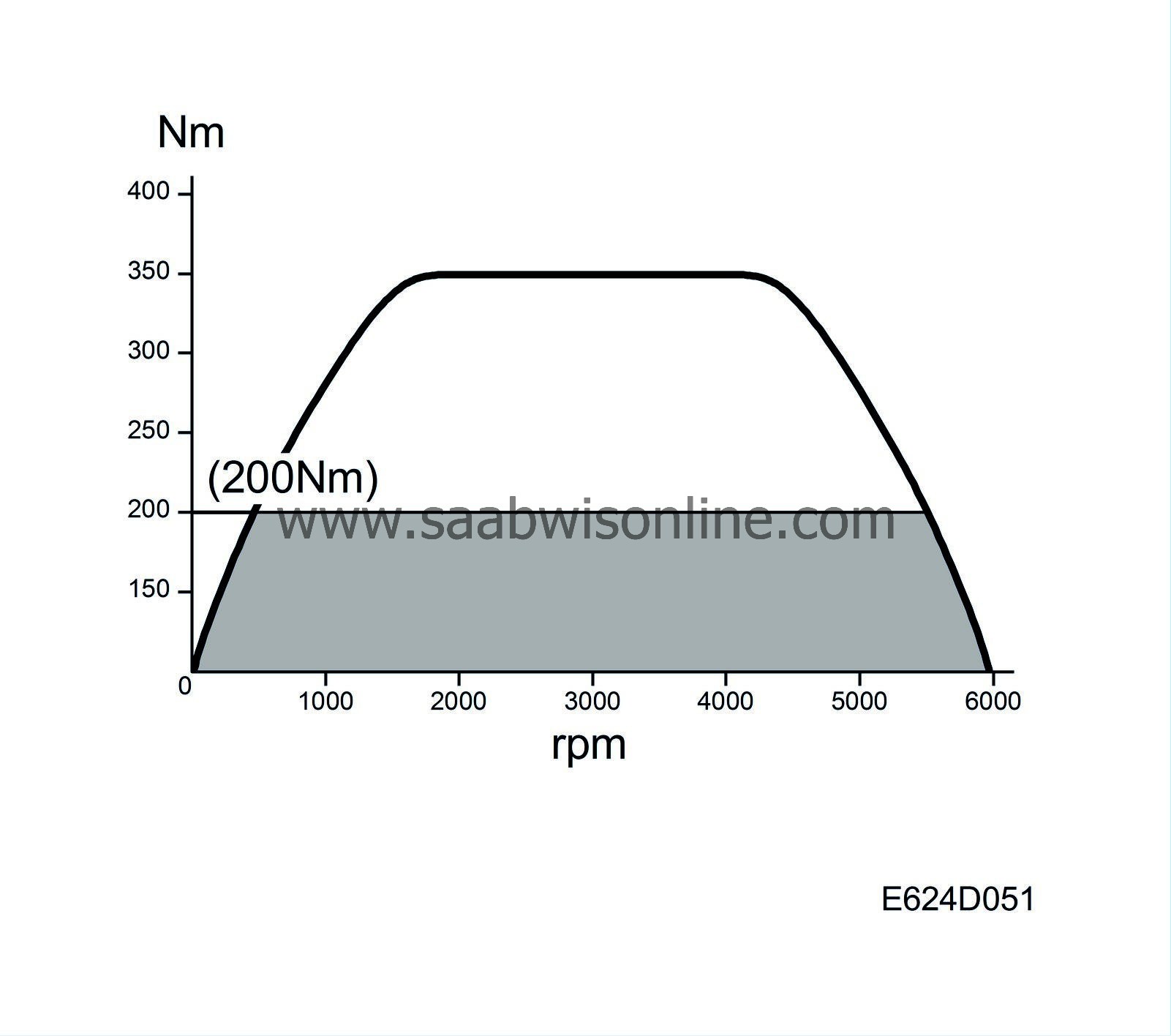
The maximum engine torque must be limited when the brake pedal is depressed for reasons of strength. The following three conditions must be fulfilled for this function to be activated:
| • |
B+ on the input from the brake light switch, pin 63.
|
|
| • |
B+ on the input from the brake and clutch pedal switches, pin 29.
|
|
| • |
Brake lights ON (Bus from TWICE)
|
|
Engine torque is limited to 200 Nm.
The torque value is converted into mg air/combustion and constitutes the maximum air mass/combustion value allowed by the automatic transmission.
| Traction Control, engine torque limitation |

Cars with certain engine types may be equipped with Traction Control. The function for traction control can be found in the TC/ABS control module. The TCS function in the TC/ABS control module works both with reduction of engine torque (request to Trionic) and brake application on the driving wheels with TCS. The rear wheel speed is used as a reference for comparison of both driving wheels individually. When one of the driving wheels has a higher speed than the rear wheels, it is described as a wheelspin.
