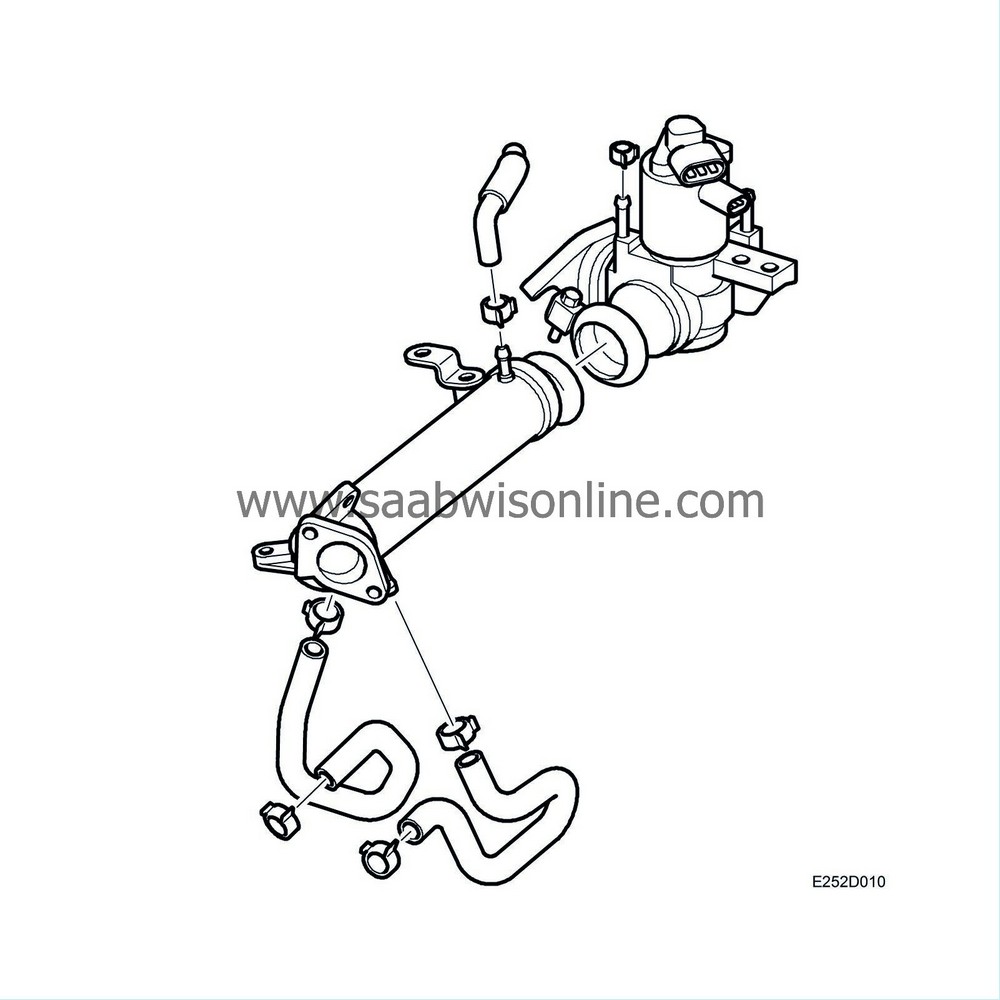
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), V6
| Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), V6 |
In an EGR system (Exhaust Gas Recirculation), the controlled amount of exhaust gases is allowed to pass to the intake side, where it is mixed with the incoming air. This results in lower temperatures and higher pressure during combustion, which will hinder the formation of NOx.
The EGR system comprises an electric valve, which opens a water-cooled connection between the exhaust manifold and the intake manifold.
The electronically controlled EGR valve has a feedback potentiometer. The feedback informs the engine control module of how far open the valve is. If the control module has calculated that more or less exhaust gas should be added to the air mixture, a PWM signal is sent to increase or decrease the valve opening.
| Desired value calculation |
The desired value calculation estimates the air mass/combustion required by the engine on each occasion. The regulating function controls the EGR valve so that this amount of air is always attained. This is achieved by allowing the amount of recirculated exhaust gases to enter the intake manifold that is required to reduce the intake air mass/combustion to the value estimated by the desired value calculation.