TC/ABS receives 2 bus messages from Trionic T7:
| • |
Engine Torque
The value of the bus message "Engine Torque” can vary between -100 Nm up to 400 Nm. TC/ABS uses the engine torque value to calculate the current driving wheel torque. |
|
| • |
Pedal position
TC/ABS uses the value to determine how much wheelspin to allow. |
|
TC/ABS uses the above values together with car speed and engine speed to calculate current gear ratios. By knowing the engine torque and current gear ratios TC/ABS can calculate the driving wheels torque.
TC/ABS sends one bus message to Trionic T7:
| • |
Max permissible torque
The value of this requested torque is used for the Traction Control. |
|
Trionic T7 converts Nm to mg air/combustion. The value constitutes the maximum value for air mass/combustion allowed by TC/ABS.
For further information about Traction Control and TC/ABS, see TC/ABS 5.3, System overview .
| Diagnostics |
Trionic can detect three different faults that affect the TC function. TC/ABS generates a DTC and TCS OFF comes on.
The three faults are:
| • |
No communication with the TC/ABS control module.
|
|
| • |
Trionic detects that TC/ABS is programmed for another engine type (the programmed type is sent from TC/ABS on P-bus, TC/ABS generates the DTC).
|
|
| • |
Fault in the Trionic throttle control (limp-home). If this fault occurs, the CHECK ENGINE lamp will also go on. The cause of the fault is in Trionic.
|
|
| Knock limitation |
In connection with knock control, the ignition is first retarded in each cylinder. If the mean ignition retardation value exceeds a certain figure, fuel mixture enrichment takes place.
If the mean retardation value continues to rise, the maximum permitted air mass/combustion will be reduced.
This reduction is progressive as ignition retardation increases.
The value constitutes the maximum air mass/combustion permitted by knock control.
| Vehicle speed limitation |

When vehicle speed reaches 240 km/h, engine torque will be limited due to limitation of the maximum permitted air mass/combustion.
| Engine speed limitation |
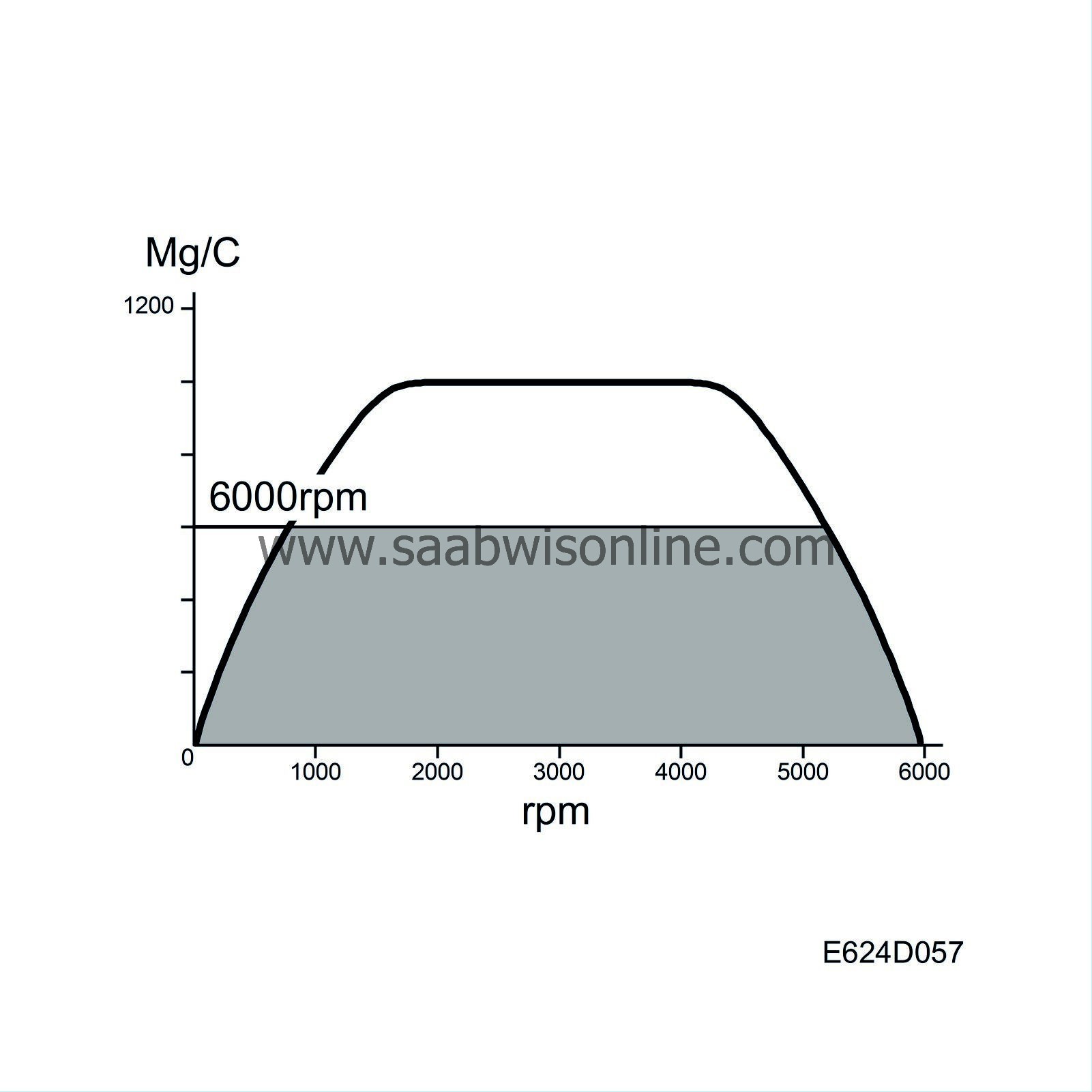
When engine speed reaches 6000 rpm, engine torque is limited due to limitation of the maximum permitted air mass/combustion.
| Turbo speed limitation |
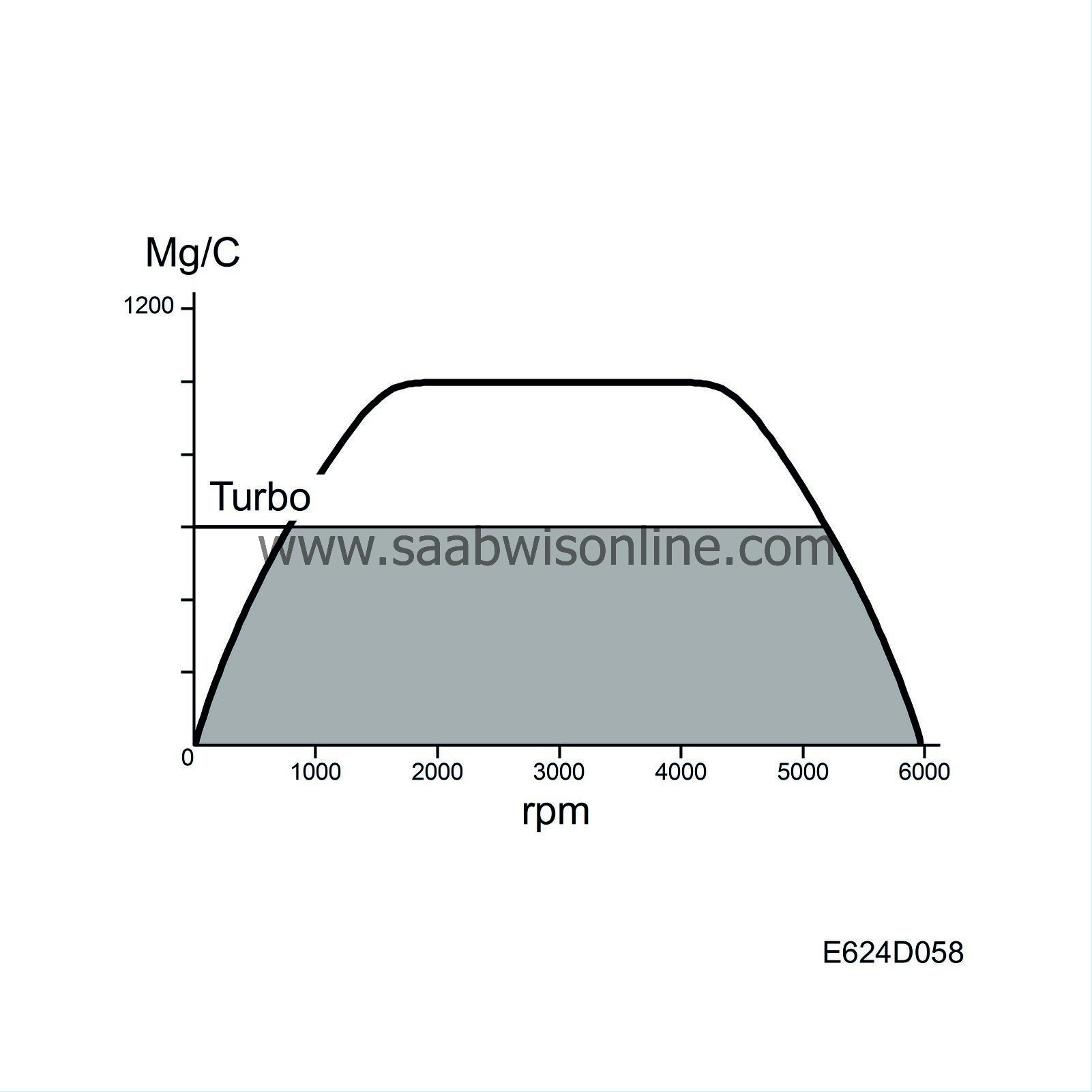
At low barometric pressures, the maximum permitted air mass/combustion is limited to protect the turbo from overrevving.